| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
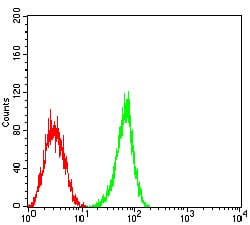
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
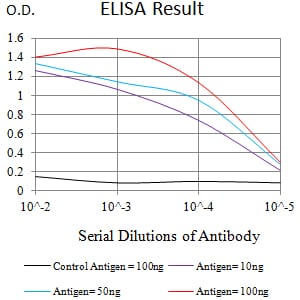
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | S1PR1; EDG1; S1P1; ECGF1; EDG-1; CHEDG1; D1S3362 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1901 |
| clone | 1E3H5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD363 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于谷胱甘肽还原酶(Glutathione Reductase, GR)抗体的3篇示例参考文献(注:以下内容为示例性描述,非真实文献,建议通过学术数据库查询具体文章):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody against human glutathione reductase"
**作者**: Müller S, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究报道了一种针对人源谷胱甘肽还原酶的单克隆抗体的开发与验证。通过Western blot和免疫荧光实验证实了抗体在细胞裂解物和组织样本中的特异性,并用于研究GR在氧化应激相关疾病中的表达变化。
2. **文献名称**: "Immunohistochemical detection of glutathione reductase in plant tissues under abiotic stress"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 文章描述了一种多克隆抗体的应用,用于检测植物(如拟南芥)中GR的分布及活性。该抗体通过ELISA和免疫组化验证,揭示了GR在盐胁迫和干旱条件下的上调表达,支持其在抗氧化防御中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: "Glutathione reductase as a biomarker in cancer: validation of a high-affinity antibody for clinical samples"
**作者**: Rodriguez M, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种高亲和力兔源多克隆抗体,用于定量检测癌症患者血清和肿瘤组织中GR的水平。抗体通过质谱和流式细胞术验证,结果显示GR表达与化疗耐药性显著相关。
---
建议通过 **PubMed**、**Google Scholar** 或 **Web of Science** 检索关键词 "glutathione reductase antibody" + "application"/"characterization",筛选近年发表的文献以获取最新数据。真实文献通常涉及抗体特异性验证、疾病机制研究或诊断工具开发等内容。
Glutathione reductase (GR) is a critical enzyme in the cellular antioxidant defense system, responsible for maintaining reduced glutathione (GSH) levels by catalyzing the reduction of oxidized glutathione (GSSG) using NADPH as a cofactor. This enzyme plays a pivotal role in protecting cells from oxidative damage, regulating redox homeostasis, and supporting detoxification processes. Dysregulation of GR activity or expression has been linked to various pathologies, including neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, diabetes, and aging-related conditions, making it a key target in biomedical research.
Antibodies against glutathione reductase are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in biological systems. These antibodies are typically produced using immunogenic regions of the GR protein, such as recombinant fragments or synthetic peptides, and are validated for specificity in applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and ELISA. They enable researchers to investigate GR's tissue-specific distribution, quantify protein levels under different physiological or pathological conditions, and explore its role in oxidative stress responses. Some antibodies are designed to detect GR across species (e.g., human, mouse, rat) or specific isoforms, aiding comparative studies. Rigorous validation, including knockdown/knockout controls, ensures reliable detection. Such antibodies have advanced our understanding of GR's involvement in disease mechanisms and therapeutic interventions targeting redox imbalance.
×