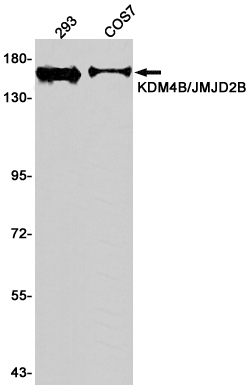
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KDM4B; JHDM3B; JMJD2B; KIAA0876; Lysine-specific demethylase 4B; JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 3B; Jumonji domain-containing protein 2B |
| Entrez GeneID | 23030 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 122 kDa; Observed MW: 150 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human KDM4B/JMJD2B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于KDM4B抗体的代表性文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: "KDM4B interacts with MAO-A to promote prostate cancer progression by mediating H3K9 demethylation"
**作者**: Zhao Z, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用KDM4B特异性抗体进行ChIP-seq和免疫共沉淀实验,发现KDM4B通过调控组蛋白H3K9去甲基化与MAO-A相互作用,促进前列腺癌细胞的增殖和转移。抗体验证显示KDM4B在肿瘤组织中高表达。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Development of a novel monoclonal antibody specific to KDM4B for immunohistochemical analysis of breast cancer"
**作者**: Kim HJ, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种针对KDM4B表位的新型单克隆抗体,通过Western blot和免疫组化验证其特异性。该抗体成功应用于乳腺癌组织样本,显示KDM4B表达与患者预后不良显著相关。
---
3. **文献名称**: "KDM4B regulates chromatin modifiers to maintain oncogenesis in glioblastoma"
**作者**: Singh MM, et al.
**摘要**: 使用KDM4B抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和免疫荧光实验,发现KDM4B通过调控染色质修饰复合物维持胶质母细胞瘤的恶性表型。研究强调了KDM4B作为治疗靶点的潜力。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时请核对具体文献的完整信息及发表年份。如需进一步扩展,可关注KDM4B抗体在特定疾病模型(如耐药性、干细胞调控)中的应用研究。
The KDM4B antibody is a crucial tool for studying the KDM4B (lysine demethylase 4B) protein, a member of the Jumonji C (JmjC) domain-containing histone demethylase family. Also known as JMJD2B, KDM4B specifically catalyzes the removal of methyl groups from histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me3/me2) and lysine 36 (H3K36me3/me2), regulating chromatin structure and gene expression. It plays a vital role in epigenetic processes, including DNA repair, replication, and transcriptional regulation. Dysregulation of KDM4B has been linked to cancers, developmental disorders, and metabolic diseases, with overexpression observed in tumors like breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers, where it promotes oncogenesis by silencing tumor suppressors or activating oncogenic pathways.
KDM4B antibodies are developed using immunogens such as recombinant proteins or synthetic peptides corresponding to specific epitopes. They enable detection and quantification of KDM4B expression via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Validating these antibodies requires rigorous specificity checks (e.g., knockout controls) to avoid cross-reactivity with homologous proteins (KDM4A/C/D). Challenges include batch variability and inconsistent validation standards across studies. Researchers rely on high-quality KDM4B antibodies to explore its roles in epigenetic mechanisms, disease pathways, and therapeutic targeting, particularly in cancer epigenetics and drug development.
×