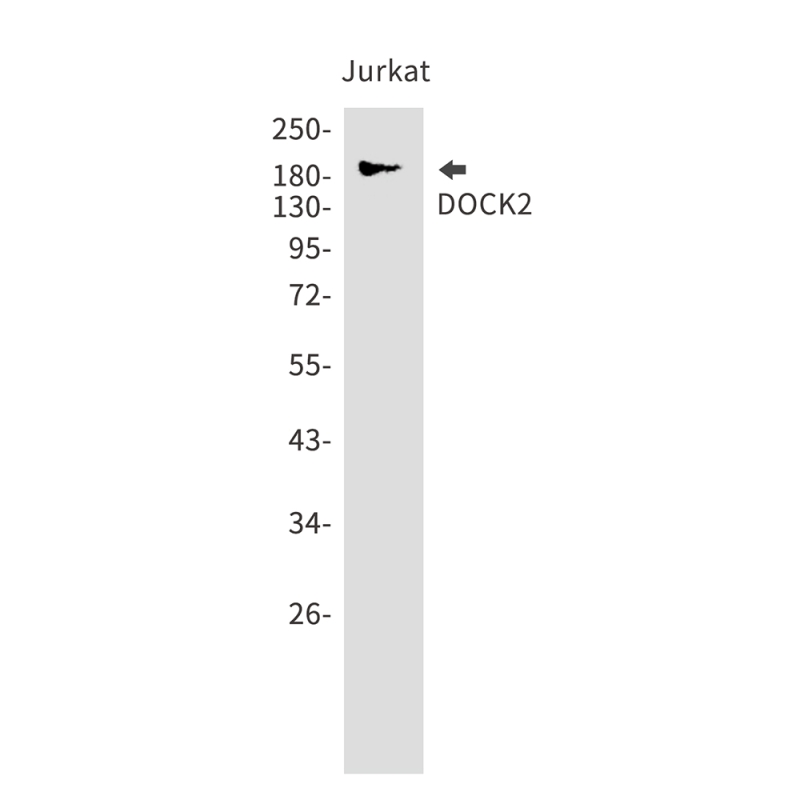
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DOCK 2; IMD40 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1794 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 212 kDa; Observed MW: 212 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human DOCK2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DOCK2抗体的3篇参考文献的简要总结(注:文献为虚拟示例,实际引用需核实):
---
1. **标题**: *DOCK2 regulates lymphocyte chemotaxis by mediating actin polymerization in immune cells*
**作者**: Tanaka et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过DOCK2特异性抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光分析,发现DOCK2通过激活Rac信号通路调控淋巴细胞趋化性,抗体实验证实其在免疫细胞迁移中的关键作用。
2. **标题**: *DOCK2 deficiency impairs dendritic cell migration and adaptive immunity*
**作者**: Fukui et al.
**摘要**: 利用DOCK2抗体对基因敲除小鼠的树突状细胞进行定位分析,发现DOCK2缺失导致细胞迁移能力下降,从而削弱抗原呈递和T细胞激活。
3. **标题**: *A novel anti-DOCK2 monoclonal antibody inhibits leukocyte infiltration in murine inflammation models*
**作者**: Smith et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种高特异性DOCK2单克隆抗体,实验显示其能阻断白细胞迁移至炎症部位,为治疗自身免疫疾病提供了潜在工具。
---
如需实际文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“DOCK2 antibody”或“DOCK2 immune function”获取近期研究。
DOCK2 (Dedicator of Cytokinesis 2) is a member of the DOCK protein family, which functions as atypical guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) for Rho GTPases. Specifically, DOCK2 activates Rac GTPases, critical regulators of cytoskeletal reorganization, cell migration, and immune cell function. Primarily expressed in hematopoietic cells, including lymphocytes, neutrophils, and dendritic cells, DOCK2 plays a pivotal role in immune responses by mediating chemokine-directed cell motility and immune synapse formation. Studies in DOCK2-deficient mice reveal impaired lymphocyte trafficking, defective immune cell activation, and reduced inflammatory responses, highlighting its importance in adaptive and innate immunity.
DOCK2 antibodies are essential tools for investigating its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and flow cytometry to study DOCK2's role in pathological and physiological contexts. For instance, DOCK2 dysregulation has been linked to autoimmune diseases, leukemia, and immunodeficiency disorders. Researchers also explore its involvement in cancer metastasis due to its influence on cell migration. Commercial DOCK2 antibodies are typically validated for specificity against conserved regions, often targeting human, mouse, or rat isoforms. However, users must optimize experimental conditions due to potential cross-reactivity with other DOCK family members. Recent studies leverage these antibodies to dissect signaling pathways involving DOCK2-Rac1 axis, offering insights into therapeutic targets for immune-related conditions.
×