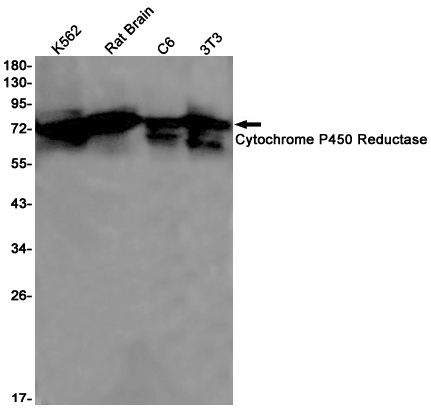
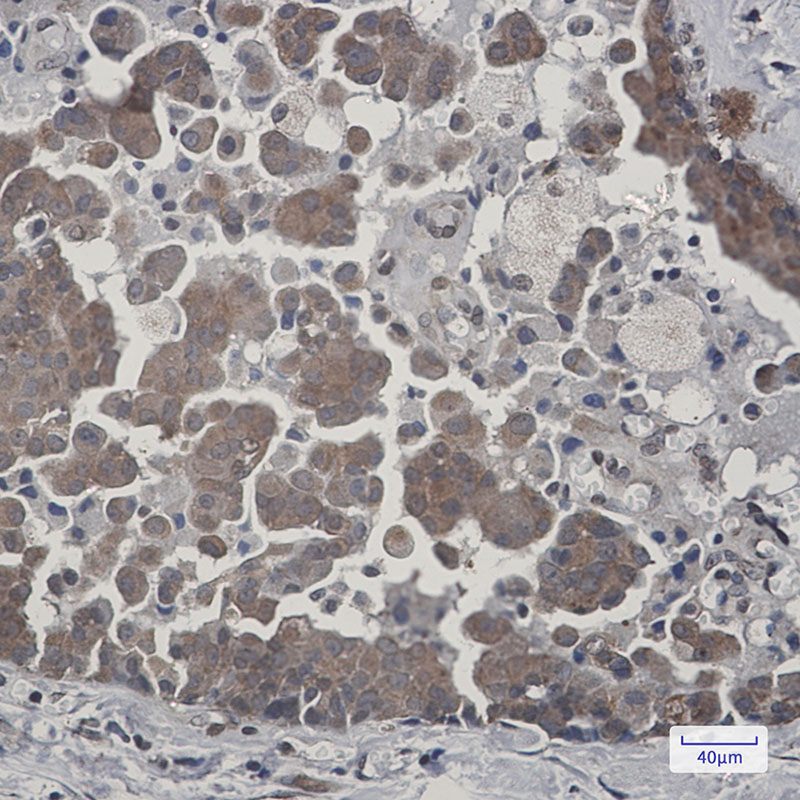
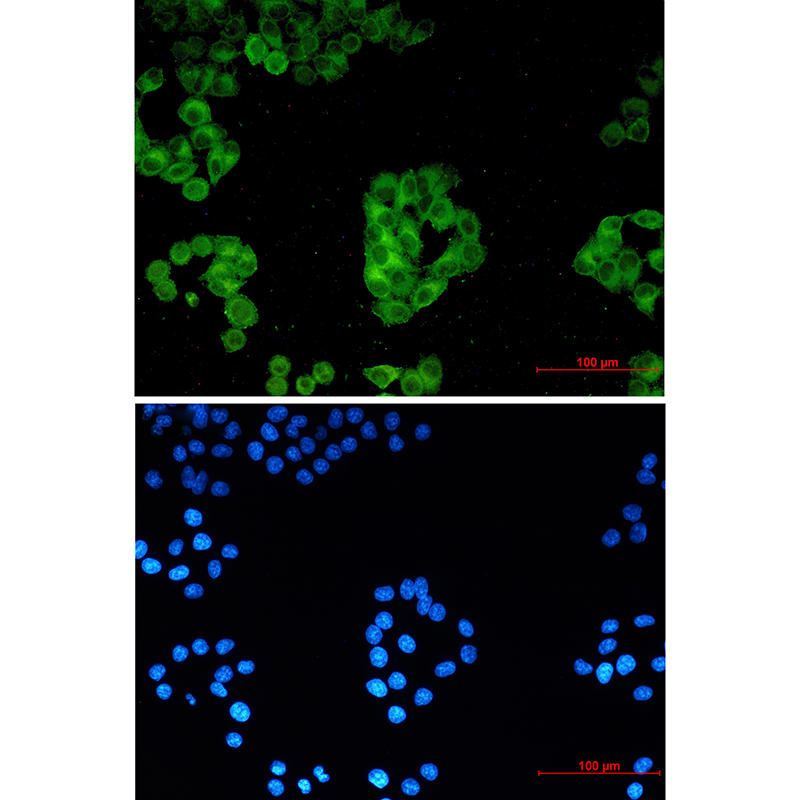
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CPR; CYPOR; P450R; por |
| Entrez GeneID | 5447 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 77 kDa; Observed MW: 77 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Cytochrome P450 Reductase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于细胞色素P450还原酶(CPR)抗体的代表性文献摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human cytochrome P450 reductase"
**作者**: Shephard EA et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了针对人源CPR的单克隆抗体,并通过免疫印迹和免疫组化验证其特异性。抗体成功用于检测肝脏和细胞模型中CPR的蛋白表达水平,为药物代谢研究提供工具。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Tissue-specific expression and subcellular localization of cytochrome P450 reductase in transgenic mice"
**作者**: Wu L et al.
**摘要**: 通过构建CPR基因敲除小鼠模型,利用特异性抗体分析CPR在肝脏、肠道等组织的分布及亚细胞定位,揭示其与药物代谢酶P450的共定位关系。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Role of cytochrome P450 reductase in nitrosamine-induced DNA damage"
**作者**: Jansson I et al.
**摘要**: 研究采用CPR抗体探究其在亚硝胺代谢中的作用,发现CPR通过调控活性氧生成参与DNA损伤过程,提示其与致癌机制的潜在关联。
---
如需具体文献链接或补充说明,请进一步告知。
Cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR), also known as NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase, is a critical flavoprotein located in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. It serves as an essential electron donor for cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, facilitating their catalytic roles in oxidative metabolism of drugs, steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, as well as biosynthesis of cholesterol and bile acids. Antibodies targeting CPR are widely used to study its expression, localization, and functional interactions in various tissues, particularly in the liver, where CYP-mediated metabolism is most active. These antibodies are typically generated by immunizing host animals (e.g., rabbits or mice) with recombinant CPR protein or synthetic peptides derived from conserved regions of the human or rodent homologs.
CPR antibodies are valuable tools in applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess protein levels in disease models (e.g., hepatic dysfunction, cancer) or under drug-induced conditions. Specificity validation often involves knockdown/knockout controls or tissue samples with known CPR expression. Due to CPR’s high conservation across mammals, many antibodies exhibit cross-reactivity with rodent models, supporting translational research. Quality-controlled batches are prioritized to minimize nonspecific binding, given the protein’s structural similarity to other flavoproteins. Researchers also employ these antibodies to explore CPR’s regulatory roles in cellular redox balance and its association with disorders linked to CYP enzyme deficiencies.
×