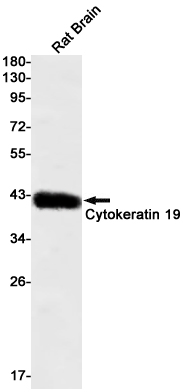
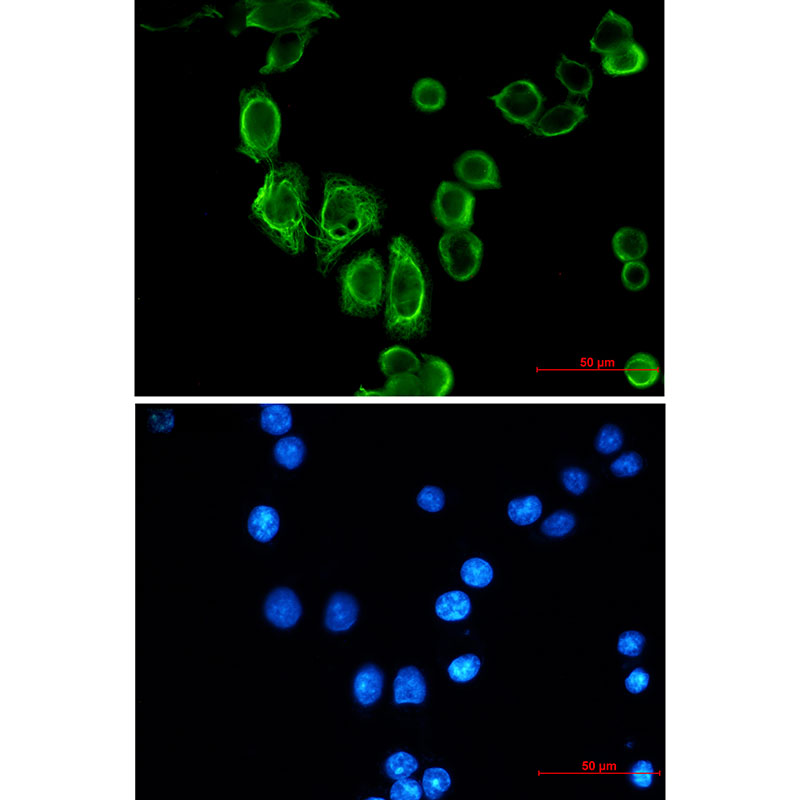
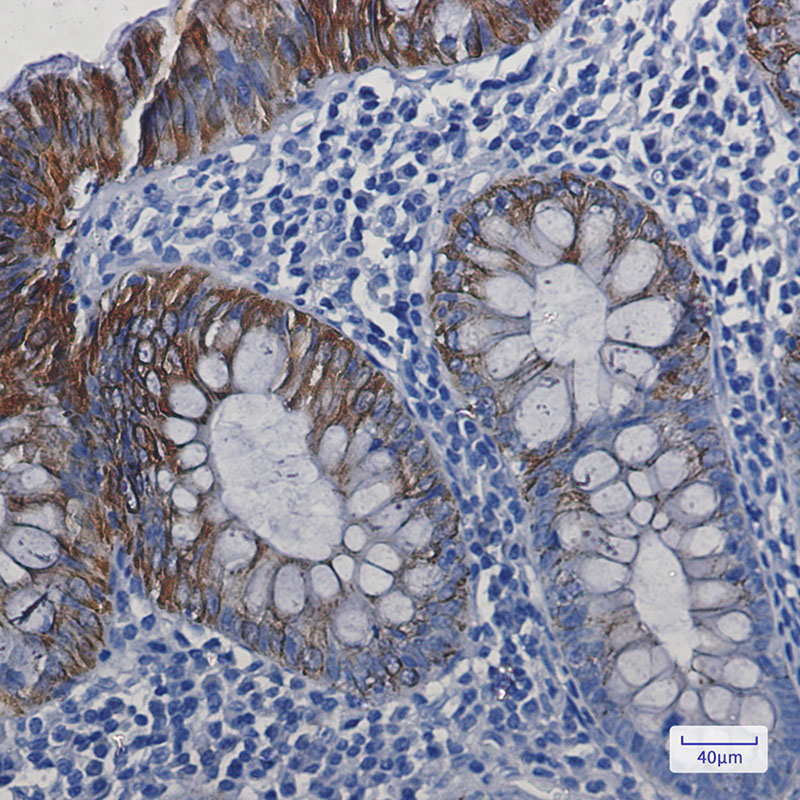
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KRT19; Keratin; type I cytoskeletal 19; Cytokeratin-19; CK-19; Keratin-19; K19 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3880 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 44 kDa; Observed MW: 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Cytokeratin 19 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Cytokeratin 19(CK19)抗体的3篇代表性文献,按研究领域分类简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Cytokeratin 19 expression in the diagnosis of thyroid papillary carcinoma*
**作者**:Miettinen, M., et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了CK19抗体在甲状腺乳头状癌鉴别诊断中的应用,发现CK19在甲状腺乳头状癌细胞中表达显著增强,可作为细针穿刺(FNA)样本中区分良恶性病变的可靠标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Detection of circulating tumor cells using cytokeratin 19 antibody in breast cancer patients*
**作者**:Pantel, K., et al.
**摘要**:通过CK19抗体检测乳腺癌患者外周血中的循环肿瘤细胞(CTC),发现CTC的存在与患者预后不良相关,提示其在转移监测中的潜在临床价值。
3. **文献名称**:*Cytokeratin 19 as a marker of cholangiocytic differentiation in liver diseases*
**作者**:Govaere, O., et al.
**摘要**:研究比较了CK19在肝细胞癌(HCC)和胆管癌(CC)中的表达差异,证实CK19抗体可用于区分两者,并揭示其在胆管细胞分化中的关键作用。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核实具体发表信息及DOI。若需补充实验技术类文献(如抗体开发),可补充早期经典研究(如Moll, R. 1982年对CK分类的奠基性工作)。
Cytokeratin 19 (CK19) is a member of the cytokeratin family, which comprises intermediate filament proteins essential for maintaining epithelial cell structure and integrity. As a type I acidic keratin with a molecular weight of approximately 40 kDa, CK19 is expressed in various epithelial tissues, including simple and pseudostratified epithelia, as well as the basal layers of stratified epithelia. Unlike many cytokeratins, CK19 lacks a C-terminal tail, contributing to its distinct biochemical properties.
CK19 antibodies are widely used in diagnostic pathology to identify epithelial-derived cells, particularly in detecting metastatic carcinomas. For instance, CK19 is a sensitive marker for lymph node micrometastases and circulating tumor cells. It is also pivotal in differentiating hepatocellular carcinoma (CK19-negative typically) from cholangiocarcinoma (CK19-positive). In thyroid pathology, CK19 overexpression aids in diagnosing papillary carcinoma.
Research highlights CK19's role in cancer biology, as its expression correlates with tumor aggressiveness, stem-like properties, and poor prognosis in breast, lung, and pancreatic cancers. Additionally, CK19 fragments (e.g., CYFRA 21-1) serve as serum biomarkers for monitoring malignancies. However, its presence in non-neoplastic conditions (e.g., reactive epithelia) necessitates careful interpretation. Ongoing studies explore CK19's functional roles in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and therapeutic targeting, underscoring its clinical and research significance.
×