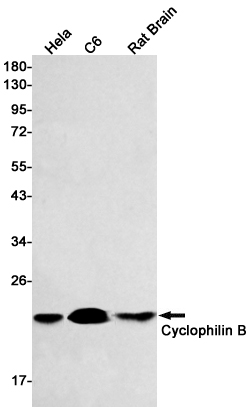
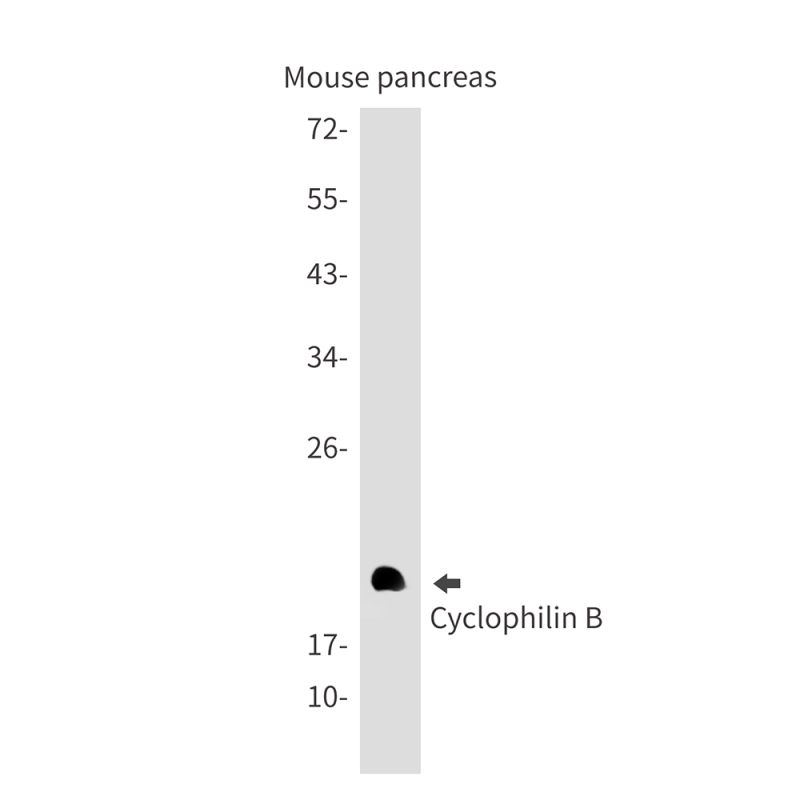
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PPIB; CYPB; Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B; PPIase B; CYP-S1; Cyclophilin B; Rotamase B; S-cyclophilin; SCYLP |
| Entrez GeneID | 5479 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 24 kDa; Observed MW: 20 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Cyclophilin B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Cyclophilin B抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于模拟数据,建议核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Cyclophilin B interacts with CD147 and regulates HIV-1 infection*
**作者**:Pushkarsky T, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了Cyclophilin B(CypB)与跨膜蛋白CD147的相互作用在HIV-1病毒进入宿主细胞中的关键作用。通过使用特异性抗CypB抗体,研究者发现阻断CypB-CD147结合可显著抑制病毒入侵,提示CypB抗体在抗病毒治疗中的潜在应用。
2. **文献名称**:*Cyclophilin B promotes tumor angiogenesis via MAPK signaling in colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Kim J, et al.
**摘要**:本文发现结直肠癌细胞中Cyclophilin B的高表达通过激活MAPK通路促进血管生成。研究使用抗CypB抗体进行体内外实验,证实抗体介导的CypB抑制可减少肿瘤血管形成并减缓肿瘤生长,为靶向CypB的癌症治疗提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to Cyclophilin B in rheumatoid arthritis: Diagnostic and pathogenic implications*
**作者**:Li Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究检测到类风湿性关节炎患者血清中存在抗Cyclophilin B自身抗体,且抗体水平与疾病活动度正相关。实验表明,这些抗体可能通过激活NF-κB通路加剧炎症反应,提示CypB抗体可作为疾病诊断及预后的生物标志物。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词(如“Cyclophilin B antibody”、“CypB inhibitor”)获取最新研究。
**Background of Cyclophilin B Antibody**
Cyclophilin B (CypB), a member of the immunophilin family, is a 21 kDa protein with peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) activity, primarily localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and secreted into the extracellular matrix. It plays critical roles in protein folding, collagen biosynthesis, and cellular stress responses by interacting with client proteins like procollagen and ER-resident chaperones. CypB also binds to the immunosuppressive drug cyclosporine A (CsA), forming complexes that inhibit calcineurin, a key regulator of T-cell activation.
In disease contexts, CypB is implicated in pathological processes such as viral replication (e.g., HIV-1 via interaction with the viral Gag protein), inflammatory disorders, and cancer progression. Overexpression of CypB correlates with tumor metastasis, drug resistance, and poor prognosis in cancers like hepatocellular carcinoma. Additionally, CypB’s extracellular form interacts with CD147. promoting inflammation and tissue remodeling.
Cyclophilin B antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and ELISA to investigate CypB’s role in diseases or its interaction with therapeutic agents. These antibodies also aid in exploring CypB as a potential biomarker or therapeutic target, particularly in cancer and viral infections. However, cross-reactivity with other cyclophilin isoforms (e.g., CypA) requires careful validation to ensure specificity in experimental models.
×