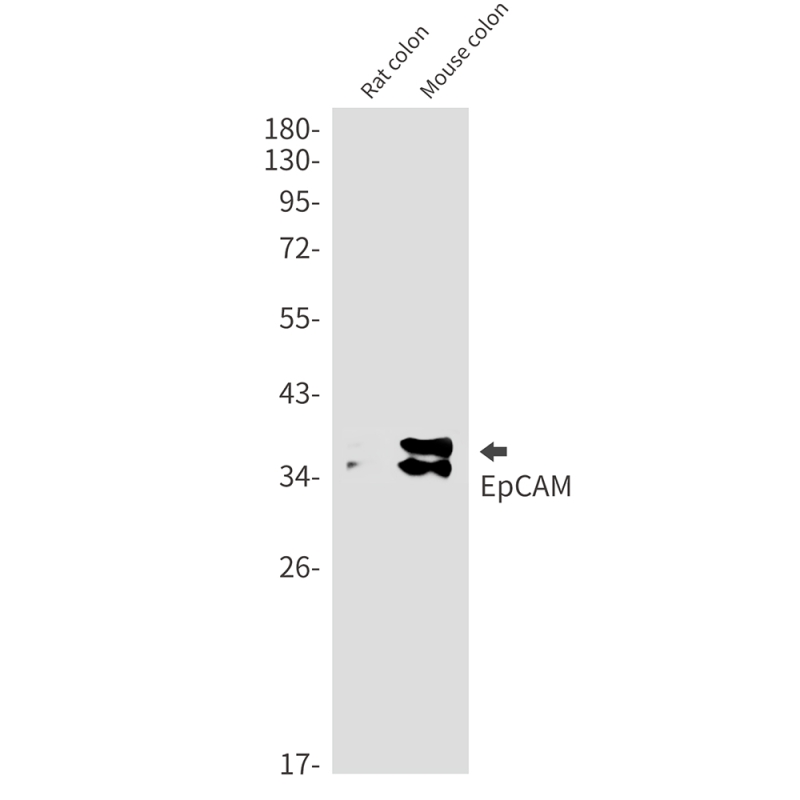
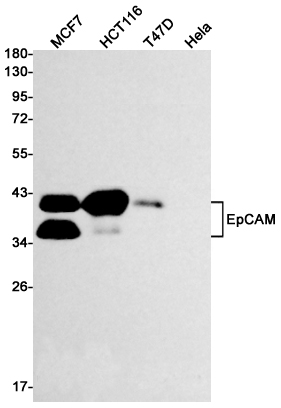
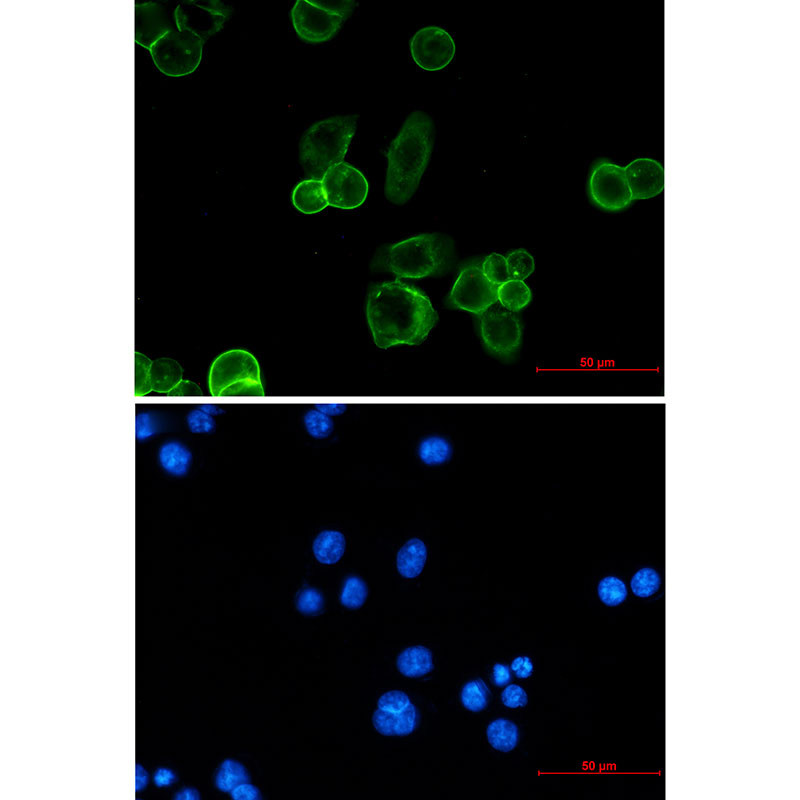
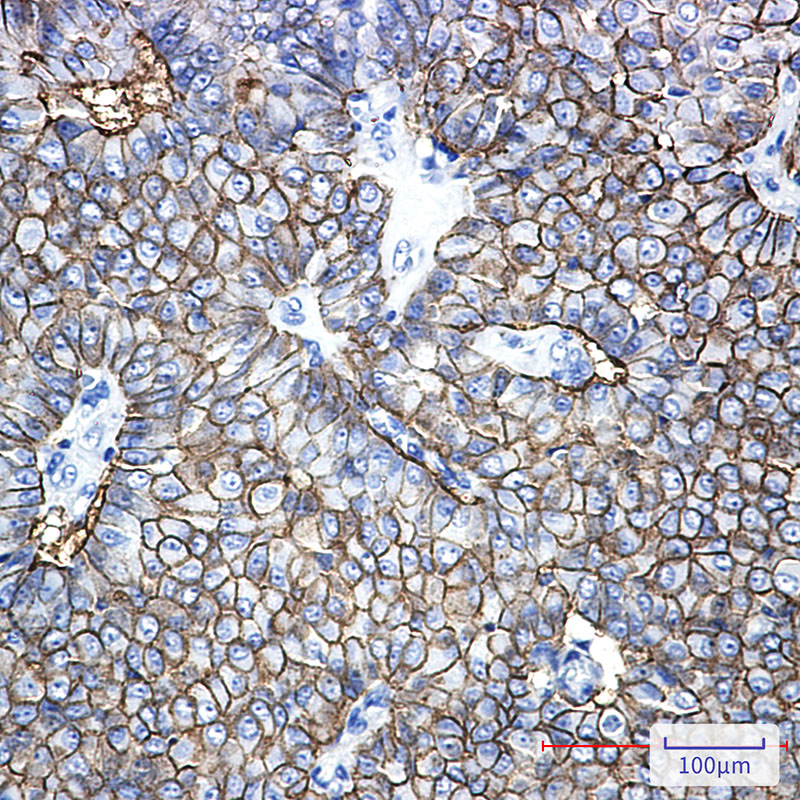
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EPCAM; GA733-2; M1S2; M4S1; MIC18; TACSTD1; TROP1; Epithelial cell adhesion molecule; Ep-CAM; Adenocarcinoma-associated antigen; Cell surface glycoprotein Trop-1; Epithelial cell surface antigen; Epithelial glycoprotein; EGP; Epithelial glycoprotein 314; EGP314; hEGP314; KS 1/4 antigen; KSA; Major gastrointestinal tumor-associated protein GA733-2; Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 1; CD326 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4072 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 35 kDa; Observed MW: 35,39 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human EpCAM |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EpCAM抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概述:
1. **文献名称**:**"The trifunctional antibody catumaxomab for the treatment of malignant ascites in patients with advanced cancer: A randomized phase II/III trial"**
**作者**:Heiss MM, et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了抗EpCAM/CD3双特异性抗体Catumaxomab在治疗恶性腹水中的疗效。III期临床试验显示,与单纯穿刺引流相比,腹腔内注射Catumaxomab显著延长了腹水复发时间,证实了EpCAM抗体在靶向肿瘤细胞治疗中的应用价值。
2. **文献名称**:**"Tumor Cell Detection in Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow Using EpCAM-Based Immunomagnetic Enrichment"**
**作者**:Allard WJ, et al.
**摘要**:本文介绍了基于EpCAM抗体的免疫磁珠富集技术(如CellSearch系统)在循环肿瘤细胞(CTC)检测中的应用,验证了其在转移性乳腺癌、结直肠癌和前列腺癌中的高灵敏度和特异性,推动了CTC作为液体活检标志物的临床转化。
3. **文献名称**:**"The EpCAM molecule in human cancers: From cell adhesion to tumor progression"**
**作者**:Gires O, et al.
**摘要**:该综述系统总结了EpCAM的分子结构、介导细胞黏附的生理功能,及其在肿瘤发生中通过Wnt/β-catenin等信号通路促进增殖和转移的机制,强调了EpCAM抗体在诊断和治疗中的双重潜力。
4. **文献名称**:**"EpCAM-Targeted 3D Printed Scaffolds for Liver Tumor Engineering"**
