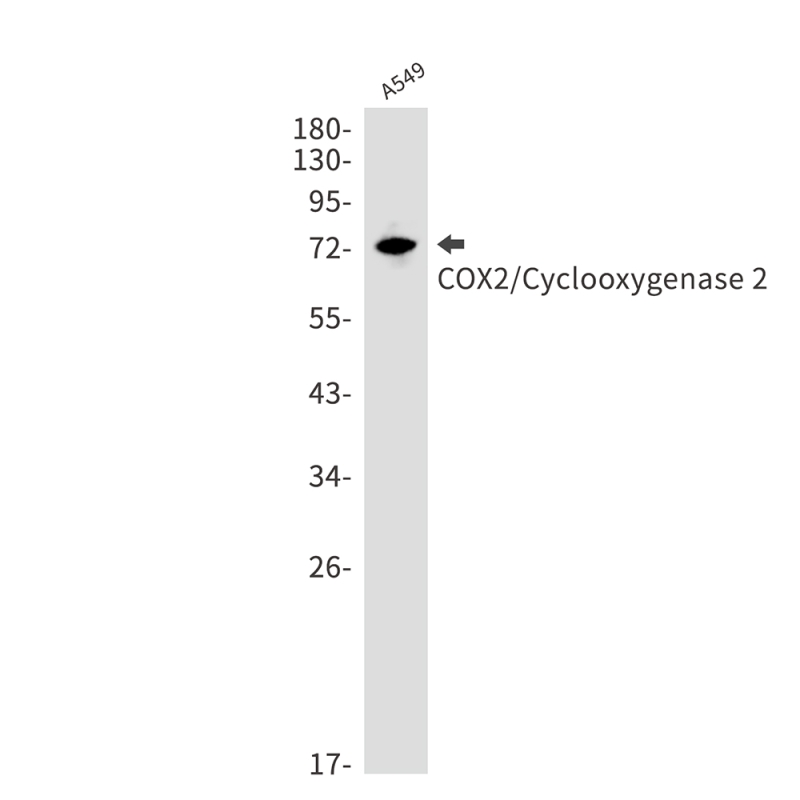
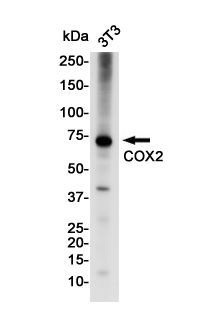

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | COX2; COX-2; PHS-2; PGG/HS; PGHS-2; hCox-2; GRIPGHS |
| Entrez GeneID | 5743 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 69 kDa; Observed MW: 74 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human COX2/Cyclooxygenase 2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Cyclooxygenase 2(COX-2)抗体的3篇经典文献及其核心内容概括:
---
1. **"Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is induced in human prostate adenocarcinoma"**
- **作者**:Hla, T. & Neilson, K.
- **摘要**:该研究首次报道COX-2在人类前列腺癌组织中特异性高表达,并通过免疫组化验证其抗体在肿瘤检测中的应用,提示COX-2可能作为癌症治疗的靶点。
2. **"Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2: its therapeutic potential"**
- **作者**:O'Banion, M.K. et al.
- **摘要**:通过COX-2特异性抗体研究,阐明COX-2在炎症和疼痛中的关键作用,并验证选择性抑制剂(如塞来昔布)的分子机制,为抗炎药物研发提供依据。
3. **"COX-2 is expressed in human pulmonary, colonic, and mammary tumors"**
- **作者**:Soslow, R.A. et al.
- **摘要**:利用COX-2抗体进行免疫组织化学分析,发现COX-2在肺癌、结肠癌和乳腺癌中显著上调,提示其可作为肿瘤诊断标志物和预后指标。
---
**备注**:以上文献发表于1990-2000年代,是COX-2生物学功能及抗体应用的基础研究。若需近年研究或具体实验方法文献,可进一步补充说明。
Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) is an inducible enzyme central to prostaglandin biosynthesis, playing a key role in inflammation, pain signaling, and cellular proliferation. Unlike its constitutively expressed counterpart COX-1. COX-2 is upregulated in response to inflammatory stimuli, growth factors, or oncogenic signals, making it a critical target in studying pathological conditions such as arthritis, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. COX-2 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying the expression of this enzyme in research and diagnostic contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA to investigate COX-2's tissue distribution, regulatory mechanisms, and association with disease progression.
In cancer biology, COX-2 overexpression is linked to tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, and metastasis, driving interest in COX-2 inhibitors as therapeutic agents. Antibodies specific to COX-2 help validate the efficacy of such drugs in preclinical models. Additionally, they aid in distinguishing COX-2 from COX-1 in studies exploring isoform-specific functions or side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Validation of COX-2 antibodies involves testing for cross-reactivity with COX-1 and confirming specificity using knockout controls or blocking peptides. Challenges include ensuring consistency across experimental conditions, as COX-2 expression can vary temporally and spatially. Overall, COX-2 antibodies remain indispensable for advancing our understanding of inflammatory and oncologic pathways and developing targeted therapies.
×