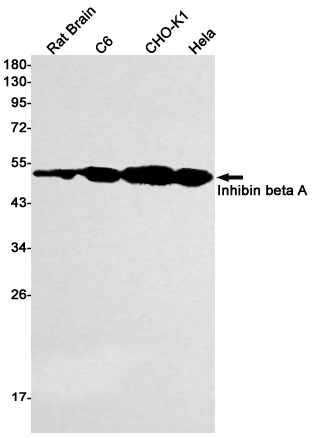
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| Aliases | INHBA; Inhibin beta A chain; Activin beta-A chain; Erythroid differentiation protein; EDF |
| Entrez GeneID | 3624 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 47 kDa; Observed MW: 44 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Inhibin beta A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Inhibin beta A抗体的3篇参考文献,按研究领域和内容分类列举:
---
### 1. **"Cloning and characterization of human inhibin βA subunit gene"**
**作者:** Roberts et al.
**摘要:** 该研究首次克隆并鉴定了人类抑制素βA亚基(INHβA)的基因结构,分析了其在生殖组织(如卵巢和睾丸)中的表达模式,并探讨了其在调控促卵泡激素(FSH)分泌中的潜在作用。
---
### 2. **"Immunohistochemical detection of inhibin βA in ovarian granulosa cell tumors and its diagnostic utility"**
**作者:** McCluggage et al.
**摘要:** 研究通过免疫组化方法验证了Inhibin beta A抗体在卵巢颗粒细胞瘤中的特异性表达,提出其可作为区分性索间质肿瘤与其他卵巢恶性肿瘤的可靠生物标志物。
---
### 3. **"Inhibin βA signaling regulates somatic cell differentiation in developing gonads"**
**作者:** Bernard et al.
**摘要:** 该文献利用Inhibin beta A抗体研究其在胚胎性腺发育中的作用,发现INHβA通过调控TGF-β/Smad通路影响生殖细胞与体细胞的相互作用,进而影响性腺分化过程。
---
### (可选)4. **"Inhibin βA as a paracrine regulator of germ cell apoptosis in the testis"**
**作者:** Yao et al.
**摘要:** 研究使用Inhibin beta A抗体揭示了该蛋白在睾丸微环境中的旁分泌功能,证明其通过调控局部细胞因子网络影响生殖细胞存活与凋亡平衡。
---
以上文献涵盖基因克隆、疾病诊断、发育生物学及生殖调控等领域,均通过Inhibin beta A抗体开展关键机制或应用研究。
Inhibin beta A (INHβA) is a subunit of inhibins and activins, which belong to the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) superfamily. Inhibins are heterodimeric glycoproteins composed of an alpha subunit (INHα) and one of two beta subunits (βA or βB), forming inhibin A (α-βA) or inhibin B (α-βB). Activins, conversely, are homodimers (e.g., activin A: βA-βA) or heterodimers (e.g., activin AB: βA-βB). INHβA plays a critical role in regulating reproductive physiology, including folliculogenesis, steroidogenesis, and pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion.
Antibodies targeting INHβA are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies are widely used in techniques such as immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blot (WB), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). In research, INHβA antibodies help investigate disorders like granulosa cell tumors, where INHβA overexpression is a diagnostic marker. They also aid in exploring roles in embryogenesis, cell differentiation, and apoptosis.
Clinically, INHβA antibodies assist in diagnosing ovarian and prostate cancers, as well as monitoring conditions like preeclampsia. Specificity is crucial, as cross-reactivity with other TGF-β family members (e.g., activins) must be minimized. Commercial INHβA antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, validated for applications across human, mouse, and rat tissues. Understanding INHβA’s regulatory mechanisms through these antibodies contributes to therapeutic developments targeting fertility disorders, cancers, and endocrine pathologies.
×