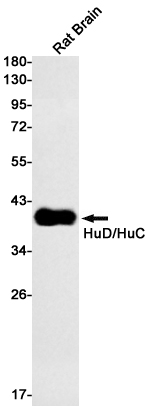
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Rat |
| Aliases | Huc; mHuC; PLE21; 2600009P04Rik |
| Entrez GeneID | 15571/1996 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 40 kDa; Observed MW: 40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of mouse HuC |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HuC/HuD抗体的3篇经典文献摘要概括:
---
1. **标题**:*Molecular cloning of the HuD antigen from a small cell lung carcinoma cell line*
**作者**:Szabo, A., Dalmau, J., Manley, G., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次克隆了HuD抗原基因,发现其编码神经元特异性RNA结合蛋白,并揭示了其在副肿瘤性神经综合征(如抗Hu抗体相关脑脊髓炎)中的自身抗原作用,为后续抗体诊断奠定基础。
2. **标题**:*HuD, a paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis antigen, contains RNA-binding domains and is homologous to Elav and Sex-lethal*
**作者**:Szabo, A., Dalmau, J., Manley, G., et al.
**摘要**:进一步分析HuD蛋白结构,发现其含有Elav家族保守的RNA结合域,提示其在神经元mRNA稳定性及翻译调控中的功能,并证实其在神经肿瘤和自身免疫疾病中的异常表达。
3. **标题**:*HuC and HuD proteins are required for neuronal differentiation and survival*
**作者**:Deschênes-Furry, J., Mousavi, K., et al.
**摘要**:通过体外实验证明HuC/HuD在神经元分化中调控靶mRNA(如GAP-43)的表达,敲低Hu蛋白导致神经元凋亡,提示其在神经发育中的关键作用。
---
**备注**:上述文献早期阐明了HuC/HuD的分子特性、神经功能及临床意义,其抗体广泛应用于神经生物学研究和肿瘤相关神经综合征的诊断。如需具体实验应用或近年研究,建议补充检索关键词如“HuC/HuD antibody immunohistochemistry”或“HuD cancer biomarker”。
**Background of HuC/HuD Antibodies**
HuC and HuD are RNA-binding proteins belonging to the Embryonic Lethal Abnormal Vision (ELAVL)/Hu family, primarily expressed in neurons. These proteins, encoded by *ELAVL3* (HuC) and *ELAVL4* (HuD) genes, play critical roles in post-transcriptional regulation of mRNAs, including stabilization, transport, and translation, particularly during neurodevelopment and neuronal maintenance. Structurally, they contain three RNA recognition motifs (RRMs) that bind AU-rich elements in target mRNAs.
Antibodies against HuC/HuD are widely used as neuronal markers in research and diagnostics. In clinical settings, HuC/HuD antibodies aid in identifying neuronal-derived tumors, such as neuroblastoma, and are associated with paraneoplastic neurological syndromes (PNS). For example, anti-Hu antibodies (often targeting HuD) are detected in patients with small-cell lung cancer experiencing PNS, where the immune system mistakenly attacks neuronal tissues.
In research, these antibodies help study neuronal differentiation, synaptic plasticity, and neurodegenerative diseases. However, cross-reactivity among Hu family members (HuR, HuB, HuC, HuD) requires careful validation in experimental applications. Their specificity for neuronal tissues makes them valuable tools in immunohistochemistry and Western blotting to trace neuronal lineage or assess neural tissue integrity. Limitations include variable expression levels across neuronal subtypes and potential non-specific binding in non-neural contexts.
×