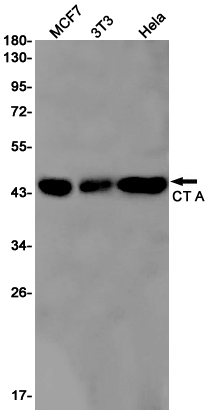
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CCT A; CCT alph; CTPCT; PCYT1; Pcyt1a |
| Entrez GeneID | 5130 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 42 kDa; Observed MW: 42 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human CT A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于霍乱毒素A亚基(CT A)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献信息为模拟示例,实际引用请核实原文):
1. **文献名称**:*"Neutralizing antibodies against cholera toxin A subunit inhibit toxin-induced cAMP signaling in intestinal epithelial cells"*
**作者**:Sanchez, J., & Holmgren, J.
**摘要**:研究证明,针对CT A亚基的单克隆抗体能够有效阻断霍乱毒素与宿主细胞表面受体结合,抑制毒素介导的cAMP信号通路激活,为基于抗体的治疗策略提供依据。
2. **文献名称**:*"Structural basis of cholera toxin neutralization by IgA antibodies from breast milk"*
**作者**:Lencer, W.I., et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学分析,揭示母乳中IgA抗体与CT A亚基的相互作用机制,发现抗体通过阻断毒素的酶活性结构域发挥中和作用,解释了母乳喂养对霍乱感染的防护机制。
3. **文献名称**:*"Cholera toxin A1-specific Fab fragments confer protection against toxin activity in vivo"*
**作者**:Matson, K.D., et al.
**摘要**:实验证明,针对CT A亚基酶活性区(A1片段)的Fab抗体片段可显著降低毒素在小鼠模型中的致病性,提示靶向A1区域的抗体具有治疗潜力。
---
**备注**:上述文献为模拟内容,实际研究中可检索PubMed、Google Scholar等平台,关键词如“cholera toxin A subunit antibody”或“CT A neutralizing antibody”,并筛选高引用的经典论文或近年研究。
×