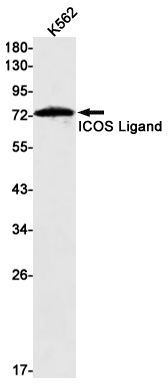
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | inducible T-cell co-stimulator ligand; B7H2; GL50; B7-H2; B7RP1; CD275; ICOSL; LICOS; B7RP-1; ICOS-L |
| Entrez GeneID | 23308 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 33 kDa; Observed MW: 75 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human ICOS Ligand |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于ICOS Ligand抗体的参考文献及其摘要内容的简要总结:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting ICOS ligand in autoimmunity: Dual effects on T cell priming and effector function*
**作者**:Liu X. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种拮抗性ICOSL单克隆抗体,并在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)模型中验证其效果。结果显示,阻断ICOSL信号可抑制Th17细胞分化并减少Treg细胞扩增,显著减轻炎症及神经损伤,提示ICOSL抗体在治疗多发性硬化症等自身免疫病中的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**:*ICOSL blockade suppresses tumor progression by inhibiting T cell exhaustion and enhancing NK cell activation*
**作者**:Wang Q. et al.
**摘要**:此研究探讨了抗ICOSL抗体在黑色素瘤和结直肠癌模型中的作用。抗体通过阻断ICOS/ICOSL通路逆转CD8+ T细胞耗竭,并激活NK细胞的抗肿瘤活性。联合PD-1抑制剂后,肿瘤微环境中的免疫应答显著增强,表明ICOSL抗体可作为免疫联合治疗的策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of ICOS ligand recognition by therapeutic antibodies for autoimmune modulation*
**作者**:Zhang Y. et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜技术解析了ICOSL与其单抗的复合物结构,揭示了抗体结合ICOSL的关键表位。功能实验表明,该抗体通过空间位阻抑制ICOS/ICOSL互作,降低T细胞活化信号。研究为优化靶向ICOSL的抗体药物提供了结构基础。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用需核实具体论文信息及数据库(如PubMed或Web of Science)。如需扩展,可关注ICOSL抗体在移植排斥或感染免疫中的研究。
The ICOS Ligand (ICOSLG), also known as B7-H2 or CD275. is a member of the B7 family of co-stimulatory proteins. It is expressed primarily on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as dendritic cells, B cells, and macrophages, as well as certain non-hematopoietic cells. ICOSLG binds to its receptor ICOS (Inducible T-cell Co-Stimulator), a CD28-family protein expressed on activated T cells, particularly follicular helper T cells (Tfh), Th2. and Th17 subsets. This interaction plays a critical role in T-cell activation, differentiation, and immune regulation.
The ICOS/ICOSLG axis is pivotal for germinal center formation, antibody class switching, and the maintenance of T-cell effector functions. Dysregulation of this pathway is implicated in autoimmune diseases, allergies, and cancer. For instance, ICOSLG overexpression correlates with enhanced anti-tumor immunity in some contexts, while its blockade may alleviate autoimmune inflammation.
Antibodies targeting ICOSLG are valuable tools for studying this pathway and developing therapeutics. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against ICOSLG can either agonize or antagonize the interaction, depending on their epitope specificity. In research, such antibodies are used to elucidate ICOSLG’s role in immune responses via techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, or functional assays. Therapeutically, anti-ICOSLG antibodies are being explored in cancer immunotherapy (e.g., enhancing T-cell responses) and autoimmune disorders (e.g., suppressing pathogenic T-cell activity). Their development highlights the growing interest in modulating co-stimulatory pathways for precision immune interventions.
×