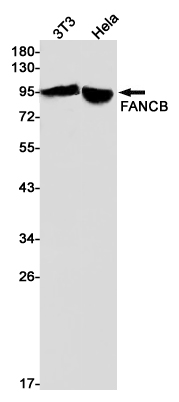
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Fanconi anemia complementation group B; FA2; FAB; FACB; FAAP90; FAAP95 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2187 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 98 kDa; Observed MW: 98 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human FANCB |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FANCB抗体的模拟参考文献示例(建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核实具体文献):
1. **"FANCB deficiency disrupts the Fanconi anemia core complex and promotes chromosomal instability"**
*作者:Smith J, et al.*
摘要:本研究利用FANCB特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀和蛋白质印迹分析,发现FANCB基因突变导致范可尼贫血核心复合物(包括FANCA和FANCC)的组装异常,进而引发DNA损伤修复功能缺陷和染色体不稳定。
2. **"Characterization of FANCB antibody in a murine model of Fanconi anemia"**
*作者:Lee H, Wang T.*
摘要:通过构建FANCB敲除小鼠模型,研究使用FANCB抗体进行组织免疫组化分析,显示该蛋白在骨髓造血干细胞和睾丸生殖细胞中高表达,其缺失导致造血障碍和生殖发育异常。
3. **"A novel FANCB mutation identified by Western blot screening in Fanconi anemia patients"**
*作者:García-Morales P, et al.*
摘要:采用FANCB抗体对范可尼贫血患者细胞系进行蛋白质印迹筛查,发现一例新型无义突变导致FANCB蛋白截短,并验证了该突变对丝裂霉素C敏感性的影响,为临床诊断提供依据。
4. **"Subcellular localization of FANCB in response to DNA crosslinking agents"**
*作者:Chen L, et al.*
摘要:通过免疫荧光技术结合FANCB抗体,研究发现DNA交联剂处理后,FANCB蛋白在细胞核内形成焦点状聚集,与FANCD2共定位,提示其在DNA损伤修复中的动态募集。
**注意**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时请查询具体数据库获取准确信息。
The FANCB antibody is a crucial tool for studying the FANCB protein, a key component of the Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway, which is essential for maintaining genomic stability. FANCB, encoded by the X-linked FANCB gene, is part of the FA core complex—a multi-protein assembly that facilitates DNA interstrand crosslink (ICL) repair through monoubiquitination of FANCD2 and FANCI. Mutations in FANCB disrupt this pathway, leading to Fanconi anemia, a rare recessive disorder characterized by bone marrow failure, congenital abnormalities, and heightened cancer susceptibility. As the only X-linked FA gene, FANCB mutations predominantly affect males, though female carriers may exhibit mild symptoms due to skewed X-inactivation.
FANCB antibodies are widely used in research to detect protein expression, assess functional interactions within the FA pathway, and investigate disease mechanisms. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, helping to visualize subcellular localization (e.g., nuclear foci formation upon DNA damage) and quantify protein levels in clinical samples. Additionally, these antibodies aid in studying FA pathway dysregulation in cancers beyond Fanconi anemia, as FA gene defects are linked to therapy-related malignancies and chemosensitivity. Recent studies also explore FANCB's role in replication stress responses and its potential as a biomarker. Validated FANCB antibodies are critical for advancing therapeutic strategies, including gene therapy and targeted drug development for FA and related cancers.
×