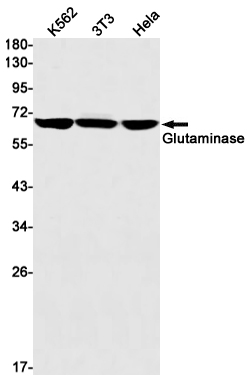
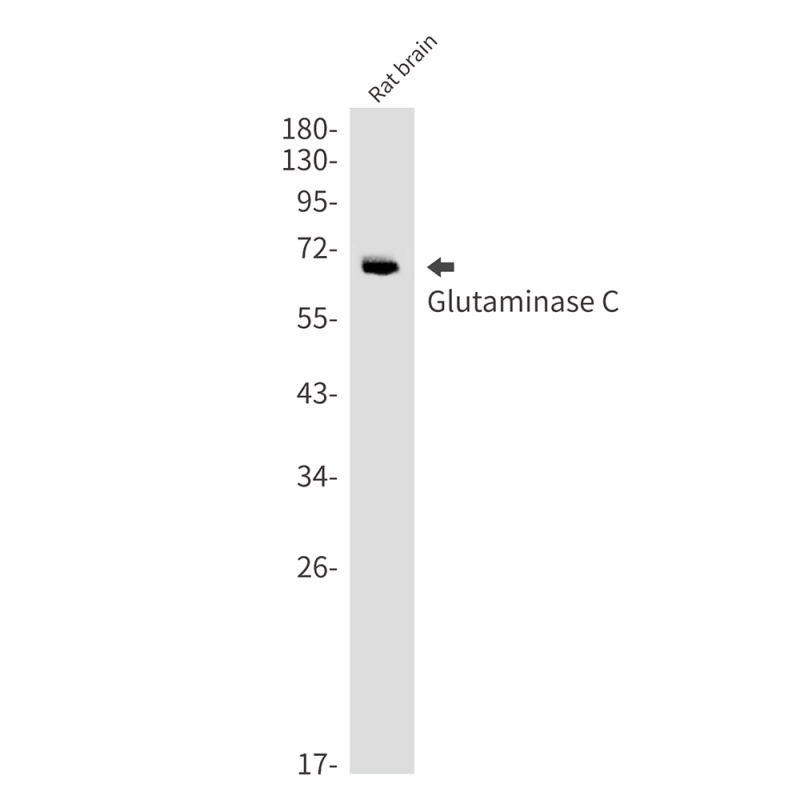
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
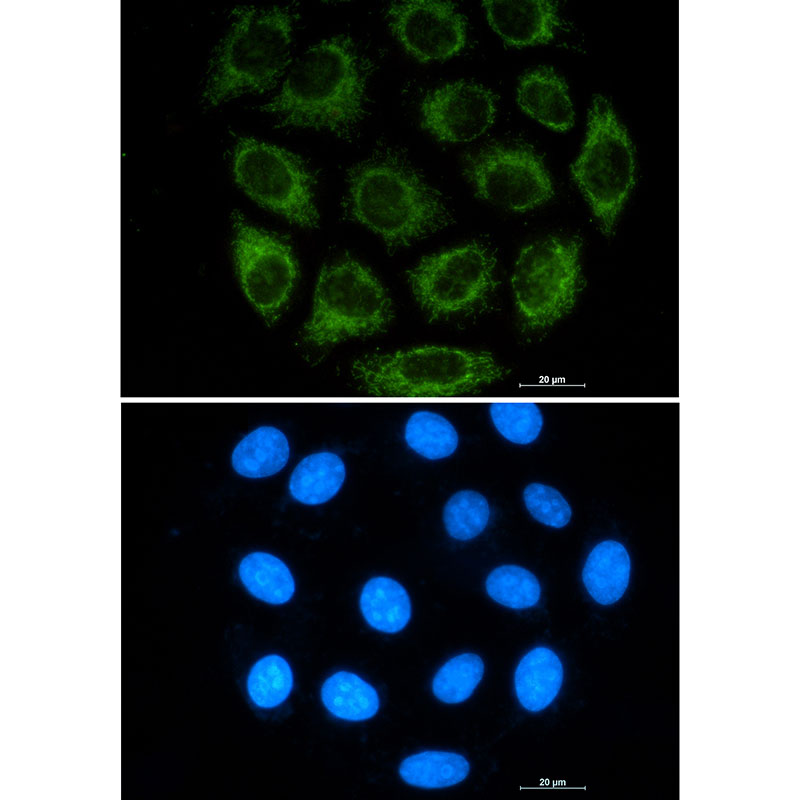
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Glutaminase kidney isoform; GLS; GLS1; KGA; K-glutaminase; GAM; GAC; Glutaminase C; L-glutamine amidohydrolase |
| Entrez GeneID | 2744 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 73 kDa; Observed MW: 68 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human Glutaminase C |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于谷氨酰胺酶(Glutaminase)抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要概览:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Glutaminase isoform expression in renal cell carcinoma and its clinical relevance*
**作者**: van der Heijden, M.S., et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过免疫组化(IHC)分析肾细胞癌中GLS和GLS2亚型表达,发现GLS高表达与肿瘤侵袭性相关,抗体特异性验证支持其作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**: *Targeting glutaminase with CB-839 enhances anti-tumor immunity in triple-negative breast cancer*
**作者**: Leone, R.D., et al.
**摘要**: 利用GLS特异性抗体(Western blot/IHC)评估CB-839抑制剂对肿瘤代谢的调控,证明抑制GLS可重塑肿瘤微环境并增强免疫治疗效果。
3. **文献名称**: *Monoclonal antibody characterization of glutaminase in human brain tumors*
**作者**: Seltzer, M.J., et al.
**摘要**: 开发并验证针对GLS1的单克隆抗体,用于胶质母细胞瘤组织检测,证实其高表达与患者预后不良相关,抗体特异性经敲除实验验证。
---
**领域覆盖**:上述文献涵盖癌症代谢(肾癌、三阴性乳腺癌、脑肿瘤),涉及抗体在基础研究(亚型定位)及治疗开发(抑制剂评估)中的应用。如需更多方向(如神经疾病),可进一步补充。
**Background of Glutaminase Antibodies**
Glutaminase (GLS) is a critical enzyme in glutamine metabolism, catalyzing the hydrolysis of glutamine to glutamate and ammonia. This reaction is pivotal in cellular energy production, nucleotide synthesis, and redox balance, particularly in rapidly proliferating cells like cancer cells. Two major isoforms exist: *GLS1* (kidney-type) and *GLS2* (liver-type), each with distinct tissue expression and regulatory mechanisms. GLS1. including splice variants KGA and GAC, is overexpressed in many cancers, supporting tumor growth via the "glutamine addiction" phenotype. GLS2. though less studied, has roles in both metabolism and oxidative stress regulation.
Antibodies targeting glutaminase are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. They enable detection of specific isoforms in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Researchers use these antibodies to explore glutaminase's role in cancer progression, neurological disorders (e.g., Alzheimer's disease), and metabolic reprogramming.
Commercial glutaminase antibodies are typically raised against peptide sequences unique to GLS1 or GLS2. ensuring isoform specificity. Validation often includes knockout/knockdown controls or recombinant protein assays. Challenges include cross-reactivity due to sequence homology between isoforms or splice variants. Recent therapeutic interest in glutaminase inhibitors (e.g., CB-839 in cancer trials) has further driven demand for reliable antibodies to assess target engagement and biomarker expression.
In summary, glutaminase antibodies are vital for advancing research into metabolic diseases and cancer, offering insights into therapeutic targeting of glutamine metabolism pathways.
×