
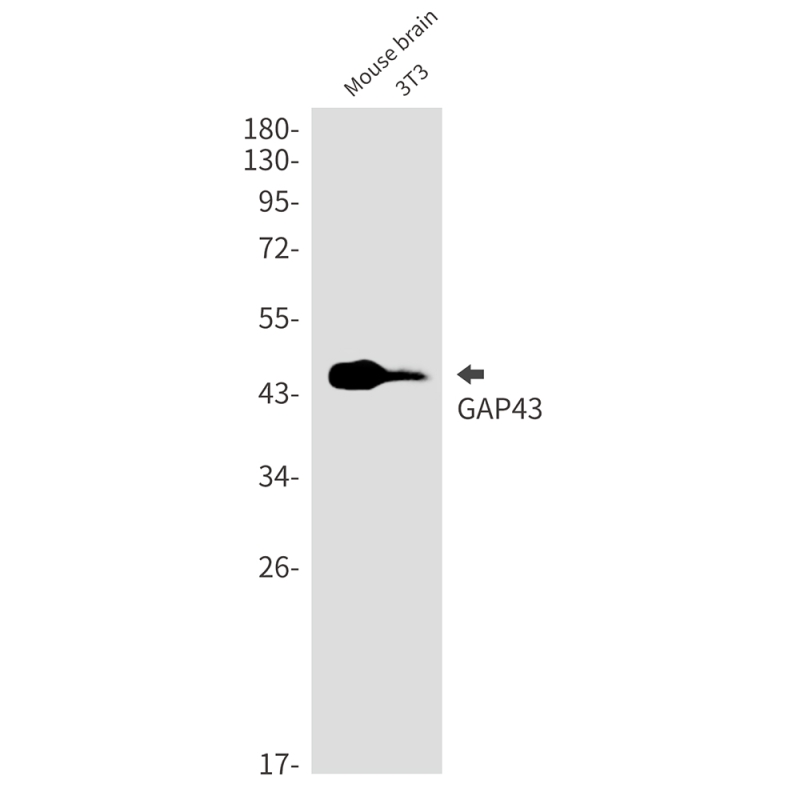
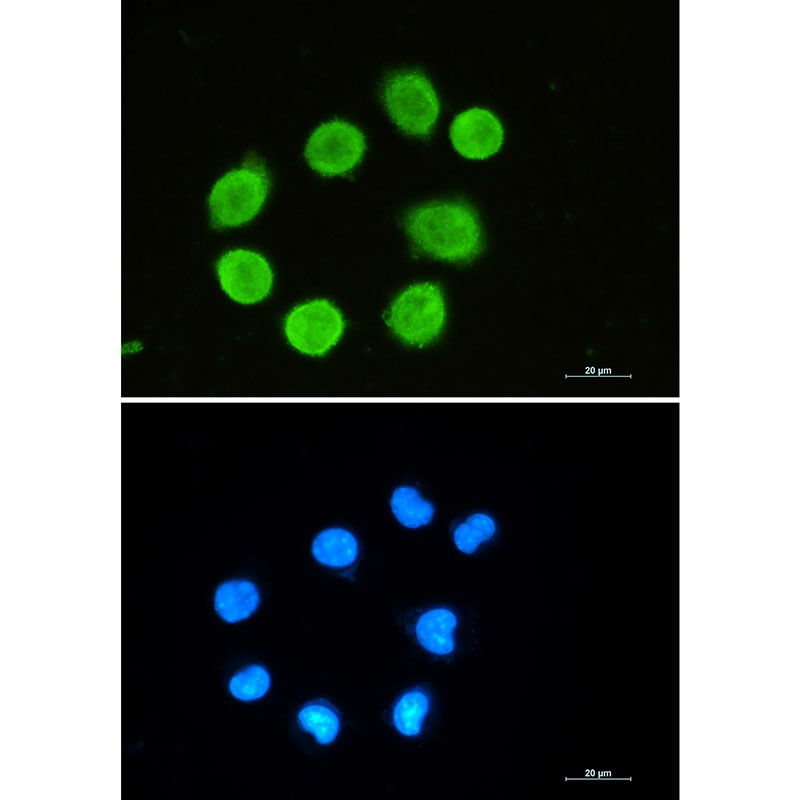
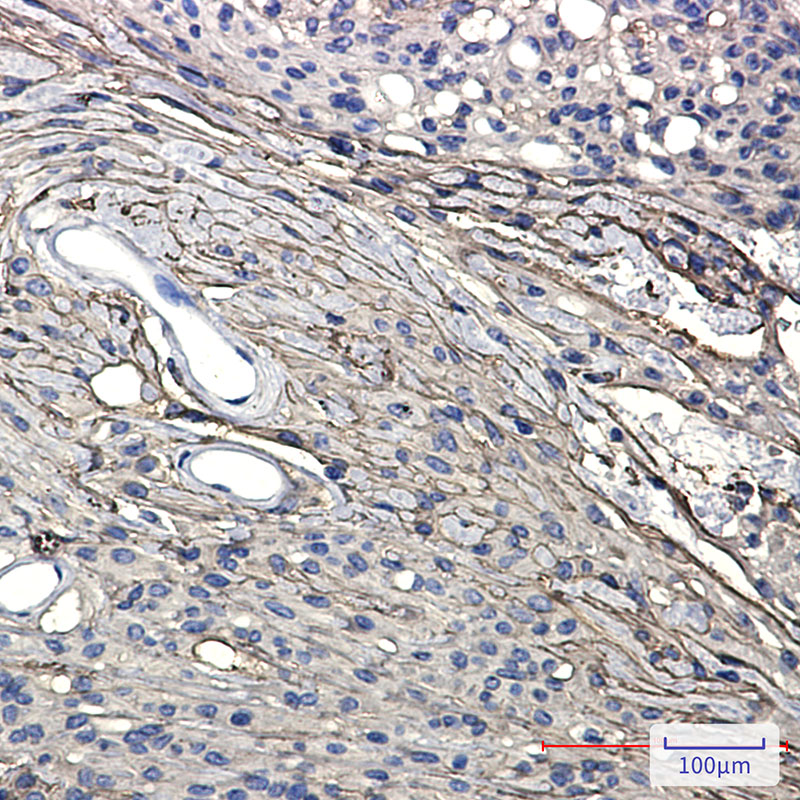
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GAP43; Neuromodulin; Axonal membrane protein GAP-43; Growth-associated protein 43; Neural phosphoprotein B-50; pp46 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2596 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 25 kDa; Observed MW: 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human GAP43 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GAP43抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**: "GAP-43: An intrinsic determinant of neuronal development and plasticity"
**作者**: Benowitz LI, Routtenberg A
**摘要**: 该文献综述了GAP43在神经发育和突触可塑性中的核心作用,强调其作为轴突生长标志物的特性。研究通过GAP43抗体的免疫组化分析,揭示了其在神经再生和脑损伤修复中的表达模式。
2. **文献名称**: "A protein induced during nerve growth (GAP-43) is a major component of growth-cone membranes"
**作者**: Skene JH, Jacobson RD, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究首次克隆并表征了GAP43蛋白,利用特异性抗体证实其在神经元生长锥中高表达,提示其参与轴突导向和突触形成,为后续神经再生研究奠定基础。
3. **文献名称**: "Monoclonal antibody markers for axonal regeneration in the central nervous system"
**作者**: Doster SK, Lozano AM, et al.
**摘要**: 文章开发了针对GAP43的单克隆抗体,证明其可特异性标记中枢神经系统损伤后的再生轴突,为评估神经修复提供了重要工具,并验证了抗体在动物模型中的应用价值。
这些研究共同突出了GAP43抗体在神经科学中的关键应用,包括发育、再生及疾病机制探索。
The growth-associated protein 43 (GAP43), also known as B-50 or neuromodulin, is a neuron-specific phosphoprotein crucial for axonal development, regeneration, and synaptic plasticity. It is highly expressed during nervous system development, particularly in growing axons and growth cones, where it regulates cytoskeletal dynamics and membrane expansion via interactions with calmodulin and protein kinase C (PKC) signaling. In adults, GAP43 levels decline but persist in regions retaining plasticity, such as the hippocampus and olfactory system, and are re-upregulated during nerve injury or regeneration.
GAP43 antibodies are essential tools for studying neural development, repair, and neurodegenerative processes. These antibodies detect GAP43 in techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence, enabling visualization of axonal outgrowth, synaptic remodeling, or regenerative responses in models of stroke, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer’s disease, or Parkinson’s disease. Specificity varies among antibodies due to post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) or epitope regions. Researchers must validate them for target applications, as cross-reactivity with unrelated proteins may occur. Commercially available clones include monoclonal (e.g., [SPM191], [7B10]) and polyclonal versions, often derived from rabbit or mouse hosts. Understanding GAP43’s role in synaptic efficacy and learning also links its detection to behavioral or cognitive studies.
×