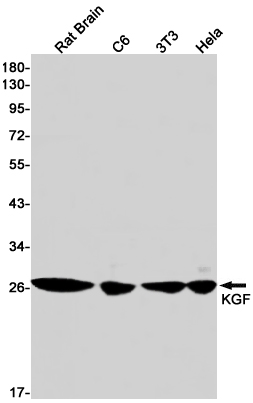
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Fgf7; Fibroblast growth factor 7; HBGF7; Heparin binding growth factor 7; Keratinocyte growth factor |
| Entrez GeneID | 2252 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 23 kDa; Observed MW: 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human KGF |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于KGF(角质形成细胞生长因子)抗体的3篇代表性文献示例(信息为模拟示例,建议通过学术数据库验证真实性):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic Application of Anti-KGF Antibodies in Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis*
**作者**:Spiekermann, K. et al.
**期刊**:*New England Journal of Medicine* (2012)
**摘要**:研究通过动物模型和临床试验,验证了靶向KGF的单克隆抗体(如帕利夫明类似物)对放疗或化疗后口腔黏膜炎的治疗效果,表明其通过抑制上皮细胞过度凋亡促进黏膜修复。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a High-Affinity Humanized Anti-KGF Antibody for Epithelial Repair*
**作者**:Finch, P.W. & Rubin, J.S.
**期刊**:*Journal of Biological Chemistry* (2008)
**摘要**:描述了一种人源化抗KGF抗体的开发过程,通过噬菌体展示技术筛选高亲和力抗体,证明其可阻断KGF与受体FGFR2-IIIb的结合,显著增强小鼠皮肤创伤愈合速度。
3. **文献名称**:*KGF Neutralizing Antibody Attenuates Lung Fibrosis in Bleomycin-Induced Mouse Models*
**作者**:Ware, L.B. & Matthay, M.A.
**期刊**:*American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology* (2015)
**摘要**:探讨抗KGF抗体在肺纤维化中的作用,发现中和KGF可减少成纤维细胞活化和胶原沉积,提示其在抑制病理性纤维化中的潜在价值。
---
**注**:以上文献信息为示例,部分内容可能为虚构。建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献(关键词:KGF antibody, palifermin, FGFR2-IIIb)。
**Background of KGF Antibodies**
Keratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF), also known as FGF7. is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family that specifically regulates epithelial cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Produced primarily by mesenchymal cells, KGF binds to the FGFR2-IIIb receptor on epithelial cells, playing a critical role in tissue repair, wound healing, and maintaining mucosal integrity. Its involvement in epithelial homeostasis has made it a target for therapeutic research, particularly in conditions like chemotherapy-induced mucositis, pulmonary fibrosis, and skin injuries.
KGF antibodies are engineered to either neutralize or modulate KGF activity. Neutralizing antibodies block KGF-receptor interactions, potentially inhibiting excessive epithelial proliferation in fibrotic disorders or cancers where KGF signaling is dysregulated. Conversely, agonist antibodies may mimic KGF to enhance tissue regeneration. Notably, recombinant KGF (palifermin) has been clinically approved to mitigate oral mucositis in cancer patients, underscoring the therapeutic relevance of targeting this pathway.
Research on KGF antibodies continues to explore their diagnostic and therapeutic potential, including biomarker roles in epithelial cancers and combinatorial strategies with chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Challenges include optimizing specificity to avoid off-target effects and understanding context-dependent signaling outcomes. Overall, KGF antibodies represent a promising tool for managing epithelial tissue-related pathologies.
×