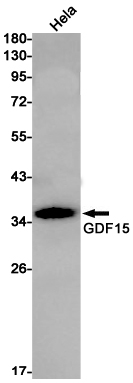
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GDF15; MIC1; PDF; PLAB; PTGFB; Growth/differentiation factor 15; GDF-15; Macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1; MIC-1; NSAID-activated gene 1 protein; NAG-1; NSAID-regulated gene 1 protein; NRG-1; Placental TGF-beta; Placental bone morphogenetic |
| Entrez GeneID | 9518 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34 kDa; Observed MW: 34 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human GDF15 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GDF15抗体的3-4篇参考文献及其摘要概述:
1. **文献名称**:*GDF15 mediates the effects of metformin on body weight and energy balance*
**作者**:Coll, A.P., et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了GDF15在二甲双胍调节体重和能量代谢中的作用,发现GDF15抗体可阻断二甲双胍诱导的体重减轻,提示GDF15信号通路可能是代谢疾病治疗的潜在靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-GDF15 monoclonal antibody reverses cancer cachexia in preclinical models*
**作者**:Mullican, S.E., et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种靶向GDF15的单克隆抗体,在癌症恶病质小鼠模型中显著抑制肿瘤相关的肌肉消耗和脂肪分解,为癌症相关代谢紊乱提供了治疗策略。
3. **文献名称**:*GDF15 neutralization alleviates platinum-based chemotherapy-induced emesis and anorexia*
**作者**:Suriben, R., et al.
**摘要**:通过中和GDF15的抗体,该研究成功减轻了化疗药物(如顺铂)引发的恶心和食欲减退副作用,表明抑制GDF15可改善化疗患者的生活质量。
4. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of GDF15 recognition by therapeutic antibodies for metabolic disorders*
**作者**:Patel, S., et al.
**摘要**:该文献解析了GDF15与其治疗性抗体结合的分子结构,揭示了抗体特异性中和GDF15的机制,为设计针对肥胖和糖尿病的新型抗体药物提供了结构基础。
这些研究涵盖了GDF15抗体在代谢疾病、癌症恶病质及化疗副作用中的治疗潜力,从机制探索到临床前应用均有涉及。
GDF15 (Growth Differentiation Factor 15), a stress-responsive cytokine belonging to the TGF-β superfamily, is implicated in diverse physiological and pathological processes, including metabolism regulation, inflammation, and cellular stress responses. Elevated GDF15 levels are observed in conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, obesity, and mitochondrial disorders. Its primary receptor, GFRAL, is expressed in the hindbrain and mediates GDF15's anorectic effects, influencing energy homeostasis.
GDF15 antibodies have emerged as therapeutic tools to modulate its activity. Neutralizing antibodies targeting GDF15 or its receptor are explored for metabolic disorders. For instance, blocking GDF15's action may counteract its appetite-suppressing effects, potentially benefiting cancer-associated cachexia or excessive weight loss. Conversely, agonistic approaches to enhance GDF15 signaling are investigated for obesity management.
In oncology, anti-GDF15 antibodies aim to mitigate chemotherapy-induced side effects, as GDF15 upregulation contributes to nausea and anorexia. Additionally, GDF15 is studied as a biomarker for disease progression, with antibodies enabling its detection in diagnostics. Challenges include balancing therapeutic efficacy with safety, given GDF15's dual roles in tissue protection and pathology. Recent preclinical studies highlight promising outcomes, though clinical translation requires further validation. Overall, GDF15 antibodies represent a versatile strategy for targeting metabolic and stress-related diseases.
×