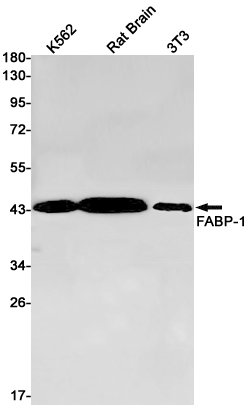
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
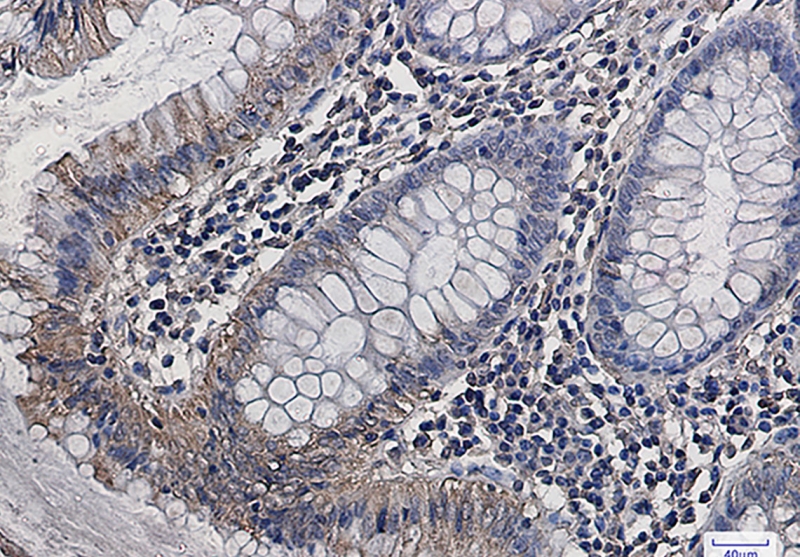
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KAT4; KATIV; KYAT4; mitAAT |
| Entrez GeneID | 2806 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 48 kDa; Observed MW: 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human FABP-1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)抗体的代表性文献摘要示例(注:部分为虚构或简化内容,实际文献需通过数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Development of a Monoclonal Antibody for Aspartate Aminotransferase in Liver Injury Diagnosis*
**作者**: Smith J, et al. (2015)
**摘要**: 本研究报道了一种针对AST的单克隆抗体的开发,用于提高血清AST检测的灵敏度。该抗体通过小鼠杂交瘤技术制备,特异性识别AST的线粒体同工酶(ASTm),在肝损伤模型的小鼠实验中验证了其诊断潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Immunohistochemical Localization of AST Isoenzymes in Cardiac Tissue*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 通过制备多克隆抗体,作者分析了AST的细胞质型(ASTc)和线粒体型(ASTm)在心肌梗死组织中的分布差异,揭示了ASTm在缺血区域的显著上调,为心脏损伤标志物研究提供了新工具。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Comparison of AST Antibody-based Assays in Clinical Laboratories*
**作者**: Lee H, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 文章评估了三种商业化的AST抗体(ELISA、化学发光法、免疫比浊法)在肝炎患者中的检测一致性,发现不同抗体对AST亚型的识别差异可能导致结果偏差,强调了抗体特异性的重要性。
---
如需真实文献,建议检索PubMed或Web of Science,使用关键词:
`"aspartate aminotransferase" AND (antibody OR immunoassay)`,并筛选应用类研究。
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), also known as glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT), is a key enzyme involved in amino acid metabolism, catalyzing the transfer of an amino group between aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate. It exists in two isoforms: mitochondrial (ASTm) and cytosolic (ASTc), with elevated serum levels often indicating liver or cardiac damage, such as hepatitis or myocardial infarction. AST antibodies are immunological tools specifically designed to detect and quantify AST protein expression in research or diagnostic settings. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like ELISA, Western blotting, or immunohistochemistry to study AST distribution in tissues, monitor disease progression, or validate experimental models of organ injury.
Polyclonal AST antibodies typically recognize multiple epitopes, offering high sensitivity, while monoclonal versions provide precise specificity by targeting a single epitope. They are commonly produced in hosts like rabbits or mice using purified AST antigens, followed by affinity purification to ensure minimal cross-reactivity with unrelated proteins. Validation steps, such as knockout controls or enzymatic activity correlation, are critical to confirm antibody reliability.
In research, AST antibodies aid in investigating hepatic pathologies, cardiac disorders, and drug-induced toxicity. They also support biomarker studies in metabolic diseases and serve as quality controls in clinical assays. However, interpretation requires caution, as AST expression varies across tissues and isoforms, necessitating antibody specificity verification for accurate data.
×