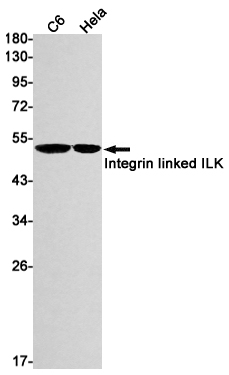
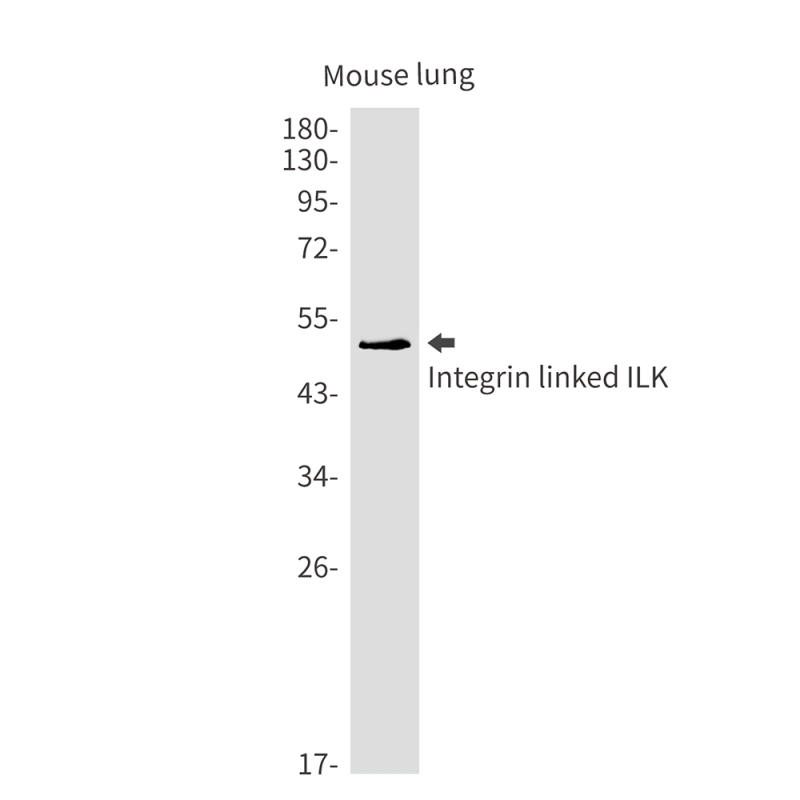
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ILK; ILK1; ILK2; Integrin-linked protein kinase; 59 kDa serine/threonine-protein kinase; ILK-1; ILK-2; p59ILK |
| Entrez GeneID | 3611 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 51 kDa; Observed MW: 51 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Integrin linked ILK |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Integrin-Linked Kinase (ILK)抗体的3篇参考文献摘要:
1. **"Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a new β1-integrin-linked protein kinase"**
- **作者**: Hannigan GE, et al. (1996)
- **摘要**: 该研究首次鉴定了ILK作为β1整合素结合蛋白激酶,揭示了其在调控细胞黏附和生存信号中的作用,并开发了特异性抗体用于检测ILK在细胞定位中的表达。
2. **"Inhibition of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) suppresses activation of protein kinase B/Akt and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of PTEN-mutant prostate cancer cells"**
- **作者**: Persad S, et al. (2000)
- **摘要**: 通过使用ILK抗体进行功能阻断实验,研究发现抑制ILK活性可降低Akt磷酸化水平,导致PTEN缺失的前列腺癌细胞凋亡,表明ILK在肿瘤发生中的关键作用。
3. **"Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) regulates cell-cell adhesion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cancer progression"**
- **作者**: McDonald PC, et al. (2008)
- **摘要**: 利用ILK抗体进行免疫沉淀和免疫荧光分析,揭示了ILK通过调控E-cadherin和β-catenin信号通路,促进癌细胞上皮间质转化(EMT)和转移的分子机制。
以上文献均通过ILK抗体的实验应用,阐明了ILK在细胞信号传导、肿瘤进展等领域的生物学功能。
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is a multifunctional intracellular protein that plays a central role in connecting integrin receptors to the cytoskeleton and downstream signaling pathways. Structurally, ILK contains an N-terminal kinase-like domain and a C-terminal phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain, enabling interactions with β-integrin cytoplasmic tails, adaptor proteins (e.g., PINCH, parvin), and signaling molecules (e.g., Akt, GSK-3β). This interaction forms the IPP complex (ILK-PINCH-parvin), critical for regulating cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and survival. Dysregulation of ILK expression or activity is implicated in pathological processes, including cancer metastasis, fibrosis, and cardiovascular diseases, making it a biomarker and therapeutic target.
Anti-ILK antibodies are essential tools for studying ILK's localization, expression levels, and functional interactions in both physiological and disease contexts. These antibodies enable techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation to explore ILK's role in mechanotransduction, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling. Specific clones (e.g., 3G9. 65.1) may vary in reactivity across species (human, mouse, rat) or applications, requiring validation for experimental models. In cancer research, ILK-targeting antibodies help assess its overexpression in tumors, correlation with metastasis, and effects on angiogenesis. Additionally, they are used to evaluate pharmacological inhibitors of ILK in preclinical studies, highlighting their versatility in bridging molecular mechanisms to therapeutic development.
×