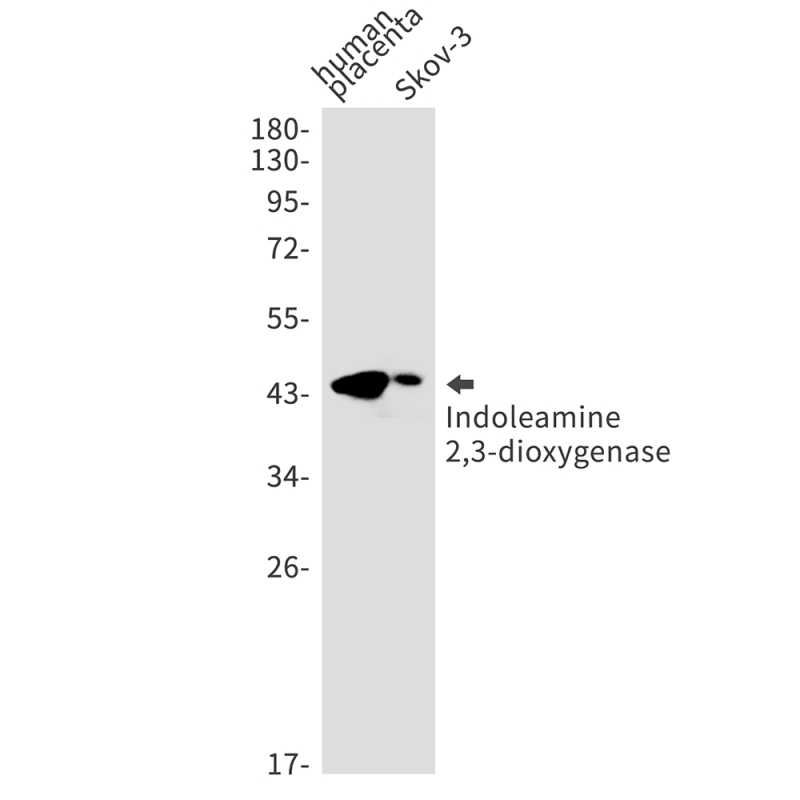
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 3-dioxygenase; IDO 1; IDO; IDO1; INDO; indolamine 2; 3 dioxygenase; Indole 2 3 dioxygenase |
| Entrez GeneID | 3620 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 45 kDa; Observed MW: 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Indoleamine 2.3-dioxygenase(IDO)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括:
1. **"Inhibition of indoleamine 2.3-dioxygenase enhances anti-tumor immunity in melanoma"**
- **Authors**: Spranger, S. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究利用IDO特异性抗体阻断IDO活性,发现其可增强T细胞对黑色素瘤的免疫应答,抑制肿瘤生长,并验证了抗体在肿瘤微环境中的免疫调节作用。
2. **"Characterization of monoclonal antibodies targeting human indoleamine 2.3-dioxygenase"**
- **Authors**: Qian, F. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究开发了高特异性的抗人IDO单克隆抗体,验证了其在免疫组化和流式细胞术中的检测能力,并证明其可用于定量分析肿瘤组织中IDO的表达水平。
3. **"Indoleamine 2.3-dioxygenase antibody blockade synergizes with immunogenic chemotherapy in preclinical models"**
- **Authors**: Holmgaard, R.B. et al.
- **摘要**: 通过抗IDO抗体联合化疗药物,研究者在小鼠模型中观察到显著的抗肿瘤协同效应,表明IDO抗体可能作为免疫治疗的辅助手段。
如需具体文献来源,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索标题及作者获取全文信息。
Indoleamine 2.3-dioxygenase (IDO) is a heme-containing enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step of tryptophan metabolism via the kynurenine pathway. By depleting local tryptophan levels and generating immunomodulatory metabolites, IDO plays a critical role in suppressing T-cell responses and promoting immune tolerance. It is highly expressed in tumor-associated immune cells, stromal cells, and certain cancer types, contributing to tumor immune evasion. IDO also participates in inflammatory, neurodegenerative, and autoimmune disorders.
IDO antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying IDO expression in research and clinical settings. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to study IDO's distribution and regulatory mechanisms in diseases. Most antibodies target specific isoforms (IDO1 or IDO2) or shared epitopes, aiding in isoform-specific functional studies. The development of IDO inhibitors, often evaluated alongside these antibodies, has shown therapeutic potential in enhancing antitumor immunity when combined with checkpoint inhibitors.
Research on IDO antibodies has expanded insights into its dual role: while chronic activity promotes immunosuppression, acute induction may support antimicrobial defense. However, clinical trials targeting IDO have faced challenges, highlighting the need for deeper mechanistic understanding. IDO antibodies remain vital for elucidating its complex interactions in cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, depression, and chronic inflammation.
×