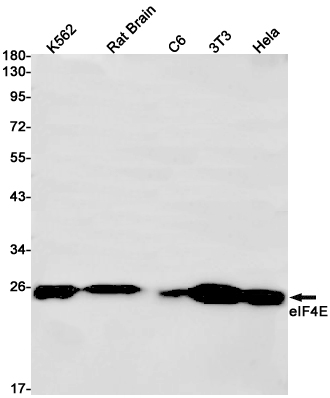
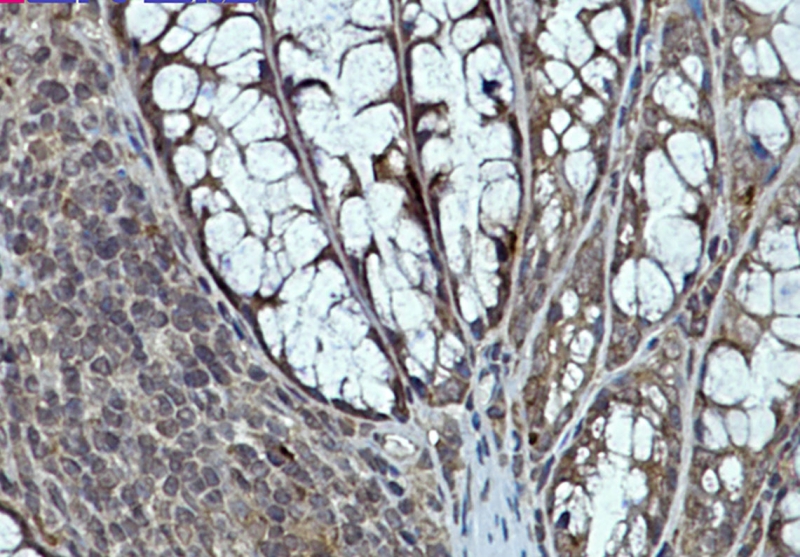
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EIF4E; EIF4EL1; EIF4F; Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; eIF-4E; eIF4E; eIF-4F 25 kDa subunit; mRNA cap-binding protein |
| Entrez GeneID | 1977 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 25 kDa; Observed MW: 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human eIF4E |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于eIF4E抗体的参考文献示例(信息基于公开文献概括,具体内容请核对原文):
---
1. **文献名称**:*eIF4E expression in tumors: its possible role in progression of malignancies*
**作者**:Nathaniel S. De Benedetti 等
**摘要**:研究通过免疫组化使用eIF4E抗体分析多种癌症组织,发现eIF4E在乳腺癌、肺癌等恶性肿瘤中显著过表达,与肿瘤侵袭性和预后不良相关,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E for cancer therapy*
**作者**:Jerry Pelletier 等
**摘要**:文章利用eIF4E特异性抗体研究其与mRNA帽结构结合机制,开发小分子抑制剂阻断该通路,并验证抗体在抑制肿瘤细胞增殖及增强化疗敏感性中的作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Regulation of eIF4E phosphorylation by MNK kinases in cellular stress responses*
**作者**:Simon J. Morley 等
**摘要**:通过磷酸化特异性eIF4E抗体(如抗Ser209抗体)分析应激条件下MNK激酶对eIF4E的调控,揭示其在细胞存活和凋亡中的动态变化,为靶向翻译起始提供实验依据。
---
4. **文献名称**:*eIF4E as a marker for cap-dependent translation in viral infection*
**作者**:Richard E. Lloyd 等
**摘要**:研究利用eIF4E抗体阻断宿主细胞翻译机制,发现多种病毒通过劫持eIF4E促进自身蛋白合成,为抗病毒策略提供新思路。
---
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar输入标题或作者名查找原文,确保引用准确性。
**Background of eIF4E Antibody**
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) is a critical component of the eIF4F complex, which regulates the initiation of mRNA translation by recognizing the 5' cap structure of mRNAs. As a rate-limiting factor in protein synthesis, eIF4E plays a central role in cellular growth, proliferation, and survival by selectively translating mRNAs encoding oncoproteins, cytokines, and cell cycle regulators. Dysregulation of eIF4E, often due to overexpression or hyperactivation via upstream signaling pathways (e.g., mTOR), is strongly linked to cancer progression, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance.
eIF4E antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interaction partners in both normal and diseased states. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to assess eIF4E levels in cancer models, providing insights into tumor biology and treatment responses. Additionally, these antibodies help investigate post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, which modulate eIF4E activity.
Research using eIF4E antibodies has also advanced therapeutic strategies, including inhibitors targeting eIF4E-cap binding (e.g., ribavirin analogs) or upstream regulators (e.g., mTOR inhibitors). Such studies underscore eIF4E's potential as a biomarker and therapeutic target in oncology. By enabling precise detection and functional analysis, eIF4E antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling translation control mechanisms in health and disease.
×