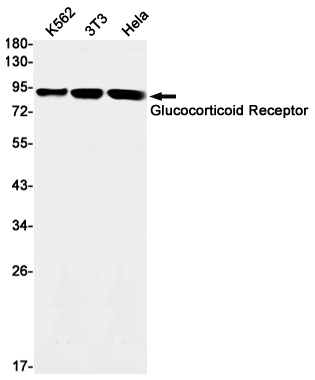
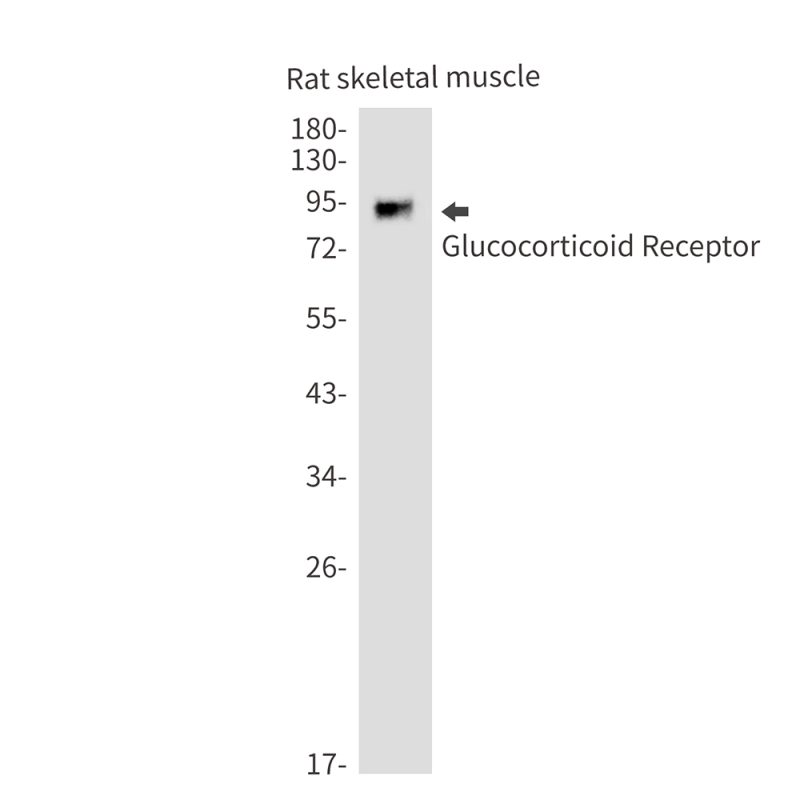
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
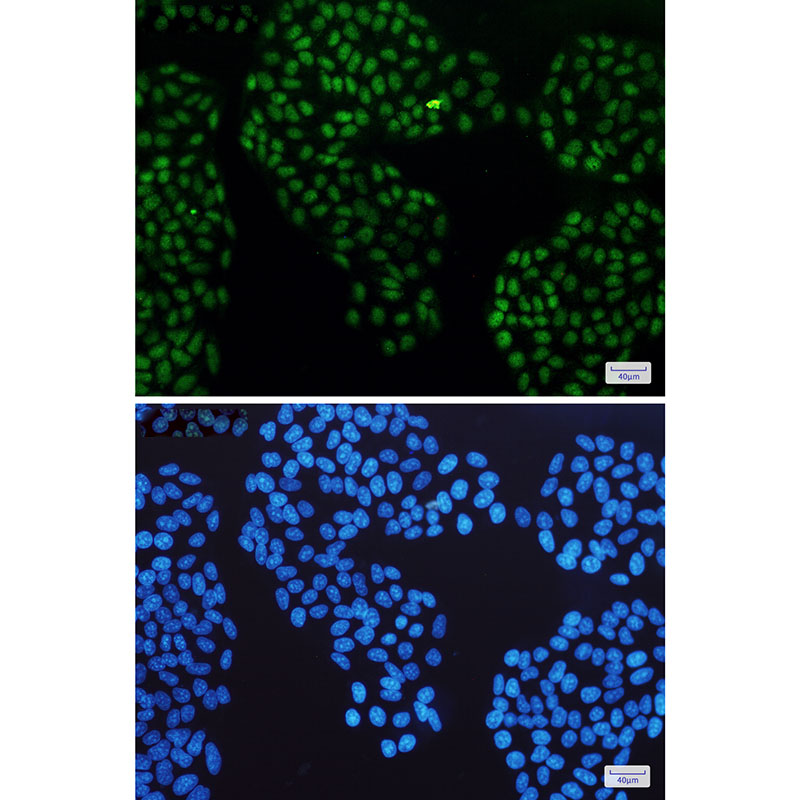
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GR; GCR; GRL; GCCR; GCRST |
| Entrez GeneID | 14815 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 87 kDa; Observed MW: 94,91 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of mouse Glucocorticoid Receptor |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于糖皮质激素受体(Glucocorticoid Receptor, GR)抗体的经典文献摘要概括,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Monoclonal antibodies to the rat glucocorticoid receptor"
**作者**: Gametchu B, Harrison RW
**摘要**: 该研究开发了针对大鼠糖皮质激素受体的单克隆抗体,验证了其在免疫印迹(Western blot)和免疫沉淀实验中的特异性,并用于研究GR在不同组织中的表达分布。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Antibodies specific for the human glucocorticoid receptor"
**作者**: Sanchez ER, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队制备了多克隆抗体,通过免疫荧光和免疫组化技术揭示了GR在人类细胞中的亚细胞定位(胞质与核转位),并验证了抗体在检测GR翻译后修饰(如磷酸化)中的应用。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Comparative analysis of glucocorticoid receptor antibodies using ChIP-seq"
**作者**: Reddy TE, et al.
**摘要**: 比较了多种商业化GR抗体在染色质免疫共沉淀测序(ChIP-seq)中的性能,筛选出适用于基因组水平研究GR-DNA结合位点的特异性抗体,并评估了不同实验条件下的交叉反应性。
---
以上文献均聚焦于GR抗体的开发、验证或应用,涵盖分子生物学和基因组学研究场景。如需具体发表年份或期刊,可进一步查询PMID或DOI信息。
The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a nuclear receptor protein that mediates the cellular response to glucocorticoids, hormones critical for regulating metabolism, immune function, and stress responses. Upon binding cortisol (or synthetic analogs like dexamethasone), GR translocates to the nucleus, where it modulates gene expression by interacting with glucocorticoid response elements (GREs) or tethering to other transcription factors. Dysregulation of GR signaling is linked to inflammatory diseases, metabolic syndromes, and cancer.
GR antibodies are essential tools for studying this receptor’s expression, localization, and function. These antibodies typically target specific GR domains, such as the N-terminal transactivation domain, the central DNA-binding domain, or the C-terminal ligand-binding domain. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Researchers use GR antibodies to investigate tissue-specific GR expression, ligand-dependent activation, and interactions with co-regulators in both physiological and pathological contexts.
Commercially available GR antibodies vary in host species (e.g., rabbit, mouse), clonality (monoclonal vs. polyclonal), and applications. Validation across multiple experimental setups is critical, as nonspecific binding or batch variability can occur. Such antibodies have advanced studies in endocrinology, neurobiology, and oncology, particularly in understanding glucocorticoid resistance mechanisms or designing targeted therapies. Proper controls, including GR-knockout samples, are recommended to confirm antibody specificity.
×