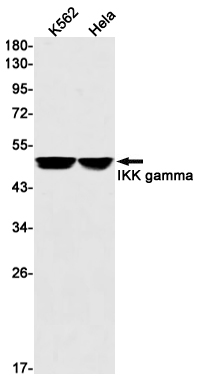
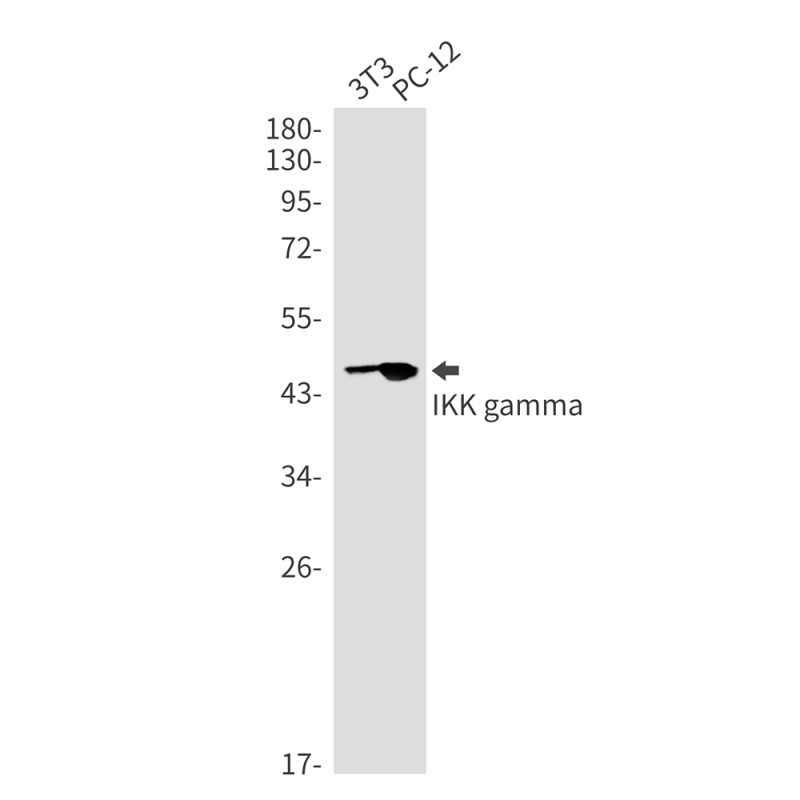
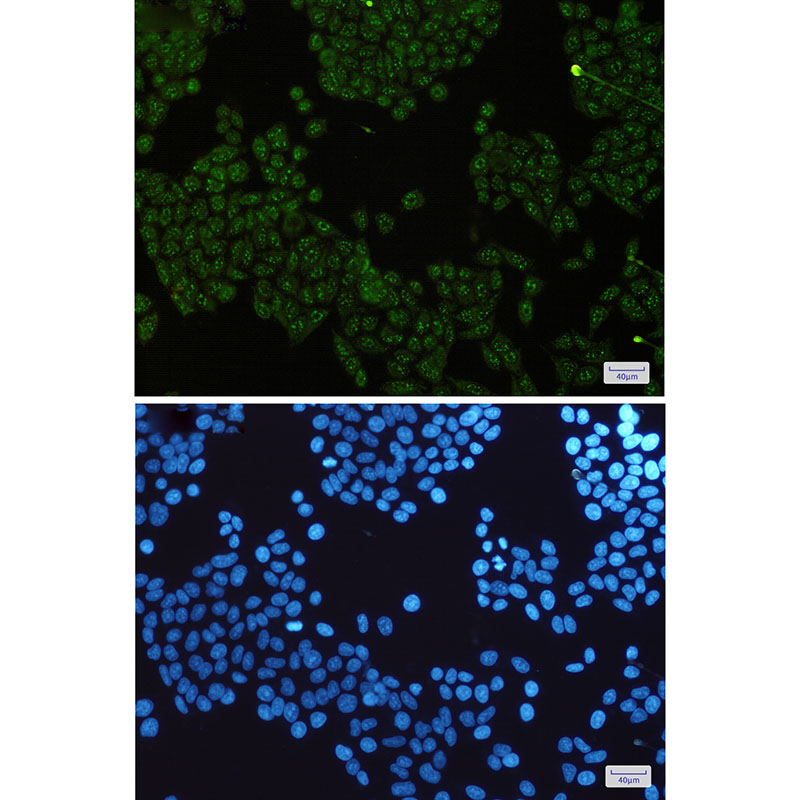
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IKBKG; FIP3; NEMO; NF-kappa-B essential modulator; NEMO; FIP-3; IkB kinase-associated protein 1; IKKAP1; Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit gamma; I-kappa-B kinase subunit gamma; IKK-gamma; IKKG; IkB kinase subunit gamma; NF |
| Entrez GeneID | 8517 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 48 kDa; Observed MW: 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human IKK gamma |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与IKKγ(NEMO)抗体相关的代表性文献,信息基于公开研究整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Structural basis for the interaction of NEMO with IκBα*
**作者**:Rushe M, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过X射线晶体学解析了IKKγ(NEMO)与IκBα蛋白的复合物结构,揭示了NEMO通过特定结构域(CC2-LZ)结合IκBα的磷酸化区域,阐明了NF-κB信号通路中关键调控机制,为相关抗体设计提供了结构基础。
---
2. **文献名称**:*A critical role for NEMO in TLR2-mediated inflammatory responses*
**作者**:Häcker H, et al.
**摘要**:通过基因敲除和抗体阻断实验,研究发现IKKγ(NEMO)在TLR2介导的炎症反应中不可或缺。使用特异性NEMO抗体证实其在MyD88依赖性信号传导中的作用,为免疫疾病治疗靶点提供依据。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Functional analysis of NEMO mutations in incontinentia pigmenti*
**作者**:Smahi A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用抗NEMO抗体检测患者细胞中IKKγ的突变体表达,发现突变导致NF-κB激活缺陷及细胞凋亡异常,解释了遗传病色素失禁症的分子机制,并提出基于抗体检测的临床诊断方法。
---
**备注**:若需获取全文,建议通过PubMed或Sci-Hub输入DOI/标题查询,或联系对应作者索取。实际应用中需根据实验需求(如WB、IP、IF等)选择已验证抗体并引用厂商说明书(如Cell Signaling Technology #2685)。
The IKK gamma antibody is a crucial tool in studying the IκB kinase (IKK) complex, a central regulator of the NF-κB signaling pathway. IKK gamma, also known as NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO) or IKK-associated protein 1 (IKKAP1), is the regulatory subunit of the IKK complex, which includes catalytic subunits IKKα (IKK1) and IKKβ (IKK2). Encoded by the IKBKG gene in humans, IKK gamma lacks enzymatic activity but is essential for the activation of NF-κB, a transcription factor involved in immune responses, inflammation, apoptosis, and cell survival.
Mutations in IKBKG are linked to severe genetic disorders like incontinentia pigmenti and ectodermal dysplasia with immunodeficiency. Researchers use IKK gamma antibodies to investigate its expression, post-translational modifications (e.g., ubiquitination), and interactions with other signaling components (e.g., RIP1. TRAF6) in pathways triggered by cytokines, pathogens, or stress. These antibodies are widely applied in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation to study NF-κB dysregulation in cancer, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammation.
Commercial IKK gamma antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (human or murine) and validated for specificity across applications. Their development has advanced drug discovery targeting NF-κB signaling, particularly for inflammatory and oncological therapies.
×