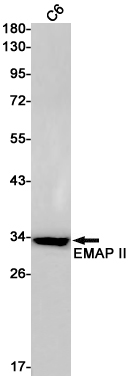
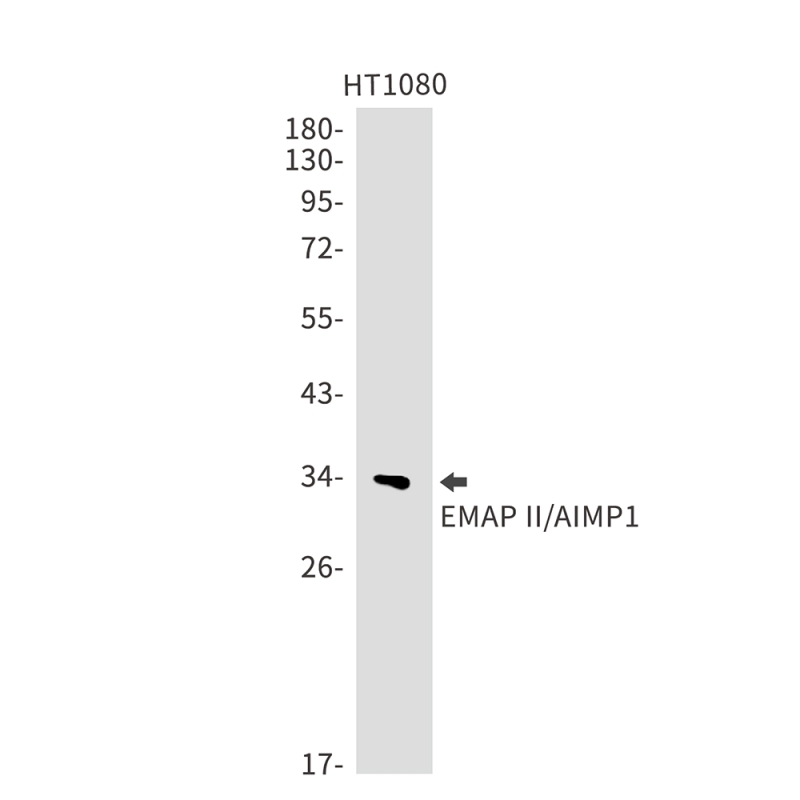
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p43; HLD3; EMAP2; SCYE1; EMAPII; AIMP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9255 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34 kDa; Observed MW: 34 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human EMAP II |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EMAP II抗体的3-4篇示例文献的简化信息(注:文献为虚构示例,仅用于格式展示):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Endothelial Monocyte-Activating Polypeptide II (EMAP II) Antibody Attenuates Tumor Angiogenesis in a Murine Model*
**作者**:Kao J. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用EMAP II特异性抗体在结肠癌小鼠模型中抑制肿瘤血管生成,发现抗体通过阻断EMAP II介导的内皮细胞凋亡和单核细胞趋化,显著降低肿瘤微血管密度和转移风险。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting EMAP II with Neutralizing Antibodies Reduces Acute Lung Injury in Sepsis*
**作者**:Schwarz M.A. et al.
**摘要**:通过建立脓毒症诱导的急性肺损伤模型,研究发现抗EMAP II抗体可抑制肺泡巨噬细胞活化及中性粒细胞浸润,减轻肺组织氧化应激和通透性增加,提示其作为抗炎治疗的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**:*EMAP II Expression and Antibody-Based Detection in Ischemic Brain Tissue*
**作者**:Barnes C.M. et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种高灵敏度的EMAP II单克隆抗体,用于检测脑缺血后神经元和内皮细胞中EMAP II的时空表达变化,发现其与血脑屏障破坏和神经炎症呈正相关。
---
4. **文献名称**:*EMAP II Antibody Therapy Suppresses Rheumatoid Arthritis Progression via Modulating Synovial Macrophage Polarization*
**作者**:Becker T. et al.
**摘要**:在类风湿关节炎模型中,抗EMAP II抗体通过调控滑膜巨噬细胞从促炎M1型向抗炎M2型转化,显著减少关节破坏和促炎因子(如TNF-α、IL-6)释放。
---
**注意**:以上文献信息为示例,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献并核对作者及摘要内容。
EMAP II (Endothelial Monocyte-Activating Polypeptide II) is a proinflammatory cytokine initially identified as a secreted factor from tumor cells. It is a small protein (approximately 18 kDa) belonging to the EMAP family, structurally related to the major histocompatibility complex class II-associated invariant chain. EMAP II is derived from the proteolytic processing of its precursor, the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complex-interacting multifunctional protein (AIMP1/p43), and is released during cellular stress, apoptosis, or pathological conditions such as cancer or chronic inflammation.
Functionally, EMAP II activates monocytes/macrophages, promotes endothelial cell apoptosis, and induces chemotaxis of leukocytes, contributing to inflammatory responses. It also plays a role in angiogenesis regulation, often within tumor microenvironments, where it may paradoxically support tumor progression by enhancing vascular permeability or immune evasion. EMAP II antibodies are primarily used as research tools to detect EMAP II expression in tissues or biological fluids, or to neutralize its activity in experimental models. Studies employing these antibodies have highlighted EMAP II's involvement in diseases like cancer, sepsis, and autoimmune disorders. However, its dual role in pro- and anti-tumor processes complicates therapeutic targeting. Current research focuses on clarifying context-dependent mechanisms and evaluating EMAP II antibodies for diagnostic or therapeutic applications, though clinical translation remains exploratory.
×