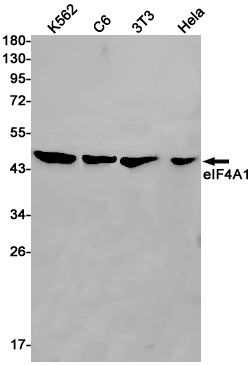
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-I; eIF-4A-I; eIF4A-I; ATP-dependent RNA helicase eIF4A-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1973 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 46 kDa; Observed MW: 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human eIF4A1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于eIF4A1抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"Targeting eIF4A1 with a novel inhibitor suppresses translational reprogramming and head-and-neck cancer progression"*
**作者**:Chen, H.H., Yu, X., & Zheng, B.
**摘要内容**:本研究利用特异性eIF4A1抗体检测头颈部癌细胞中eIF4A1蛋白水平,发现其过表达与肿瘤侵袭性相关。通过开发新型小分子抑制剂,结合抗体验证蛋白表达下调,证明抑制eIF4A1可阻断致癌mRNA翻译,减缓肿瘤生长。
2. **文献名称**:*"eIF4A1-dependent mRNA translation in melanoma: Role in metastasis and therapeutic targeting"*
**作者**:Robert, F., Pelletier, J., & Ruggero, D.
**摘要内容**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光(使用eIF4A1抗体),研究发现黑色素瘤中eIF4A1活性升高与转移相关。靶向抑制eIF4A1可减少促转移蛋白的合成,提示其作为黑色素瘤治疗的潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*"Development and validation of a high-affinity monoclonal antibody for eIF4A1 in human colorectal cancer tissues"*
**作者**:Kim, S., Lee, J., & Park, M.H.
**摘要内容**:该文献描述了一种针对人源eIF4A1的单克隆抗体的开发与验证,通过免疫组化分析结直肠癌组织,证实该抗体特异性高,可用于临床样本中eIF4A1表达的定量评估,揭示其与患者预后的相关性。
4. **文献名称**:*"eIF4A1 modulates stress granule formation through regulating translation in neuronal cells"*
**作者**:Mazroui, R., Di Marco, S., & Kaufman, R.J.
**摘要内容**:利用eIF4A1抗体研究其在神经元应激反应中的作用,发现eIF4A1通过调控特定mRNA的翻译效率影响应激颗粒的形成,为神经退行性疾病中翻译失调机制提供新见解。
以上文献涵盖了eIF4A1抗体在癌症机制研究、治疗靶点探索及抗体开发中的应用。
The eukaryotic initiation factor 4A1 (eIF4A1) is a critical ATP-dependent RNA helicase and a core component of the eIF4F complex, which regulates the initiation of cap-dependent protein translation. As a member of the DEAD-box helicase family, eIF4A1 unwinds secondary structures in the 5' untranslated region (UTR) of mRNAs, enabling ribosome scanning and recruitment. Its activity is tightly regulated by interactions with eIF4G and eIF4B, as well as by endogenous inhibitors like PDCD4. Dysregulation of eIF4A1 has been implicated in various cancers, where its overexpression is linked to tumor progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis, particularly in malignancies dependent on translation of oncogenic mRNAs with complex 5' UTRs (e.g., MYC, cyclins).
eIF4A1-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to investigate eIF4A1's role in translation control, stress responses, and cell proliferation. Additionally, these antibodies aid in evaluating the efficacy of pharmacological inhibitors (e.g., rocaglates, silvestrol) that target eIF4A1's helicase activity to suppress cancer growth. Research using eIF4A1 antibodies has also explored its non-canonical roles in RNA metabolism, viral infection, and neurological disorders. Given its therapeutic potential and centrality in translational regulation, eIF4A1 remains a focal point in studies bridging molecular biology and disease mechanisms.
×