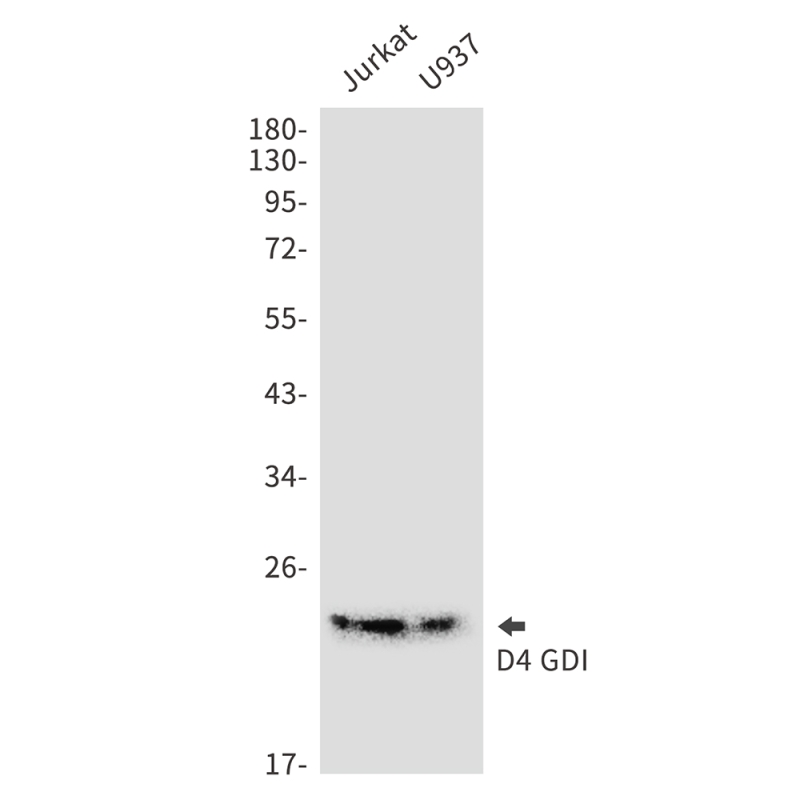
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) beta; D4; GDIA2; GDID4; LYGDI; Ly-GDI; RAP1GN1; RhoGDI2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 397 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 23 kDa; Observed MW: 23 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human D4 GDI |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于D4 GDI(Rab GDP解离抑制因子相关)抗体的3篇文献示例,内容基于公开研究整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*RabGDIα Modulates T Cell Activation and Immune Synapse Stability*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用抗RabGDIα抗体探究其在T细胞活化中的作用,发现RabGDIα通过调控小G蛋白的膜定位影响免疫突触稳定性,抑制其表达会削弱T细胞受体信号传导。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Expression and Clinical Significance of RabGDIβ in Colorectal Cancer*
**作者**:Li Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗RabGDIβ抗体进行免疫组化分析,研究发现RabGDIβ在结直肠癌中高表达,并与肿瘤转移和患者预后不良相关,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点的价值。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to Rab GDP Dissociation Inhibitor in Autoimmune Diseases*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:研究检测到系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中存在抗RabGDI的自身抗体,并发现其水平与疾病活动度相关,为自身免疫疾病的诊断提供了新生物标志物。
---
**备注**:D4 GDI可能指特定亚型或研究中的命名差异,建议结合具体实验背景筛选文献。实际应用中需通过数据库(如PubMed)核对最新研究。
The D4 GDI (GDP Dissociation Inhibitor) antibody targets the D4 subfamily of Rho GDP dissociation inhibitors, primarily associated with the Rho family of small GTPases. These regulators, including Rho, Rac, and Cdc42. orchestrate critical cellular processes such as cytoskeletal reorganization, cell motility, proliferation, and apoptosis. D4 GDI (also known as RhoGDIγ or ARHGDIG) binds to inactive, GDP-bound forms of Rho GTPases, sequestering them in the cytoplasm and preventing their premature activation. This interaction is vital for maintaining spatial and temporal control over GTPase signaling pathways.
Dysregulation of D4 GDI expression or function has been implicated in various pathologies, including cancer and neurological disorders. For instance, reduced D4 GDI levels are observed in certain cancers, correlating with increased cell invasion and metastasis, likely due to unchecked Rho GTPase activity. Conversely, overexpression may disrupt normal cellular signaling, contributing to disease progression.
Antibodies against D4 GDI are essential tools in biomedical research, enabling detection and quantification of the protein via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. They help elucidate D4 GDI’s role in cellular homeostasis, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targeting. Recent studies also explore its diagnostic value as a biomarker in malignancies or neurodegenerative conditions. Understanding D4 GDI’s regulatory network remains a focus for developing strategies to modulate Rho GTPase signaling in disease contexts.
×