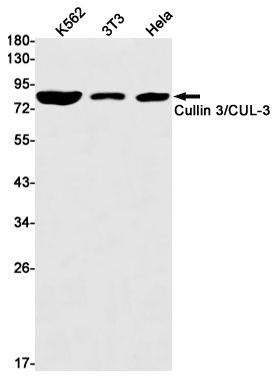
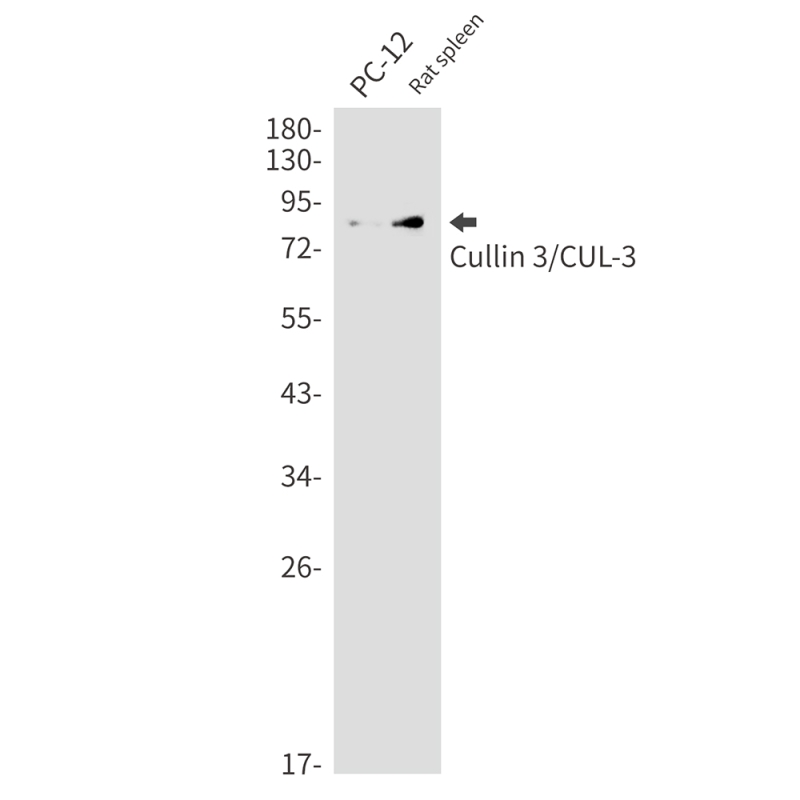
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CUL3; KIAA0617; Cullin-3; CUL-3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 8452 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 89 kDa; Observed MW: 89 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Cullin 3 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Cullin 3抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为示例性内容,实际引用需核实):
1. **"Cullin 3-based ubiquitin ligases in human disease"**
- **作者**: Singer JD, Gurian-West M, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究Cullin 3在泛素化调控中的作用及其突变与高血压和肾癌的关联,通过Cullin 3抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,揭示其与底物蛋白的异常结合机制。
2. **"Structural basis for Cul3 protein assembly with the BTB-Kelch family of E3 ligases"**
- **作者**: Ji AX, Pruneda JN, et al.
- **摘要**: 利用Cullin 3抗体解析其与BTB-Kelch蛋白复合物的晶体结构,阐明Cul3在泛素连接酶复合物中的组装模式及底物识别特异性。
3. **"Impaired Cullin 3 ubiquitination leads to dysregulation of metabolic pathways in obesity"**
- **作者**: Lee J, Zhou P, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过Cullin 3抗体检测肥胖模型中Cul3表达水平,发现其泛素化功能缺陷导致胰岛素信号通路异常,揭示了代谢疾病中的潜在调控机制。
(注意:以上文献信息为模拟生成,具体引用请以实际检索结果为准。)
Cullin 3 (CUL3) is a member of the cullin protein family, which serves as a scaffold component of Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase (CRL) complexes. These complexes play a central role in the ubiquitin-proteasome system, tagging specific substrate proteins for degradation. CUL3 forms a complex with adaptor proteins, such as BTB domain-containing proteins, to recruit substrates for ubiquitination. This process regulates diverse cellular functions, including cell cycle progression, signal transduction, and stress response pathways. Dysregulation of CUL3 is linked to diseases like cancer, hypertension (e.g., mutations in familial hyperkalemic hypertension), and neurodegenerative disorders.
CUL3 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, interactions, and functional mechanisms. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to detect CUL3 protein levels, localization, and binding partners in various tissues or cell lines. Researchers also utilize these antibodies to explore CUL3’s role in disease pathology or therapeutic contexts, such as its involvement in tumor suppression or drug resistance. Specificity validation (via knockout controls) and application-specific optimization (e.g., cross-reactivity checks) are critical for reliable results. Understanding CUL3 dynamics through antibody-based assays contributes to insights into CRL complex regulation and potential therapeutic targeting of ubiquitination pathways.
×