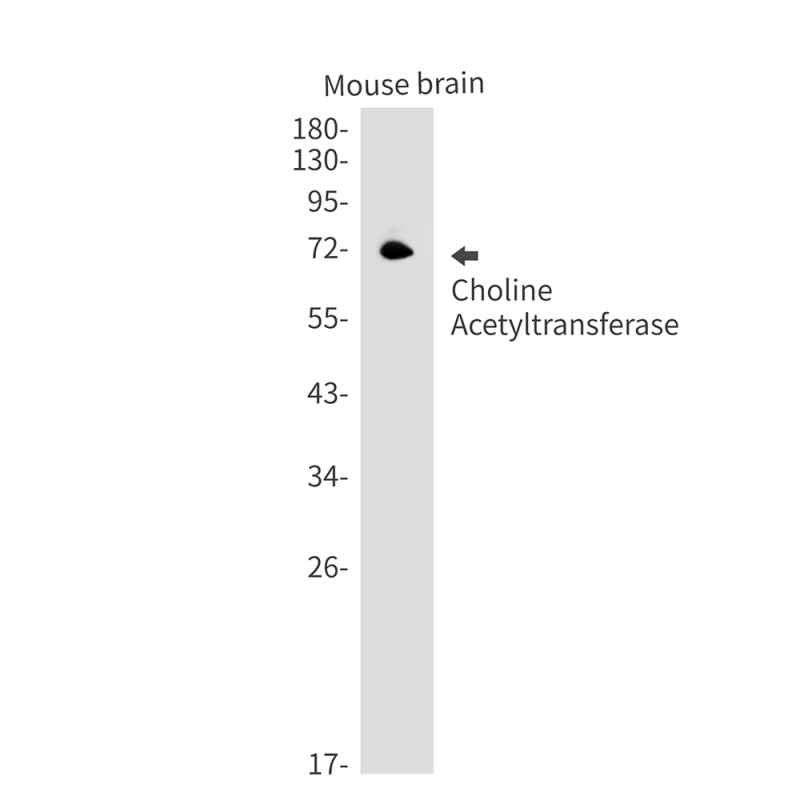

| WB | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
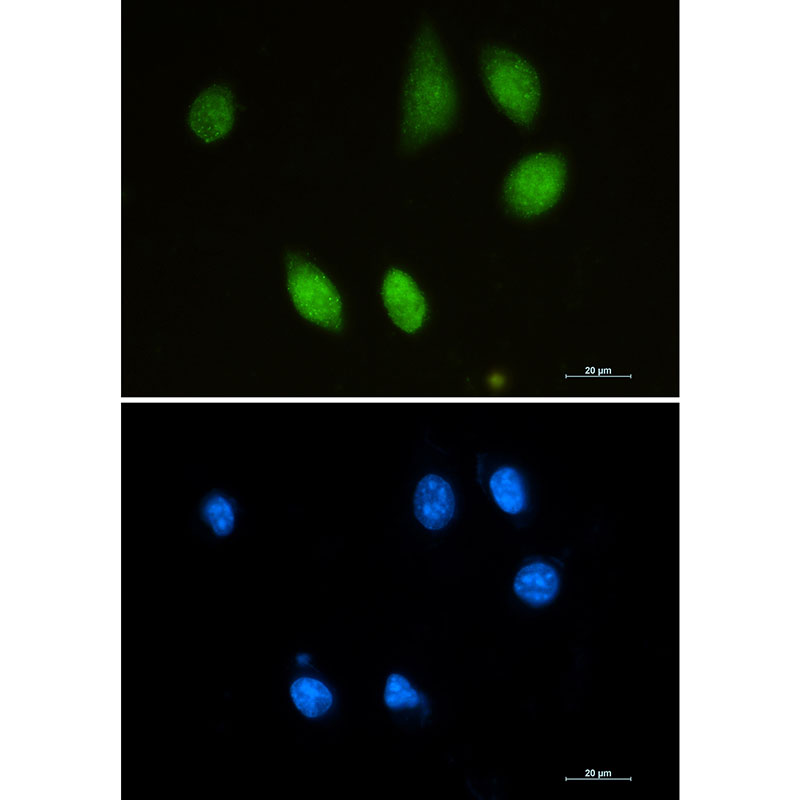
| IF | 1/20 | Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CHAT; Choline O-acetyltransferase; CHOACTase; ChAT; Choline acetylase |
| Entrez GeneID | 1103 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 83 kDa; Observed MW: 72 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Choline Acetyltransferase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Choline Acetyltransferase(ChAT)抗体相关的经典文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**: "Monoclonal antibodies to choline acetyltransferase for neuroanatomical mapping"
**作者**: Bruce H. Wainer et al. (1981)
**摘要**: 首次报道了针对ChAT的单克隆抗体制备,验证了其在哺乳动物脑组织中对胆碱能神经元的特异性标记能力,为后续神经解剖学研究奠定基础。
2. **文献名称**: "Production and characterization of a polyclonal antibody to human choline acetyltransferase"
**作者**: Michael J. Bannon et al. (1988)
**摘要**: 开发了高特异性的多克隆抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫组化验证其对人类ChAT的识别能力,并应用于阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织胆碱能神经元缺失的研究。
3. **文献名称**: "Species-specific detection of choline acetyltransferase by antibodies: Comparative studies in rodents and primates"
**作者**: Takaomi C. Saido et al. (1993)
**摘要**: 系统分析了不同物种(大鼠、小鼠、猴)中ChAT抗体的交叉反应性,发现部分抗体存在物种限制性,为跨物种胆碱能系统研究提供抗体选择依据。
Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing acetylcholine, a critical neurotransmitter involved in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. ChAT catalyzes the transfer of an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to choline, forming acetylcholine, which plays essential roles in motor control, memory, learning, and autonomic functions. Antibodies targeting ChAT are widely used as research tools to identify and study cholinergic neurons, which are characterized by their expression of this enzyme. These antibodies enable the visualization and quantification of ChAT-expressing cells in tissues, aiding investigations into cholinergic system organization and dysfunction.
ChAT antibodies are commonly employed in techniques such as immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and Western blotting. They are particularly valuable in neuroscience research, including studies of neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s), where cholinergic neuron loss is a hallmark. Additionally, they help explore autonomic nervous system disorders and neuromuscular junction pathologies. Both monoclonal and polyclonal ChAT antibodies are available, with specificity validated across species like humans, mice, and rats. However, users must confirm cross-reactivity for their experimental models, as sequence variations may affect antibody performance.
Challenges include potential cross-reactivity with unrelated proteins or splice variants, necessitating rigorous validation via knockout controls or peptide blocking. Proper storage and optimized dilution protocols are critical for maintaining antibody efficacy. Overall, ChAT antibodies remain indispensable for mapping cholinergic pathways and understanding their roles in health and disease.
×