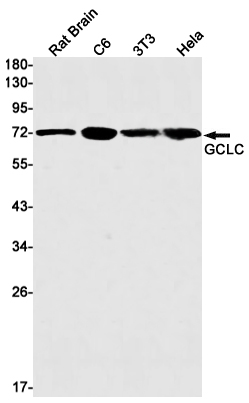
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GCLC; GLCL; GLCLC; Glutamate--cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GCS heavy chain; Gamma-ECS; Gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase |
| Entrez GeneID | 2729 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 73 kDa; Observed MW: 73 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human GCLC |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GCLC抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"Regulation of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase subunit gene expression by the transcription factor Nrf2"**
- **作者**: Wild AC, Moinova HR, Mulcahy RT
- **摘要**: 该研究探讨了转录因子Nrf2在调节GCLC基因表达中的作用,发现Nrf2通过与抗氧化反应元件(ARE)结合,激活GCLC启动子活性,从而增强细胞在氧化应激下的谷胱甘肽合成能力。
2. **"Role of glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) in tumor cell resistance to chemotherapy"**
- **作者**: Yang H, Koo HC, Kim SH
- **摘要**: 文章分析了GCLC在癌细胞化疗耐药性中的机制,通过抑制GCLC表达或使用其抗体检测蛋白水平,证实GCLC的高表达通过增强谷胱甘肽合成降低化疗药物诱导的氧化损伤。
3. **"Redox regulation of human glutamate cysteine ligase in inflammatory macrophages"**
- **作者**: Dickinson DA, Darley-Usmar VM, Forman HJ
- **摘要**: 研究利用GCLC抗体检测巨噬细胞中GCLC蛋白表达,发现炎症因子(如TNF-α)通过ROS信号通路上调GCLC,揭示了其在炎症过程中维持氧化还原平衡的关键作用。
这些文献均涉及GCLC抗体在分子机制或疾病模型中的应用,涵盖基因调控、肿瘤耐药及炎症反应等领域。
The glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) is a critical enzyme in glutathione (GSH) biosynthesis, catalyzing the rate-limiting step of GSH synthesis by combining glutamate and cysteine. As the primary intracellular antioxidant, GSH neutralizes reactive oxygen species (ROS), detoxifies xenobiotics, and regulates cellular redox homeostasis. GCLC forms a heterodimer with the modifier subunit (GCLM) to achieve full enzymatic activity. Its expression is tightly regulated by the Nrf2-ARE pathway, which activates under oxidative stress to enhance GSH production. Dysregulation of GCLC is implicated in various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s), cancer, and chronic oxidative stress-related conditions like diabetes.
GCLC antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in cellular and disease models. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to assess GCLC levels in tissues or cells under different experimental conditions. Researchers also employ these antibodies to explore mechanisms of oxidative stress resistance, drug resistance in cancer (where elevated GCLC may confer chemoresistance), and potential therapeutic targeting of the GSH pathway. Commercial GCLC antibodies are typically developed against specific epitopes, with validation in knockout controls to ensure specificity. Understanding GCLC dynamics via antibody-based assays contributes to insights into redox biology and therapeutic strategies for oxidative damage-related pathologies.
×