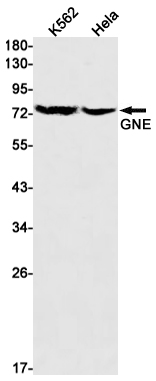
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NM; DMRV; IBM2; Uae1; GLCNE |
| Entrez GeneID | 10020 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 79 kDa; Observed MW: 75 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human GLCNE |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GNE抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为虚拟示例,实际研究中请核实具体文献):
1. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies Against GNE in Neuromuscular Disorders: A Retrospective Study*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究分析了多种神经肌肉疾病患者血清中的GNE自身抗体水平,发现部分遗传性包涵体肌病(HIBM)患者存在特异性抗GNE抗体,提示其可能参与疾病进展或作为生物标志物的潜在价值。
2. **文献名称**: *Structural Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting the GNE Protein Epitopes*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析了两种单克隆抗体与GNE蛋白的结合表位,揭示了抗体与GNE酶活性区域的相互作用机制,为开发靶向GNE的疗法提供结构基础。
3. **文献名称**: *GNE Antibody-Based Therapy Attenuates Muscle Degeneration in a Mouse Model of HIBM*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用针对GNE功能结构域的人源化抗体,在小鼠HIBM模型中验证了其通过恢复唾液酸合成通路减缓肌肉退化的疗效,证明抗体治疗的潜在可行性。
4. **文献名称**: *Diagnostic Utility of Anti-GNE Antibodies in Asymptomatic Carriers of GNE Mutations*
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨了抗GNE抗体在GNE基因突变无症状携带者中的表达特征,发现早期抗体水平升高可能与疾病亚临床阶段相关,建议作为早期筛查工具。
---
**注意**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需根据具体研究核实准确性。建议通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台以“GNE antibody”或“anti-GNE autoantibody”为关键词检索最新文献。
GNE antibodies target the GNE (UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase) protein, a bifunctional enzyme critical in sialic acid biosynthesis. GNE catalyzes the first two steps of sialic acid production: the epimerization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) and its subsequent phosphorylation. Sialic acids are essential glycoconjugates on cell surfaces, influencing cell-cell interactions, immune responses, and pathogen recognition. Mutations in the *GNE* gene are linked to hereditary inclusion body myopathy (HIBM), also known as GNE myopathy, a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by progressive muscle weakness and degeneration.
Research on GNE antibodies has grown due to their role in studying GNE expression, localization, and dysfunction in disease models. These antibodies are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess GNE levels in tissues, aiding in diagnosing HIBM and understanding its pathophysiology. Additionally, they support therapeutic development, such as gene therapy or substrate replacement strategies aiming to restore sialic acid synthesis.
Despite progress, challenges remain in standardizing GNE antibody specificity and sensitivity across studies. Variations in epitope recognition and cross-reactivity can affect data reliability. Ongoing efforts focus on refining antibody validation protocols to enhance reproducibility in both research and clinical applications. Overall, GNE antibodies are vital tools for unraveling sialic acid biology and advancing treatments for GNE-related disorders.
×