
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
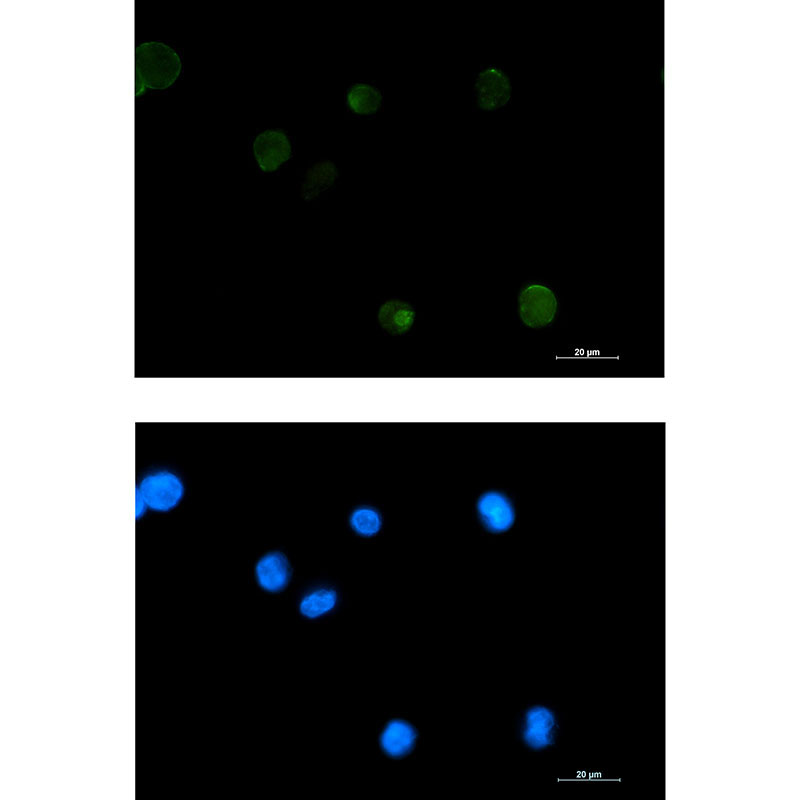
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
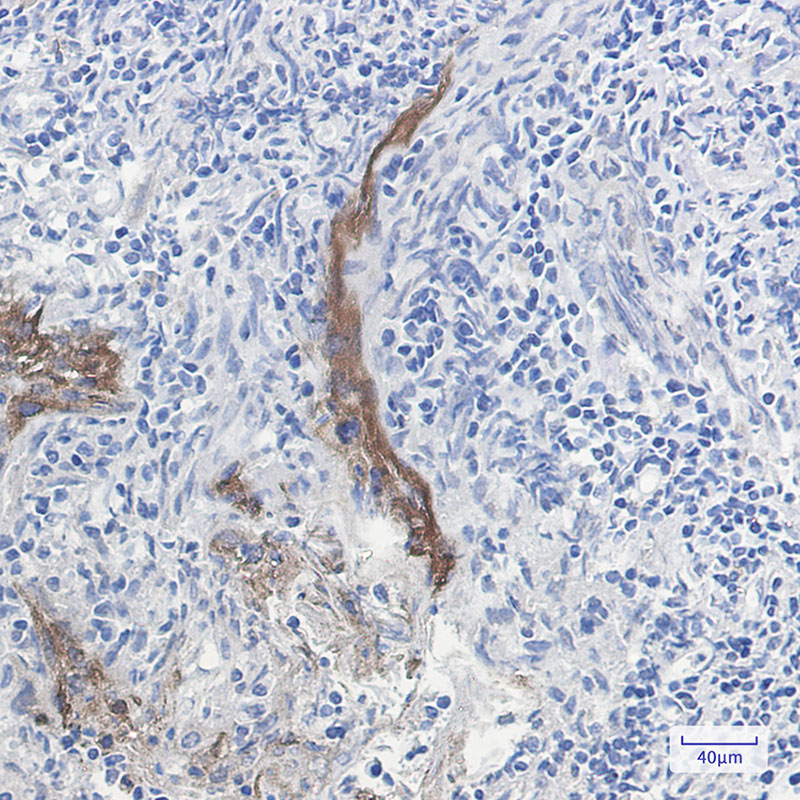
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ECM1; Extracellular matrix protein 1; Secretory component p85 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1893 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 61 kDa; Observed MW: 61 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Extracellular matrix protein 1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于细胞外基质蛋白1(ECM1)抗体的代表性文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**: *Extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1) is overexpressed in malignant epithelial tumors*
**作者**: Han Z, et al. (2013)
**摘要**: 该研究使用抗ECM1抗体检测多种癌症组织中ECM1的表达,发现其在乳腺癌、肺癌等上皮性肿瘤中显著上调,提示其可能通过调节肿瘤微环境促进转移。
2. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies against ECM1 are linked to lipoid proteinosis and skin inflammation*
**作者**: Arita K, et al. (2007)
**摘要**: 通过抗ECM1抗体分析,发现脂质蛋白沉积症患者体内存在ECM1自身抗体,揭示了ECM1在皮肤基底膜结构中的作用及其突变导致的病理机制。
3. **文献名称**: *ECM1 regulates angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis through VEGF signaling*
**作者**: Wang X, et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 利用特异性抗ECM1抗体阻断实验,证明ECM1通过激活VEGF通路促进类风湿性关节炎滑膜血管生成,为靶向治疗提供潜在策略。
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索最新研究,并核实作者及期刊信息。
Extracellular Matrix Protein 1 (ECM1) is a secreted glycoprotein involved in regulating extracellular matrix organization, angiogenesis, and cellular signaling. First identified in 1997. ECM1 interacts with components like perlecan, fibulin-1. and matrix metalloproteinases, influencing tissue remodeling, epidermal differentiation, and vascular development. Dysregulation of ECM1 is linked to pathologies including cancers (e.g., breast, liver, thyroid), autoimmune disorders (e.g., systemic sclerosis), and lipoid proteinosis, a rare genetic disease caused by ECM1 mutations.
Antibodies targeting ECM1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, and ELISA to detect ECM1 in tissue samples, serum, or cell lysates. ECM1 exists in multiple splice variants (e.g., ECM1a, ECM1b), and specific antibodies are designed to distinguish these isoforms. Research applications include investigating ECM1's role in tumor progression (e.g., promoting metastasis via epithelial-mesenchymal transition) or its diagnostic potential as a biomarker in certain cancers. Commercially available antibodies include monoclonal and polyclonal types, validated for cross-reactivity and specificity across human and murine models. Challenges remain in standardizing detection methods due to ECM1's post-translational modifications and tissue-specific expression patterns.
×