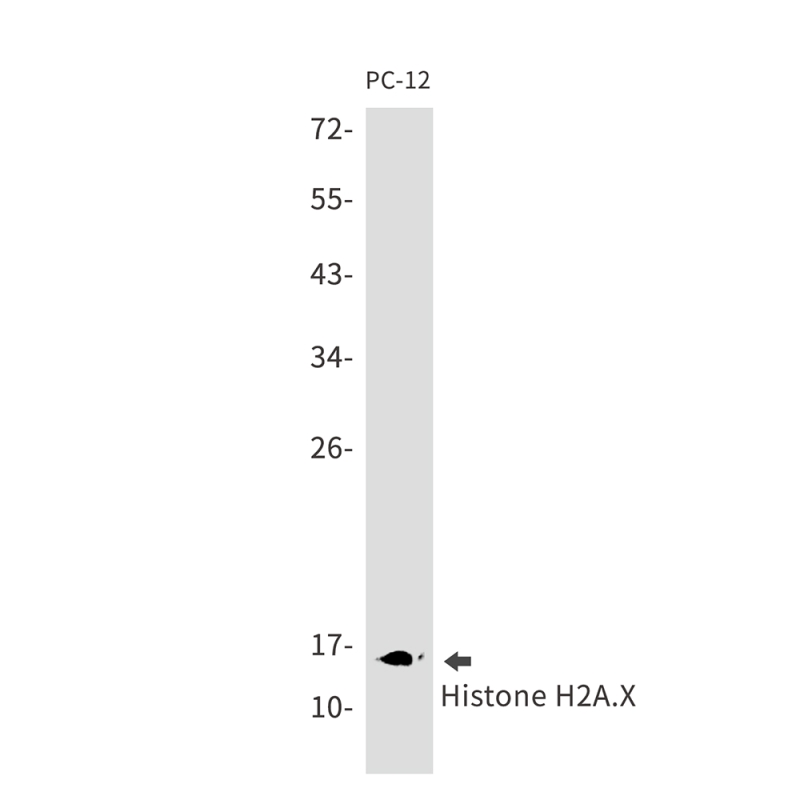
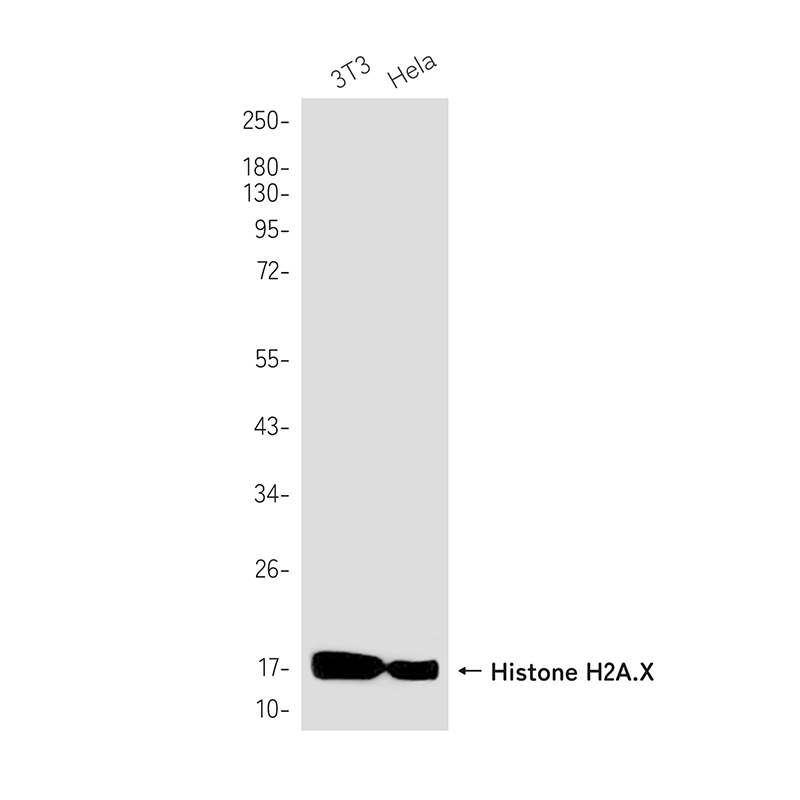
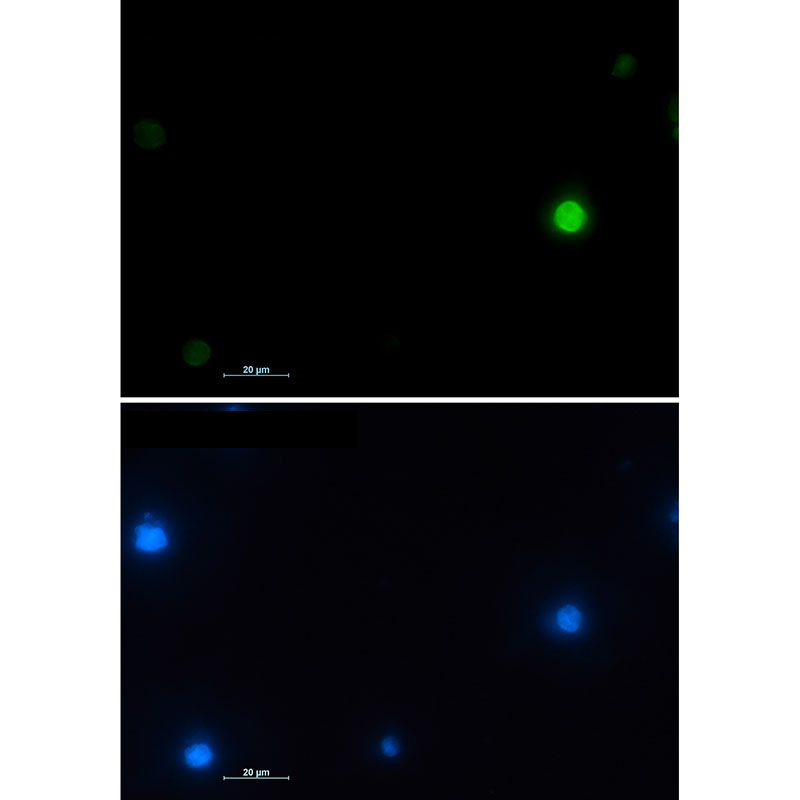
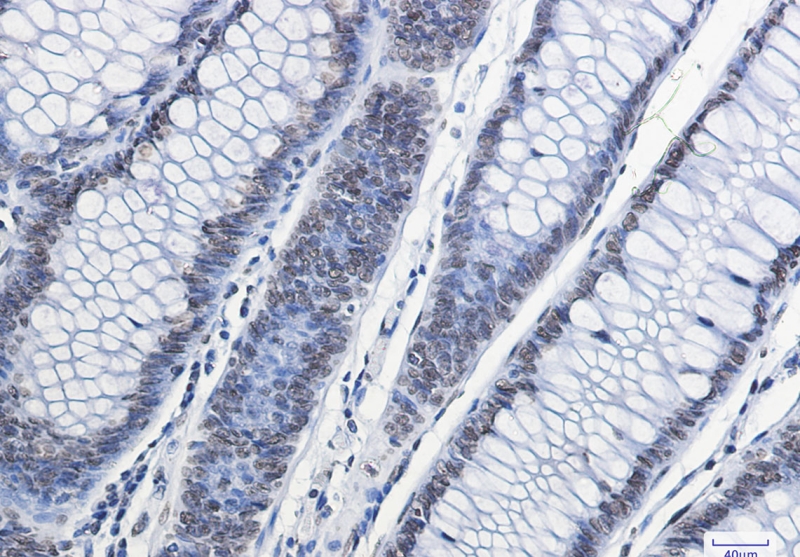
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | H2A.X; H2AFX; H2a/x; HIST5-2AX; Histone H2A.X |
| Entrez GeneID | 3014 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 15 kDa; Observed MW: 15 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Histone H2A.X |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Histone H2A.X抗体的经典文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139*
**作者**:Rogakou, E.P., Pilch, D.R., Orr, A.H., Ivanova, V.S., Bonner, W.M.
**摘要**:首次报道H2A.X在DNA双链断裂(DSB)后被磷酸化形成γ-H2A.X,并开发特异性抗体用于检测,证实其作为DSB标志物的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Characteristics of γ-H2AX foci at DNA double-strand breaks sites*
**作者**:Sedelnikova, O.A., Rogakou, E.P., Panyutin, I.G., Bonner, W.M.
**摘要**:利用H2A.X抗体通过免疫荧光技术定量分析电离辐射诱导的γ-H2A.X焦点,揭示其与DSB数量及修复动态的直接相关性。
3. **文献名称**:*γH2AX and cancer*
**作者**:Bonner, W.M., Redon, C.E., Dickey, J.S., Nakamura, A.J., Sedelnikova, O.A., et al.
**摘要**:综述γ-H2A.X抗体在癌症研究中的应用,包括评估放疗/化疗疗效及肿瘤基因组不稳定性,强调其作为治疗响应生物标志物的潜力。
---
这些文献奠定了γ-H2A.X抗体在DNA损伤检测领域的核心地位,并推动了其在分子生物学与临床医学中的广泛应用。
