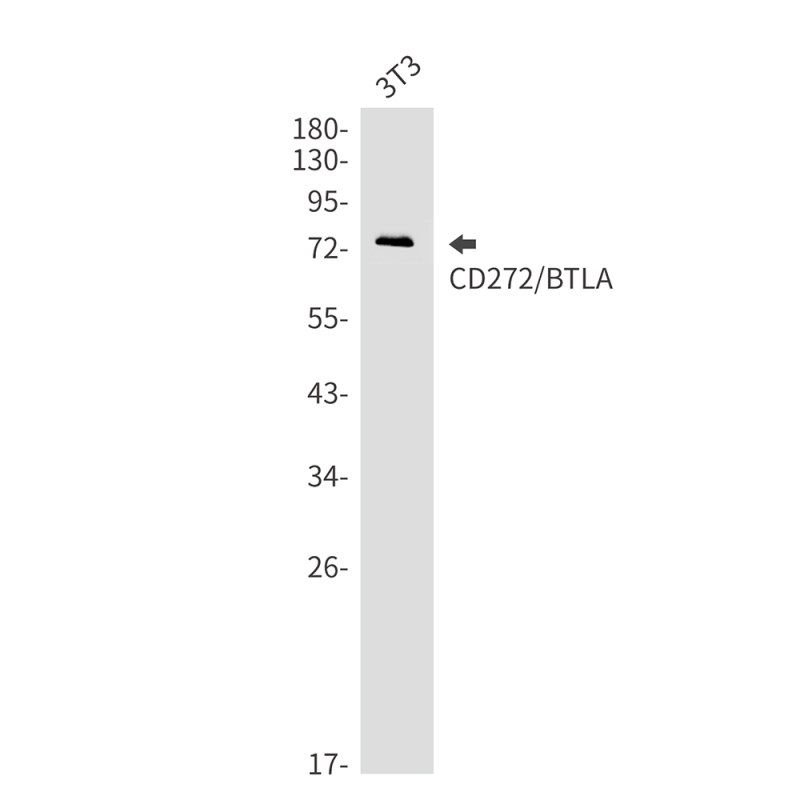
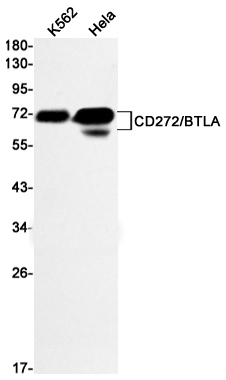
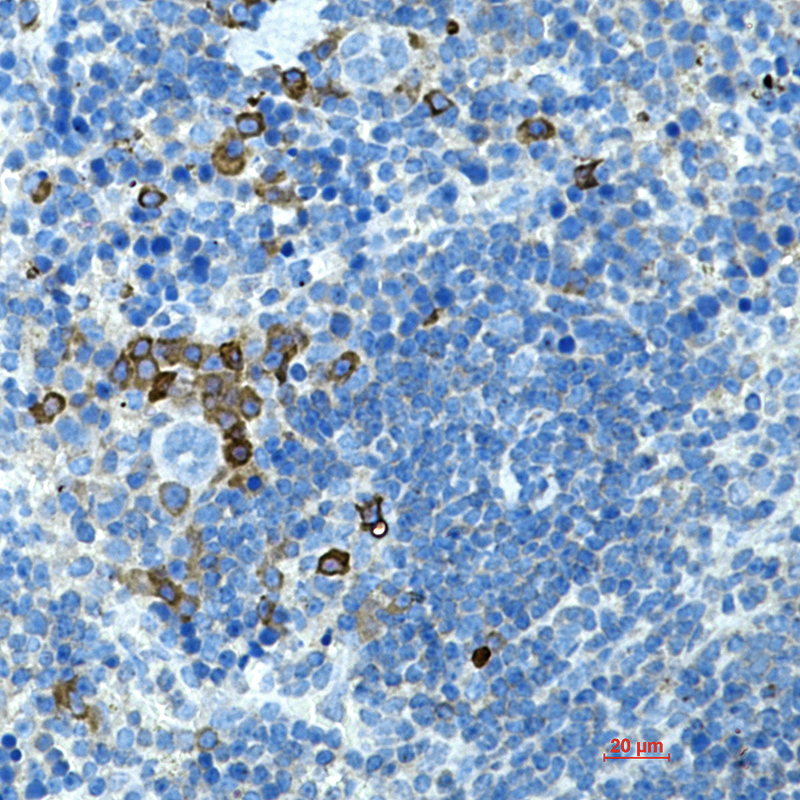
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | A630002H24; B-and T-lymphocyte-associated protein |
| Entrez GeneID | 208154 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34 kDa; Observed MW: 55-80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of mouse CD272 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD272(BTLA)抗体的3篇代表性文献示例,涵盖其功能及治疗潜力:
1. **文献名称**:*"BTLA-HVEM checkpoint regulates CD8+ T cell exhaustion in chronic viral infection"*
**作者**:Watanabe, N., et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了CD272(BTLA)与其配体HVEM在慢性病毒感染中通过抑制CD8+ T细胞功能导致免疫耗竭的机制,提示阻断BTLA信号可能恢复T细胞抗病毒活性。
2. **文献名称**:*"Targeting BTLA in cancer immunotherapy: insights from preclinical models"*
**作者**:Murphy, K.M., et al.
**摘要**:通过小鼠模型证明抗CD272抗体可增强抗肿瘤免疫反应,与PD-1抑制剂联用显著抑制肿瘤生长,为BTLA作为癌症免疫治疗新靶点提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*"BTLA modulates regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in autoimmune disease"*
**作者**:Sordo-Bahamondes, M., et al.
**摘要**:探讨CD272在自身免疫疾病中通过调节Treg细胞功能维持免疫耐受的作用,抗BTLA抗体可能通过打破过度抑制状态增强效应T细胞活性。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需根据具体研究检索真实发表的论文。
CD272. also known as BTLA (B and T lymphocyte attenuator), is an immune checkpoint protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is expressed on immune cells, including T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. Structurally, CD272 contains an extracellular immunoglobulin domain, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs). It interacts with the herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), a TNF receptor family member, to deliver inhibitory signals that dampen T-cell activation and immune responses. This interaction helps maintain immune tolerance and prevent excessive inflammation.
CD272 antibodies are therapeutic tools designed to modulate this pathway. Antagonistic antibodies blocking CD272-HVEM binding aim to enhance anti-tumor immunity by relieving T-cell suppression, potentially synergizing with other checkpoint inhibitors like anti-PD-1. Conversely, agonistic antibodies may suppress overactive immune responses in autoimmune or inflammatory diseases. Preclinical studies highlight CD272's role in cancer, autoimmunity, and infectious diseases, but clinical translation remains limited. Challenges include understanding context-dependent effects and optimizing antibody specificity. Current research focuses on elucidating CD272's regulatory mechanisms and exploring combinatorial therapies to improve treatment efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
×