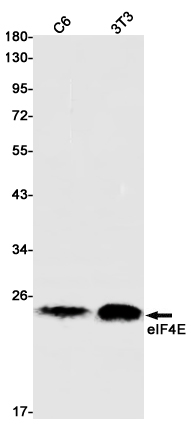
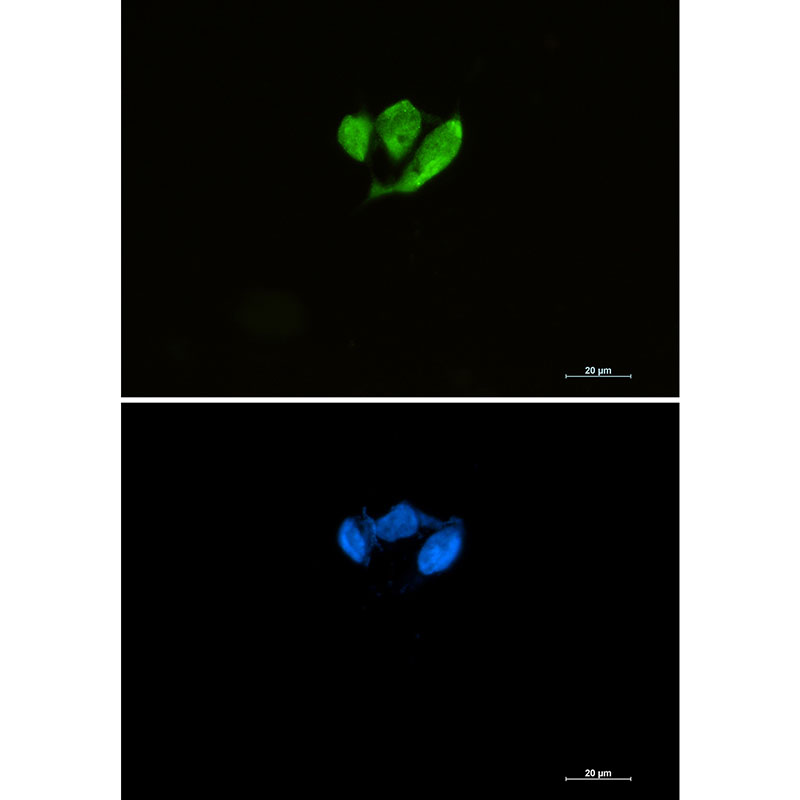
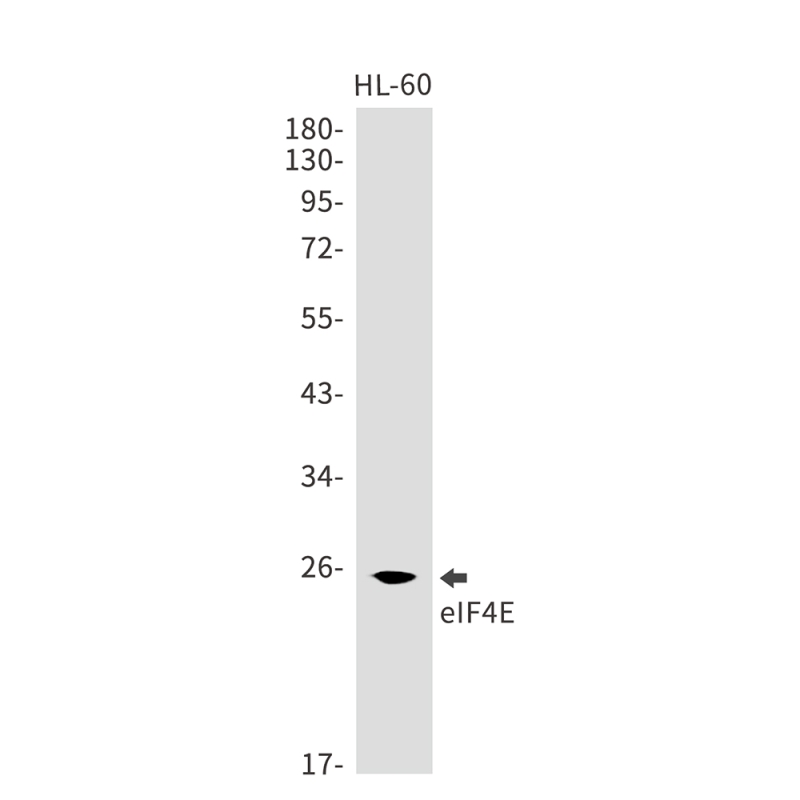
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EIF4E; EIF4EL1; EIF4F; Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; eIF-4E; eIF4E; eIF-4F 25 kDa subunit; mRNA cap-binding protein |
| Entrez GeneID | 1977 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 25 kDa; Observed MW: 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human eIF4E |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于eIF4E抗体的参考文献示例(简化版):
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E for cancer therapy*
**作者**:Graff JR, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用eIF4E抗体检测多种癌细胞中eIF4E的过表达,发现抑制eIF4E可减少肿瘤生长,为靶向翻译起始因子的抗癌策略提供依据。
2. **文献名称**:*The translational landscape of mTOR signalling steers cancer initiation and metastasis*
**作者**:Hsieh AC, et al.
**摘要**:通过eIF4E抗体分析mTOR通路对翻译的调控,发现eIF4E磷酸化在肿瘤发生和转移中的作用,提出靶向eIF4E相关复合物的治疗潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*eIF4E phosphorylation promotes tumorigenesis and is associated with prostate cancer progression*
**作者**:Furic L, et al.
**摘要**:使用eIF4E特异性抗体验证其磷酸化形式在癌症样本中的表达升高,揭示eIF4E与4E-BP1结合失调促进肿瘤进展的机制。
4. **文献名称**:*The eIF4E-binding proteins 1 and 2 are novel regulators of cell proliferation and survival*
**作者**:Rousseau D, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫印迹(eIF4E抗体)和免疫荧光技术,证明eIF4E在临床肿瘤样本中异常激活,并与患者预后不良相关。
(注:以上文献名为简化概括,实际引用需核对原文标题及细节。)
eIF4E (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E) is a critical component of the mRNA translation machinery, primarily involved in recognizing the 7-methylguanosine cap structure at the 5' end of eukaryotic mRNAs. As a subunit of the eIF4F complex, it plays a pivotal role in initiating protein synthesis by recruiting ribosomes to capped mRNAs. Dysregulation of eIF4E is closely linked to cancer progression, as its overexpression enhances the translation of oncogenic proteins (e.g., cyclin D1. c-Myc) and promotes cell proliferation, survival, and metastasis. Consequently, eIF4E has emerged as a biomarker and therapeutic target in oncology research.
Antibodies targeting eIF4E are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both normal and pathological contexts. These antibodies enable detection and quantification of eIF4E via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Researchers also use them to investigate post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) and interactions with binding partners (e.g., eIF4G, 4E-BPs) in signaling pathways such as mTOR and MAPK. Commercially available eIF4E antibodies include monoclonal and polyclonal variants, often validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat models. Their applications extend to drug discovery, particularly in evaluating inhibitors targeting eIF4E activity or cap-binding function. However, cross-reactivity with homologous proteins or isoforms (e.g., eIF4E2) requires careful validation to ensure experimental accuracy.
×