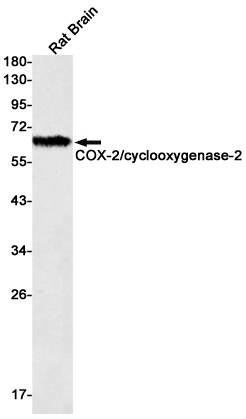
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
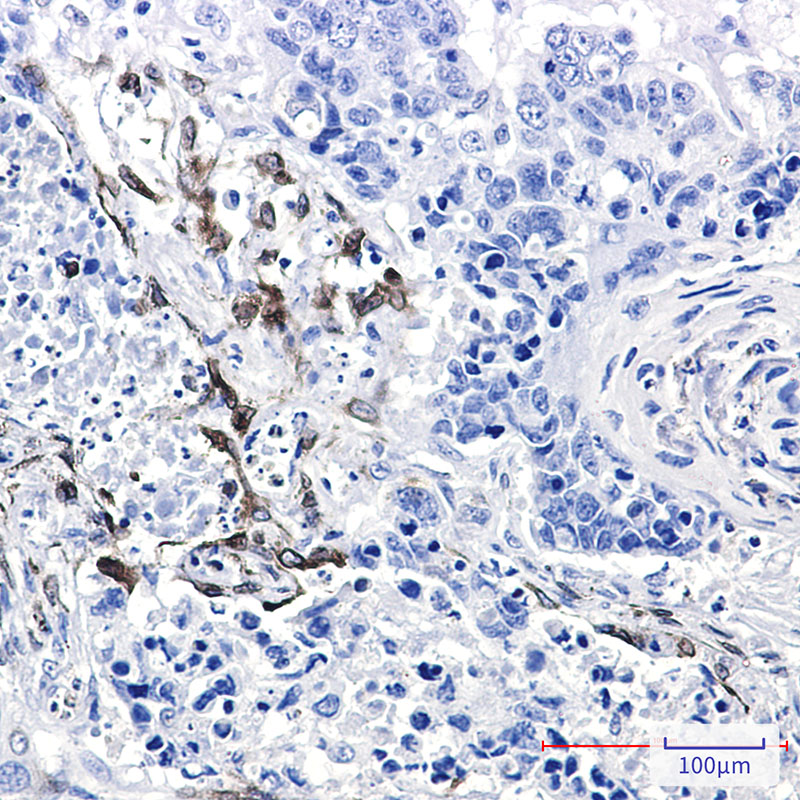
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | COX2; COX-2; PHS-2; PGG/HS; PGHS-2; hCox-2; GRIPGHS |
| Entrez GeneID | 5743 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 69 kDa; Observed MW: 69 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human COX2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下为3篇关于Cyclooxygenase 2(COX-2)抗体的经典文献,涵盖其应用及特异性验证:
1. **"Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2"**
*作者:J.R. Vane, R.M. Botting (1998)*
摘要:探讨COX-2在炎症中的作用,验证多种COX-2抗体的选择性,用于区分COX-1与COX-2在组织中的表达差异,支持抗体的特异性研究。
2. **"Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human colon cancer cells: Differential effects of exisulind"**
*作者:B.S. Reddy et al. (2000)*
摘要:通过Western blot和免疫组化分析COX-2在结肠癌细胞中的表达,使用特异性抗体验证药物对COX-2的调控作用,强调抗体在癌症研究中的关键应用。
3. **"Immunohistochemical localization of cyclooxygenase-2 in human gastric carcinoma"**
*作者:H. Kushima et al. (1999)*
摘要:评估COX-2抗体在胃癌组织中的免疫组化表现,确认抗体特异性并揭示COX-2过表达与肿瘤发展的关联,为抗体在病理诊断中的可靠性提供依据。
注:以上文献可在PubMed或Web of Science通过标题检索获取详细信息。若需近年研究,建议补充检索关键词“COX-2 antibody validation”或“anti-COX-2 applications”。
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is an inducible enzyme central to the synthesis of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins, playing a key role in inflammation, pain, and fever. Unlike its constitutively expressed isoform COX-1. COX-2 is upregulated in response to cytokines, growth factors, or tissue injury. It is implicated in pathological conditions such as chronic inflammation, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer, where its overexpression promotes tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Antibodies targeting COX-2 are critical tools for studying its expression, regulation, and function in both research and diagnostic contexts.
COX-2 antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and ELISA to detect protein levels in tissues or cell lysates, aiding in the identification of disease biomarkers. In cancer research, these antibodies help assess COX-2's association with tumor progression and prognosis. They also serve to validate experimental models, such as knockout mice, and evaluate the efficacy of COX-2 inhibitors (e.g., NSAIDs). Commercially available COX-2 antibodies include monoclonal and polyclonal variants, with monoclonal antibodies offering higher specificity for precise localization. However, cross-reactivity with COX-1 or other proteins remains a validation challenge. Recent applications extend to exploring COX-2's role in immune modulation and its interaction with signaling pathways like NF-κB. As therapeutic agents, COX-2-targeting biologics are under investigation, though most clinical inhibitors remain small-molecule drugs.
×