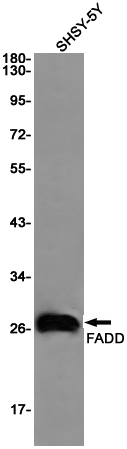
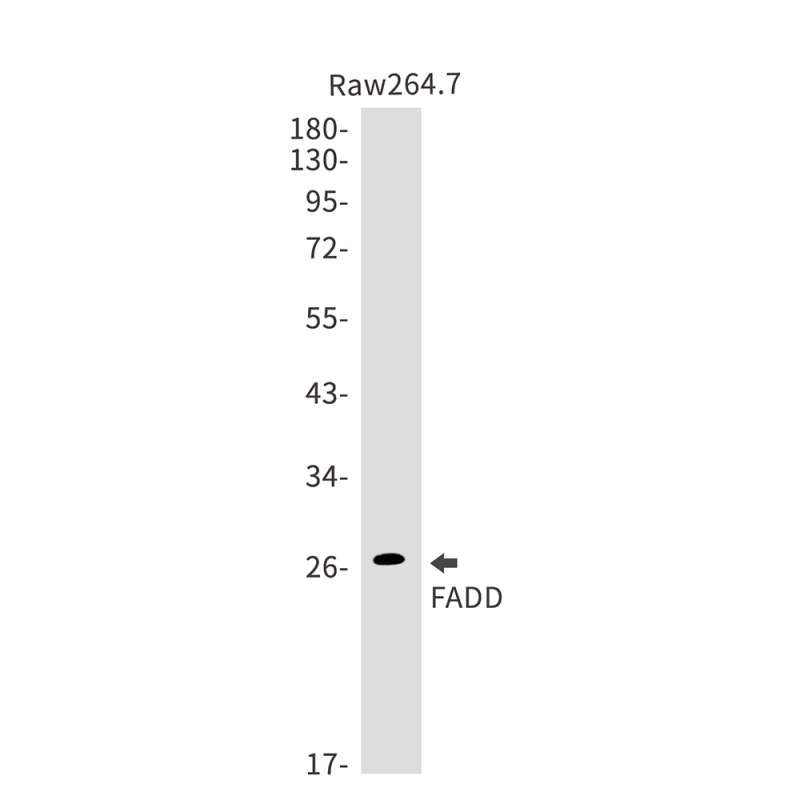
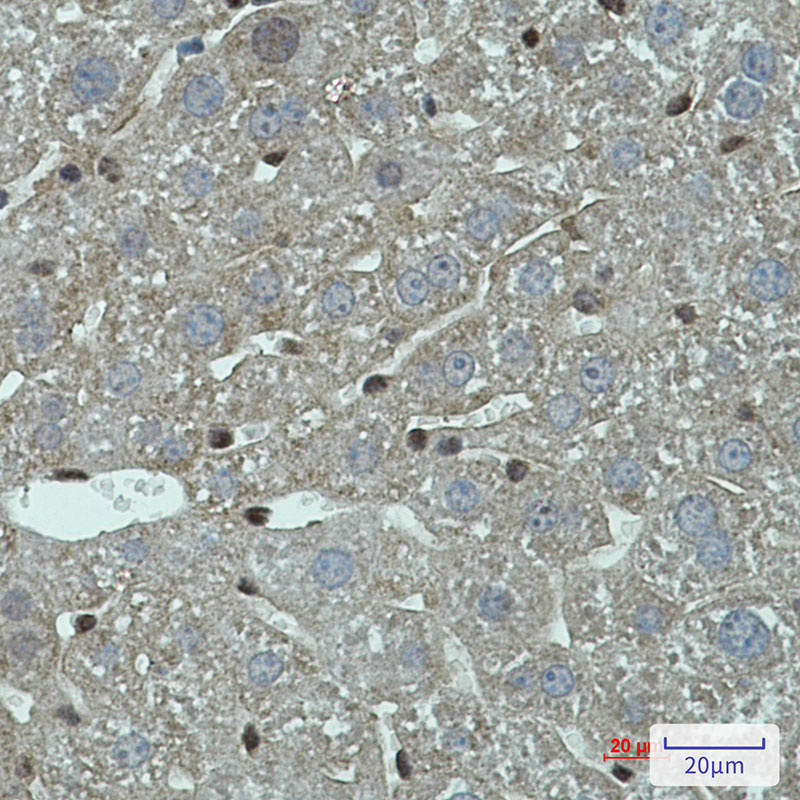
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Mort1/FADD |
| Entrez GeneID | 14082 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 23 kDa; Observed MW: 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of mouse FADD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于FADD抗体的参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis*
**作者**:Chinnaiyan, A.M. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次鉴定了FADD蛋白,揭示了其通过死亡结构域(Death Domain)与Fas受体相互作用,并阐明了FADD在Fas介导的细胞凋亡信号通路中的核心作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of FADD by RIPK1 regulates necroptosis signaling*
**作者**:Micheau, O. & Tschopp, J.
**摘要**:研究发现FADD可通过RIPK1介导的磷酸化修饰调控程序性坏死(necroptosis),揭示了FADD在凋亡与坏死通路中的双重功能及其分子机制。
3. **文献名称**:*FADD deficiency in mice results in defective immune development and lethal perinatal cardiomyopathy*
**作者**:Park, H.H. et al.
**摘要**:通过构建FADD基因敲除小鼠模型,发现FADD缺失导致胚胎期免疫系统发育异常及心肌病,强调了FADD在胚胎发育和免疫稳态中的必要性。
4. **文献名称**:*FADD expression as a prognostic biomarker in human cancers*
**作者**:Zhang, Y. et al.
**摘要**:通过分析多种癌症临床样本,发现FADD蛋白表达水平与肿瘤恶性程度及患者预后显著相关,提示其作为癌症诊断或治疗靶点的潜力。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用需核对具体原文及作者信息。)
FADD (Fas-associated protein with death domain) is a pivotal adaptor protein involved in programmed cell death (apoptosis) and inflammatory signaling. Structurally, it contains an N-terminal death effector domain (DED) and a C-terminal death domain (DD), enabling interactions with other apoptosis-related proteins. FADD primarily mediates extrinsic apoptosis by bridging death receptors (e.g., Fas, TNF-R1) to initiator caspases (e.g., caspase-8/10) through the formation of the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). This activation triggers caspase cascades, leading to cell death. Beyond apoptosis, FADD participates in non-apoptotic processes, including cell cycle regulation, innate immunity, and necroptosis, depending on cellular context and post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation at Ser194 in humans).
FADD antibodies are essential tools for studying these pathways. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation to detect FADD expression, localization, and protein interactions. Dysregulation of FADD is linked to diseases such as cancer (e.g., reduced expression in lung/breast tumors), autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. Researchers also utilize FADD-deficient models or inhibitory antibodies to dissect its role in specific signaling cascades. However, interpretation requires caution, as FADD's dual pro-survival and pro-death roles can vary across cell types and stress conditions. Commercial FADD antibodies are typically validated for specificity using knockout cell lines to ensure reliability in experimental settings.
×