Histone H2A.X is a variant of the core histone H2A, playing a critical role in maintaining genomic stability and orchestrating the DNA damage response (DDR). Its defining feature is a conserved C-terminal SQEY motif, which becomes phosphorylated at serine 139 (γ-H2A.X) in response to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). This phosphorylation event, mediated by kinases like ATM, ATR, or DNA-PK, serves as a molecular beacon to recruit repair proteins and facilitate chromatin remodeling at damage sites.
Antibodies targeting H2A.X or γ-H2A.X are indispensable tools in studying DNA damage and repair mechanisms. They enable the visualization and quantification of DSBs through techniques such as immunofluorescence, Western blotting, or flow cytometry. γ-H2A.X foci formation is widely used as a biomarker for genotoxic stress in cancer research, radiation biology, and toxicology. These antibodies also help investigate the role of H2A.X in chromatin dynamics, apoptosis, and cellular senescence.
In translational contexts, γ-H2A.X antibodies aid in evaluating the efficacy of DNA-damaging therapies (e.g., chemotherapy, radiotherapy) and assessing environmental or pharmaceutical genotoxicity. Their specificity and sensitivity make them critical for understanding how dysregulated DDR contributes to diseases like cancer, neurodegeneration, and aging. Commercial H2A.X antibodies are typically validated across species, including human, mouse, and rat, ensuring broad experimental applicability.
×