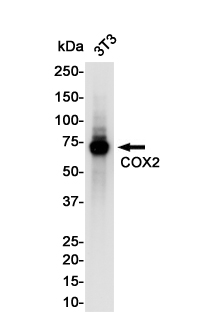
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cyclooxygenase-2; COX-2; Glucocorticoid-regulated inflammatory cyclooxygenase; Gripghs; PES-2; PHS II; Prostaglandin H2 synthase 2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 19225 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 69 kDa; Observed MW: 74 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of mouse COX2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Cyclooxygenase 2(COX-2)抗体的代表性文献摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Cyclooxygenase-2: a therapeutic target in inflammation*
**作者**:Simon LS
**摘要**:探讨COX-2在炎症疾病中的表达及其作为药物靶点的潜力,通过免疫组化实验证明COX-2抗体在炎症组织中的特异性标记。
2. **文献名称**:*Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human colorectal carcinoma*
**作者**:Kargman SL et al.
**摘要**:利用COX-2抗体进行Western blot和免疫组织化学分析,发现结直肠癌组织中COX-2蛋白表达显著高于正常组织,提示其与肿瘤进展相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Selective COX-2 inhibitors: a review of their therapeutic potential and safety*
**作者**:Sheng H et al.
**摘要**:通过COX-2抗体的免疫定位研究,验证了COX-2抑制剂在减少胃肠道副作用方面的优势,并评估其临床应用安全性。
4. **文献名称**:*Cyclooxygenase-2 in neurodegenerative disorders*
**作者**:Williams CS et al.
**摘要**:采用COX-2抗体在小鼠模型中检测神经炎症反应,证实COX-2在阿尔茨海默病等疾病中的异常表达及潜在干预策略。
---
以上文献聚焦于COX-2抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、免疫组化)及其在疾病机制和药物开发中的作用。如需具体引用格式,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar查询原文。
Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) is an inducible enzyme that plays a key role in prostaglandin synthesis, particularly during inflammation, pain, and cellular proliferation. Unlike its constitutive isoform COX-1. COX-2 is upregulated in response to cytokines, growth factors, or pathological stimuli, making it a critical mediator in inflammatory diseases, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. COX-2-specific inhibitors (e.g., celecoxib) are widely used as anti-inflammatory drugs but may carry cardiovascular risks, driving research into alternative therapeutic strategies.
COX-2 antibodies are essential tools for studying the enzyme's expression, localization, and regulation in both normal and diseased tissues. They enable researchers to detect COX-2 protein levels via techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and ELISA, aiding in the identification of COX-2 overexpression in cancers (e.g., colorectal, breast) or inflammatory conditions (e.g., arthritis, atherosclerosis). Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies targeting specific COX-2 epitopes help distinguish it from COX-1. minimizing cross-reactivity. Additionally, these antibodies are used to validate the efficacy of COX-2 inhibitors in preclinical models and explore its role in neuroinflammation or neurodegenerative pathways. Recent studies also investigate COX-2's crosstalk with tumor microenvironments and immune cells, highlighting its dual pro- and anti-tumor effects. Despite advancements, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity across species and applications, necessitating rigorous validation. Overall, COX-2 antibodies remain pivotal in advancing mechanistic insights and therapeutic targeting of COX-2-related pathologies. (298 words)
×