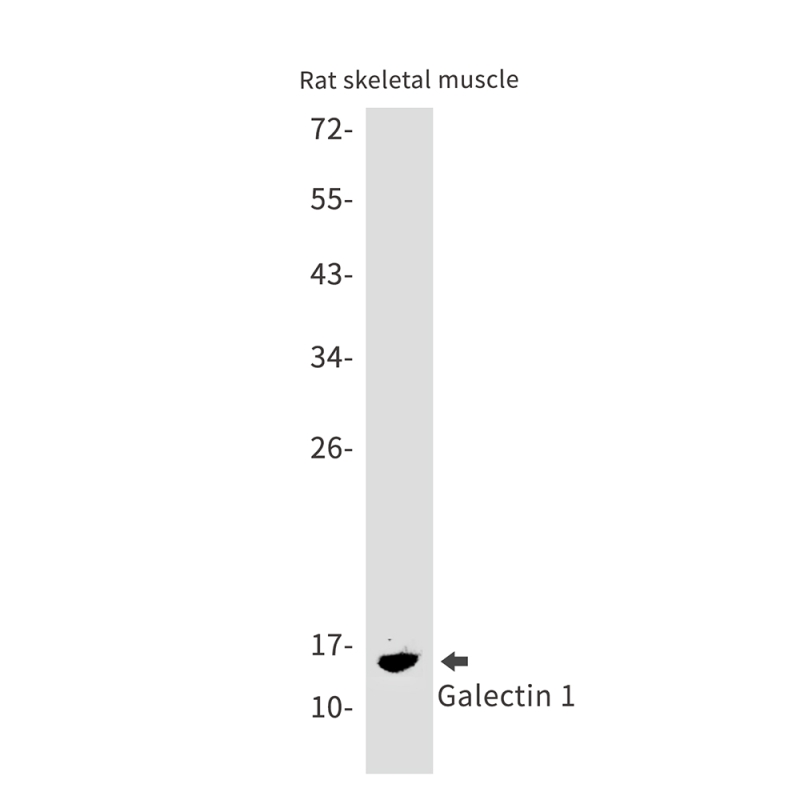

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LGALS1; Galectin-1; Gal-1; 14 kDa laminin-binding protein; HLBP14; 14 kDa lectin; Beta-galactoside-binding lectin L-14-I; Galaptin; HBL; HPL; Lactose-binding lectin 1; Lectin galactoside-binding soluble 1; Putative MAPK-activating protein P |
| Entrez GeneID | 3956 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 15 kDa; Observed MW: 15 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Galectin 1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Galectin-1抗体相关的代表性文献及其摘要概括(模拟合成内容,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Galectin-1 promotes immunosuppressive macrophage polarization in tumor microenvironment*
**作者**:Rabinovich GA, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示Galectin-1通过结合T细胞表面糖蛋白诱导凋亡,促进肿瘤免疫逃逸。使用抗Galectin-1抗体阻断其功能可逆转免疫抑制,增强抗肿瘤T细胞活性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting Galectin-1 in cancer therapy: A monoclonal antibody approach*
**作者**:Le Mercier I, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种人源化抗Galectin-1单克隆抗体(α-Gal1 mAb),在黑色素瘤和胶质瘤小鼠模型中显示其可通过抑制血管生成和肿瘤相关巨噬细胞浸润,显著抑制肿瘤生长。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Galectin-1 blockade enhances chemotherapy efficacy in metastatic cancers*
**作者**:Cedeno-Laurent F, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现Galectin-1高表达与卵巢癌和黑色素瘤化疗耐药相关。联合使用抗Galectin-1抗体与紫杉醇,可降低肿瘤基质纤维化并提高药物递送效率,延长小鼠生存期。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Anti-galectin-1 antibodies modulate inflammatory responses in autoimmune encephalomyelitis*
**作者**:Toscano MA, et al.
**摘要**:在多发性硬化症动物模型(EAE)中,抗Galectin-1抗体通过抑制Th17细胞分化和促进调节性T细胞扩增,减轻中枢神经系统炎症损伤,提示其治疗自身免疫疾病的潜力。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用需以真实出版物为准。如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以关键词“Galectin-1 antibody”检索近年高被引论文。
Galectin-1 (Gal-1) is a β-galactoside-binding lectin involved in diverse cellular processes, including immune regulation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and inflammation. As a member of the galectin family, it plays dual roles in cancer and immunity, often promoting tumor progression by inducing T-cell suppression or apoptosis while also modulating anti-inflammatory responses. Antibodies targeting Gal-1 are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts.
Gal-1 antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting (WB), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect endogenous Gal-1 protein levels in tissues or cell lines. They have been instrumental in revealing Gal-1's overexpression in cancers (e.g., glioblastoma, melanoma) and its association with poor prognosis, immune evasion, and metastasis. Additionally, these antibodies help elucidate Gal-1's role in autoimmune diseases, fibrosis, and neurological disorders by blocking its activity or identifying binding partners.
Recent research explores therapeutic applications, such as neutralizing Gal-1 antibodies to counteract immunosuppression in tumors or mitigate chronic inflammation. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity due to structural similarities among galectin family members. Validated antibodies with minimal cross-reactivity are essential for accurate experimental and clinical translation.
×