**作者**:Lu Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用EpCAM抗体修饰3D打印支架,特异性捕获肝癌细胞并构建体外肿瘤模型,为药物筛选和个性化治疗提供了新型平台,展示了EpCAM抗体在生物工程领域的拓展应用。
---
以上文献涵盖EpCAM抗体在靶向治疗、诊断技术、机制解析及生物工程中的多样化应用,时间跨度从基础研究到临床转化。
EpCAM (Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule), also known as CD326. is a transmembrane glycoprotein predominantly expressed on the surface of epithelial cells. First identified in the 1980s, EpCAM plays a critical role in cell-cell adhesion, intracellular signaling, and the regulation of proliferation. Its overexpression is observed in many epithelial-derived cancers (e.g., breast, colon, and lung cancers), correlating with tumor aggressiveness, metastasis, and poor prognosis. This makes EpCAM a valuable biomarker for cancer detection and therapeutic targeting.
EpCAM antibodies are monoclonal or polyclonal reagents designed to specifically bind to EpCAM’s extracellular domain. In diagnostics, these antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) and flow cytometry to identify epithelial-derived tumors or circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in liquid biopsies. Therapeutically, EpCAM-targeting antibodies have been engineered into bispecific antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), or CAR-T cell therapies to deliver cytotoxic agents or enhance immune-mediated tumor killing. Examples include catumaxomab (a trifunctional antibody) for malignant ascites treatment.
However, challenges persist, such as variable EpCAM expression across tumor subtypes, potential off-target effects on normal epithelial tissues, and acquired resistance. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing antibody specificity, exploring combination therapies, and leveraging EpCAM’s role in cancer stem cell maintenance. Overall, EpCAM antibodies remain pivotal tools in both cancer research and clinical applications.
×