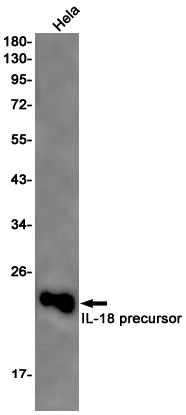
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
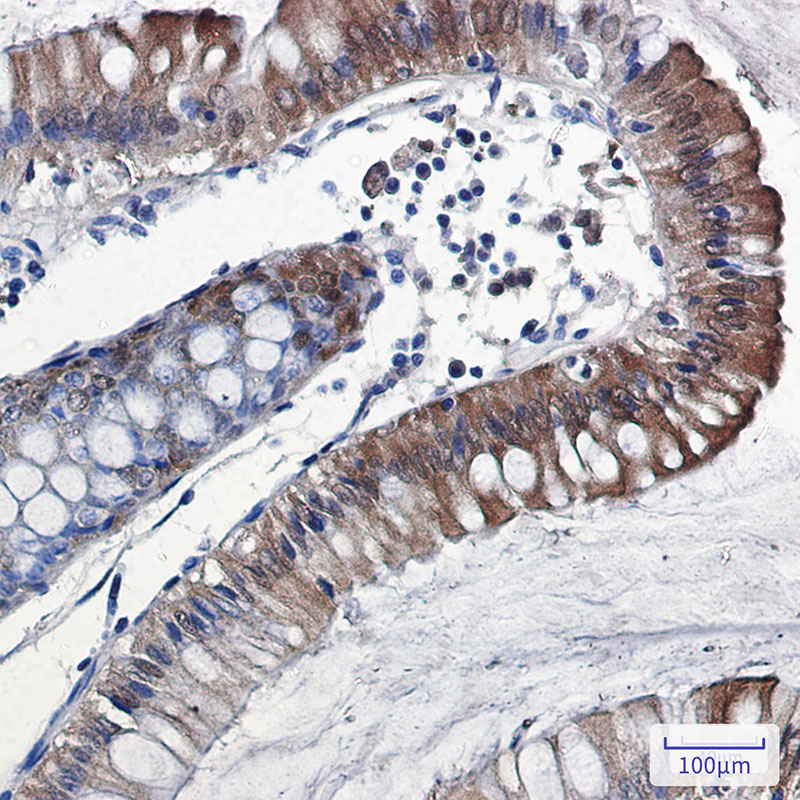
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL-18; IL18; IGIF; IL-1g; IL1F4; interleukin-18 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3606 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 22 kDa; Observed MW: 17 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human IL18 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于IL-18抗体的代表性文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*Interleukin-18 as a drug target in inflammatory disease*
**作者**:Charles A. Dinarello et al.
**摘要**:综述了IL-18在炎症性疾病(如类风湿性关节炎、痛风)中的作用机制,重点讨论了中和抗体或IL-18结合蛋白(如Tadekinig alfa)通过阻断IL-18信号通路减轻炎症反应的临床前及临床试验进展。
2. **文献名称**:*Tadekinig alfa (IL-18BP) in adult-onset Still's disease: a phase II pilot study*
**作者**:Cem Gabay et al.
**摘要**:报道了一项Ⅱ期临床试验结果,显示重组人IL-18结合蛋白(Tadekinig alfa)可显著降低成人Still病患者的血清IL-18水平及疾病活动度,验证了靶向IL-18的治疗潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*IL-18 neutralization ameliorates inflammation and mucosal damage in experimental colitis*
**作者**:Kenji Nakanishi et al.
**摘要**:通过小鼠结肠炎模型证明,抗IL-18中和抗体可减少促炎细胞因子(如IFN-γ)分泌,缓解肠道组织损伤,提示IL-18抗体在炎症性肠病中的治疗价值。
4. **文献名称**:*Targeting IL-18 in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis with neutralizing antibodies*
**作者**:Fabrizio De Benedetti et al.
**摘要**:研究发现系统性幼年特发性关节炎患者IL-18水平异常升高,动物模型显示抗IL-18抗体可抑制炎症级联反应,为临床试验提供了理论依据。
Interleukin-18 (IL-18), a pro-inflammatory cytokine belonging to the IL-1 superfamily, plays a pivotal role in innate and adaptive immunity. Produced primarily by macrophages, dendritic cells, and epithelial cells, it is initially synthesized as an inactive precursor requiring cleavage by caspase-1 or other proteases (e.g., neutrophil-derived proteases) to become bioactive. IL-18 signals through the IL-18 receptor (IL-18Rα/β), activating NF-κB and MAPK pathways to induce IFN-γ production, particularly in synergy with IL-12. This cytokine is implicated in inflammatory diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease), metabolic disorders (obesity, type 2 diabetes), and autoimmune conditions.
IL-18-neutralizing antibodies have emerged as therapeutic tools to block IL-18/IL-18R interactions, thereby dampening excessive inflammation. Preclinical studies demonstrate their efficacy in reducing disease severity in models of colitis, arthritis, and sepsis. Clinically, monoclonal antibodies like Tadekinig alfa (recombinant IL-18-binding protein) and specific anti-IL-18 mAbs are under investigation, showing promise in early-phase trials for conditions such as macrophage activation syndrome and adult-onset Still’s disease. Challenges include optimizing target specificity, managing potential immunosuppressive side effects, and addressing the complexity of IL-18's dual roles (pro- and anti-inflammatory) in different pathological contexts. Ongoing research also explores biomarkers to identify patient subsets most likely to benefit from IL-18 blockade therapies.
×