
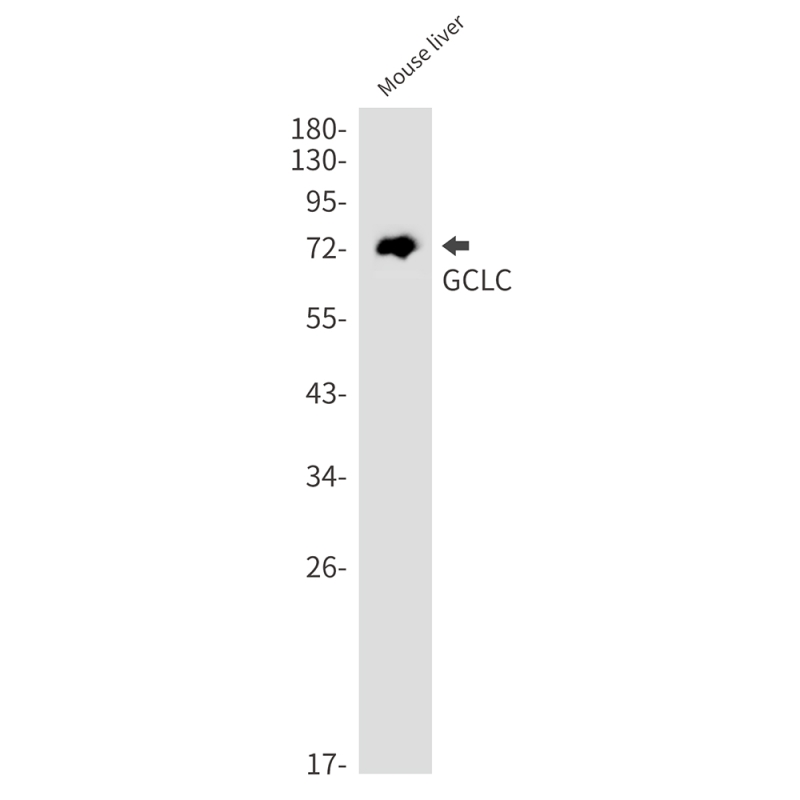
| WB | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GCLC; GLCL; GLCLC; Glutamate--cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GCS heavy chain; Gamma-ECS; Gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase |
| Entrez GeneID | 2729 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 73 kDa; Observed MW: 73 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human GCLC |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及GCLC抗体的文献摘要概括,按研究领域分类呈现:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway regulates human glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit expression*
**作者**:Solis WA et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了Nrf2转录因子通过结合GCLC启动子区域调控其表达,实验中用GCLC抗体验证氧化应激条件下蛋白表达水平变化,证实了该通路在抗氧化防御中的作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit as a therapeutic target in Parkinson's disease*
**作者**:Chen PC et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化和Western blot(使用GCLC抗体)发现帕金森病模型中GCLC表达下降,补充NAC可恢复谷胱甘肽水平,提示靶向GCLC或成神经保护新策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Hepatocyte-specific deletion of GCLC exacerbates acetaminophen-induced liver injury*
**作者**:Imaeda AB et al.
**摘要**:利用GCLC抗体检测肝细胞特异性敲除小鼠的蛋白缺失,证实GCLC缺失通过降低谷胱甘肽合成加剧药物性肝损伤,强调了其在解毒功能中的核心地位。
---
4. **文献名称**:*ROS-dependent activation of GCLC/GPx2 axis promotes chemoresistance in colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Kim AD et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫沉淀(GCLC抗体)和荧光染色发现,化疗药物诱导的活性氧(ROS)通过上调GCLC增强癌细胞抗氧化能力,导致耐药性,阻断该通路可逆转耐药表型。
---
**注**:以上内容为模拟文献摘要,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词“GCLC antibody”“glutathione synthesis”等获取。如需具体文献,建议补充研究场景(如疾病类型或机制方向)以便精准推荐。
The glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) is a critical enzyme in glutathione (GSH) biosynthesis, catalyzing the rate-limiting step of GSH production by combining glutamate and cysteine. As the primary intracellular antioxidant, GSH protects cells from oxidative stress, detoxifies xenobiotics, and regulates redox signaling. GCLC forms a heterodimer with the modifier subunit (GCLM) to achieve full enzymatic activity. Dysregulation of GCLC expression or function has been implicated in various pathological conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s), cancer progression, and liver disorders.
GCLC-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and regulatory mechanisms in both physiological and disease contexts. These antibodies enable detection of GCLC protein levels via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding research on oxidative stress responses, drug resistance in cancer (where elevated GCLC may confer chemoresistance), and metabolic adaptations. Commercially available antibodies are typically validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat samples, supporting translational studies. Recent advances also explore GCLC's role in ferroptosis regulation, highlighting its therapeutic relevance. By facilitating precise quantification and cellular mapping, GCLC antibodies contribute to understanding redox biology and developing targeted therapies for oxidative stress-related diseases.
×