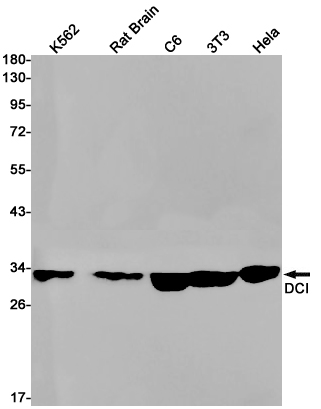
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
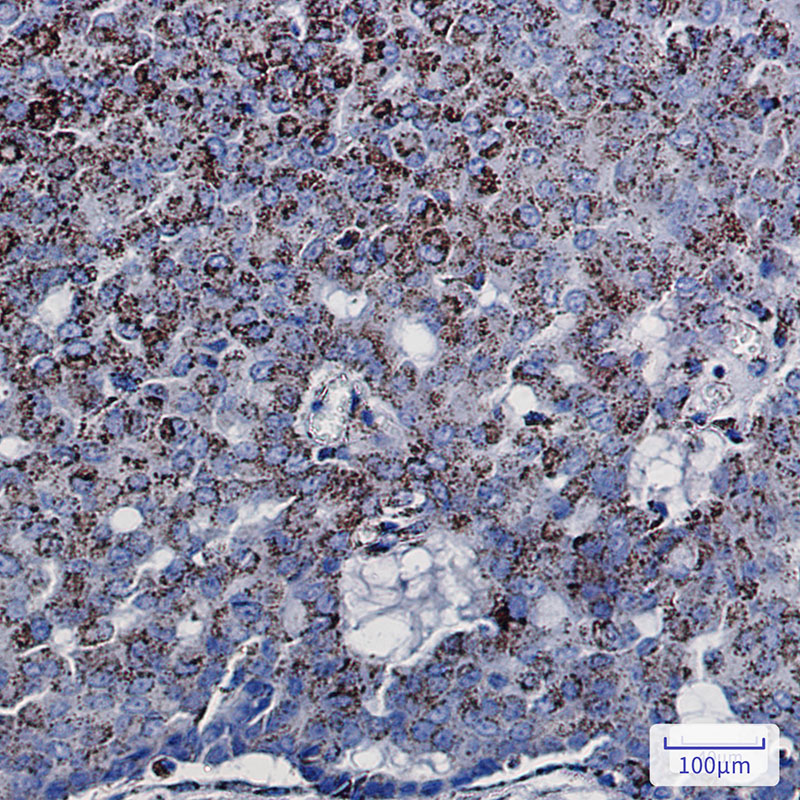
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ECI1; DCI; Enoyl-CoA delta isomerase 1; mitochondrial; 3; 2-trans-enoyl-CoA isomerase; Delta(3); Delta(2)-enoyl-CoA isomerase; D3; D2-enoyl-CoA isomerase; Dodecenoyl-CoA isomerase |
| Entrez GeneID | 1632 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 33 kDa; Observed MW: 33 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human DCI |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DCI(可能与副肿瘤性神经综合征相关抗体,如抗-Hu、抗-Yo等)的参考文献示例。由于“DCI抗体”并非标准术语,以下文献可能与相关领域相关,建议核对术语准确性:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Paraneoplastic anti-Hu-associated encephalomyelitis/sensory neuronopathy*
**作者**:Graus F, et al.
**摘要**:研究抗-Hu抗体(ANNA-1)在副肿瘤性神经综合征中的作用,尤其与小细胞肺癌(SCLC)相关。该抗体靶向神经元核抗原,导致脑脊髓炎和感觉神经元病变。
2. **文献名称**:*CV2/CRMP5 autoantibodies in paraneoplastic neurological syndromes*
**作者**:Honnorat J, et al.
**摘要**:探讨CV2/CRMP5抗体在副肿瘤性小脑变性及周围神经病变中的临床意义,强调其与胸腺瘤和SCLC的关联。
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-Yo-associated cerebellar degeneration in ovarian cancer*
**作者**:Darnell RB, et al.
**摘要**:分析抗-Yo抗体(靶向Purkinje细胞抗原)与妇科肿瘤相关小脑退行性病变的关系,揭示抗体介导的自身免疫机制。
4. **文献名称**:*Disrupted in Cancer 1 (DICE1) as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer*
**作者**:Kwon J, et al.
**摘要**:研究DICE1基因在肺癌中的抑癌作用,涉及蛋白表达缺失与肿瘤进展的关系,可能与抗体开发相关(非直接抗体研究,但提供DICE1背景)。
---
**注意**:若“DCI抗体”指特定靶点(如双链DNA抗体或新型标志物),建议提供更准确的术语或研究背景以便进一步检索。
DCI (Doublecortin-Interacting) antibodies are immunological tools primarily used to study the protein doublecortin (DCX), a microtubule-associated protein critical for neuronal migration and neurogenesis. Discovered in the late 1990s, DCX is expressed in developing neurons during brain formation and is a well-established marker for newly generated neurons (neuroblasts) in the central nervous system. Mutations in the DCX gene are linked to X-linked lissencephaly and subcortical band heterotopia, neurodevelopmental disorders characterized by abnormal brain folding and neuronal migration defects.
DCI antibodies enable researchers to detect and visualize DCX in tissues, cell cultures, or experimental models via techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, or immunofluorescence. These antibodies have been instrumental in advancing understanding of neurodevelopmental processes, neural stem cell differentiation, and brain repair mechanisms. They are also used in studying neurological diseases, brain tumors (e.g., gliomas expressing DCX), and regenerative medicine approaches. Recent applications extend to tracking neurogenesis in adult brains, offering insights into cognitive functions and neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. However, specificity challenges require careful validation to avoid cross-reactivity with similar proteins. Overall, DCI antibodies remain pivotal in bridging molecular neurobiology with clinical research.
×