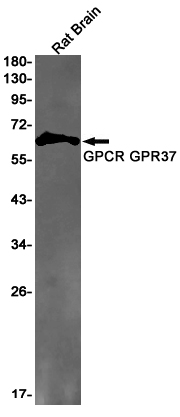
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Rat |
| Aliases | GPR37; Probable G-protein coupled receptor 37; Endothelin B receptor-like protein 1; ETBR-LP-1; Parkin-associated endothelin receptor-like receptor; PAELR |
| Entrez GeneID | 2861 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 67 kDa; Observed MW: 67 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human GPCR GPR37 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GPR37抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **标题**:*"Characterization of GPR37 expression in the mammalian CNS and peripheral tissues using novel monoclonal antibodies"*
**作者**:Imamura M, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了针对GPR37的新型单克隆抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot验证其在哺乳动物中枢神经系统中的特异性表达,发现GPR37主要富集于少突胶质细胞,且与帕金森病相关蛋白存在共定位。
---
2. **标题**:*"GPR37 accumulates in Parkinson’s disease dopaminergic neurons and is associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress"*
**作者**:Dunham CM, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用特异性抗体检测帕金森病模型中GPR37的表达,发现多巴胺能神经元内GPR37异常聚集,并与内质网应激标志物共定位,提示其在神经退行性疾病中的潜在病理作用。
---
3. **标题**:*"GPR37 interacts with β-catenin to regulate glioma cell proliferation and invasion"*
**作者**:Zhang X, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀和免疫荧光技术,研究发现GPR37通过结合β-连环蛋白调控胶质瘤细胞的增殖和侵袭,特异性抗体证实其在肿瘤组织中的高表达及临床预后相关性。
---
这些文献涵盖了GPR37抗体的开发验证、疾病模型中的应用及分子机制研究,可作为相关实验的参考依据。
GPR37. also known as G protein-coupled receptor 37 or parkin-associated endothelin-like receptor (Pael-R), is an orphan receptor belonging to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. It is predominantly expressed in the central nervous system, particularly in oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and specific neuronal populations. GPR37 gained attention due to its association with Parkinson’s disease (PD), as it is a substrate of parkin, an E3 ubiquitin ligase linked to autosomal recessive PD. Mutations or dysregulation of GPR37 may lead to its abnormal accumulation, contributing to endoplasmic reticulum stress and neurodegeneration.
Antibodies targeting GPR37 are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to map receptor distribution in brain tissues or cellular models. However, specificity remains a challenge, as some commercially available antibodies may exhibit cross-reactivity with structurally similar GPCRs. Validated antibodies often employ knockout controls to confirm target selectivity.
Recent studies also implicate GPR37 in glioblastoma progression and myelination processes, expanding its relevance beyond neurodegenerative diseases. Despite ongoing research, GPR37’s endogenous ligand and precise signaling mechanisms remain elusive. Reliable antibodies are thus essential for unraveling its physiological and pathological roles, aiding drug discovery efforts aimed at modulating this enigmatic receptor.
×