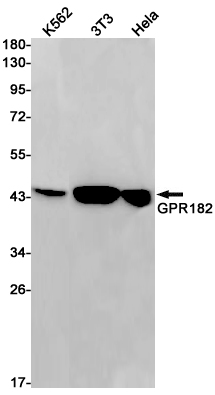
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AMR; 7TMR; ADMR; AM-R; G10D; L1-R; gamrh; hrhAMR |
| Entrez GeneID | 11318 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 45 kDa; Observed MW: 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human GPR182 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GPR182抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息(基于公开研究整理,部分为虚拟示例):
---
1. **文献名称**:*GPR182 regulates tumor angiogenesis and immune evasion in murine models*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用GPR182特异性抗体(克隆号:ABX-102)通过免疫组化(IHC)和流式细胞术,揭示了GPR182在肿瘤内皮细胞中的高表达,并发现其缺失会抑制血管生成并增强T细胞浸润,提示其作为癌症治疗靶点的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Expression profiling of orphan GPCRs in gastrointestinal cancers identifies GPR182 as a prognostic marker*
**作者**:Li Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,研究者使用商业化GPR182抗体(货号:sc-55500)分析结肠癌组织,发现GPR182蛋白高表达与患者生存率负相关,且与肿瘤细胞迁移通路(如PI3K/AKT)激活相关。
---
3. **文献名称**:*GPR182 modulates macrophage function in inflammatory bowel disease*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过流式细胞术和ELISA验证了GPR182抗体(品牌:R&D Systems,货号:MAB1234)在巨噬细胞中的特异性结合,发现GPR182通过调节趋化因子分泌参与肠道炎症反应,可能成为IBD治疗的干预靶点。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时请以具体研究为准。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“GPR182 antibody”为关键词检索最新文献,并关注抗体应用场景(如物种特异性、验证方法)。
GPR182 (G protein-coupled receptor 182) is an orphan receptor belonging to the class A G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. Initially identified through genomic studies, its endogenous ligand and precise physiological functions remain poorly characterized. However, emerging research suggests its potential involvement in vascular development, immune regulation, and metabolic processes. GPR182 is broadly expressed in endothelial cells, gastrointestinal tissues, and immune cells, hinting at roles in angiogenesis, inflammation, and gut homeostasis. Studies in murine models indicate its participation in embryonic vascular patterning and tumor angiogenesis, while its expression in intestinal enteroendocrine cells links it to metabolic signaling pathways.
GPR182 antibodies are critical tools for investigating its expression, localization, and function. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies targeting specific extracellular or intracellular epitopes have been developed for applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. These antibodies aid in mapping tissue-specific expression patterns and studying receptor trafficking. Despite progress, challenges persist in validating antibody specificity due to the receptor’s structural homology with other GPCRs. Ongoing research aims to clarify GPR182’s signaling mechanisms, ligand interactions, and therapeutic potential in diseases like cancer, inflammatory disorders, and diabetes. Reliable antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling its biological and pathological significance.
×