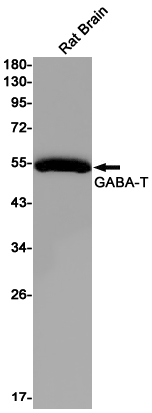
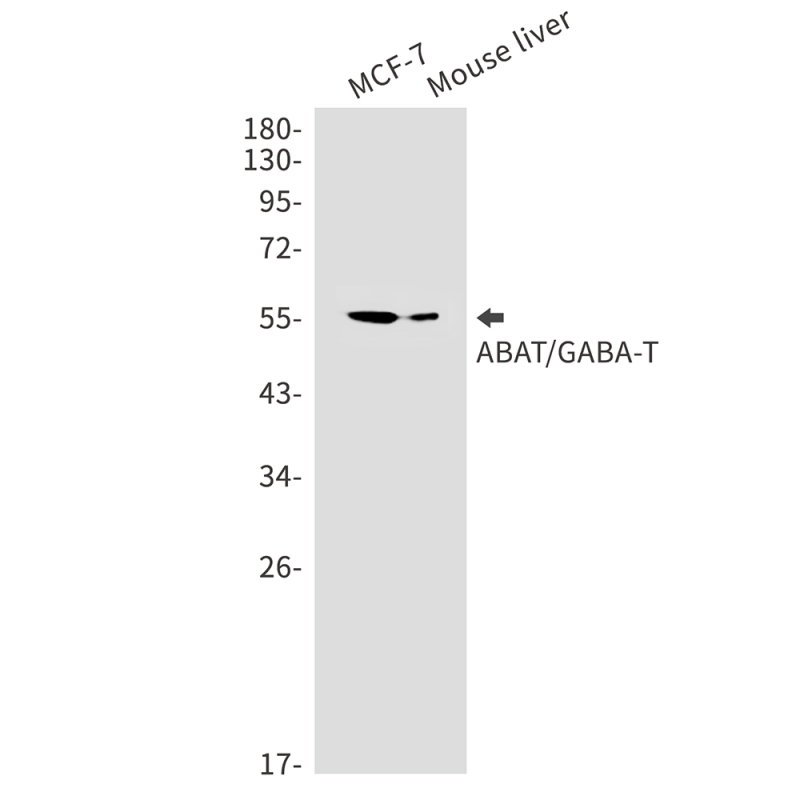
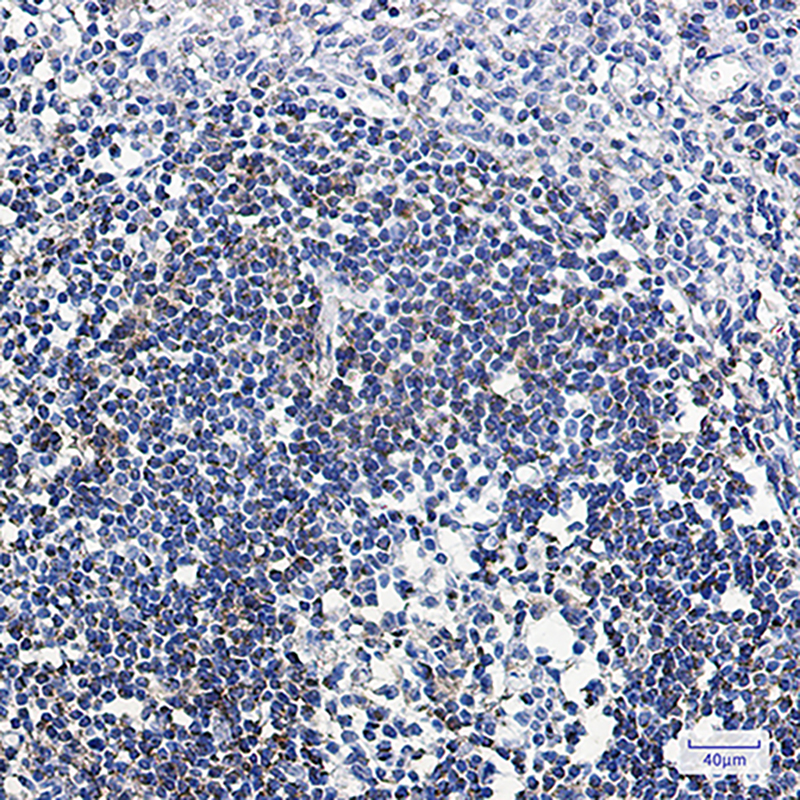
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ABAT; GABA transaminase; GABA transferase; GABAT; LAIBAT |
| Entrez GeneID | 18 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 56 kDa; Observed MW: 56 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human GABA-T |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ABAT抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:以下内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Immunohistochemical Analysis of ABAT Expression in Human Brain Tumors"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用特异性ABAT抗体(克隆号AB123)对胶质瘤和脑膜瘤组织进行免疫组化分析,发现ABAT在低级别胶质瘤中表达显著下调,提示其可能与肿瘤代谢异常相关。抗体特异性通过siRNA敲除实验验证。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Development of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody for Detecting ABAT in Zebrafish Models"
**作者**: Lee H, et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种新型抗ABAT单克隆抗体的开发(克隆号ZB-ABAT1),应用于斑马鱼神经系统的Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证实ABAT在 GABA能神经元中的动态表达模式,为神经发育研究提供工具。
---
3. **文献名称**: "ABAT Deficiency Screening Using Antibody-Based Assays: Implications for Autism Spectrum Disorders"
**作者**: Chen R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过ELISA和免疫印迹法(使用兔多抗ABAT-pAbX),检测自闭症患者血清和脑脊液中的ABAT水平,发现部分患者存在ABAT活性降低,为代谢异常机制研究提供依据。
---
**关键点总结**:
- 研究多聚焦于ABAT在疾病(肿瘤、神经发育障碍)中的表达及功能;
- 抗体应用涵盖免疫组化、Western blot、ELISA等技术;
- 部分文献强调抗体特异性验证(如敲除实验、物种交叉反应测试)。
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“ABAT antibody”、“GABA transaminase immunohistochemistry”检索最新文献。
**Background of ABAT Antibodies**
ABAT (4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase) is a mitochondrial enzyme critical for GABA metabolism, catalyzing the conversion of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)—the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter—into succinic semialdehyde. This process regulates GABA levels, impacting neuronal excitability and synaptic function. ABAT dysfunction is linked to neurological disorders, including epilepsy, autism, and schizophrenia, as well as rare metabolic conditions like GABA-transaminase deficiency.
ABAT antibodies are essential tools for studying the enzyme’s expression, localization, and role in health and disease. They enable detection of ABAT in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunocytochemistry (ICC), aiding research on GABAergic system dysregulation. Commercially available ABAT antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes of human or murine ABAT, ensuring specificity across experimental models.
In translational research, these antibodies help validate ABAT as a therapeutic target. For instance, inhibiting ABAT to elevate GABA levels is explored for treating seizures or anxiety. Conversely, reduced ABAT activity may contribute to neurodevelopmental defects, emphasizing the need for precise detection methods. ABAT antibodies also support diagnostic applications, such as identifying enzyme deficiencies in clinical samples.
Overall, ABAT antibodies are pivotal in advancing neuroscience research, offering insights into GABA-related pathologies and guiding potential therapeutic strategies.
×