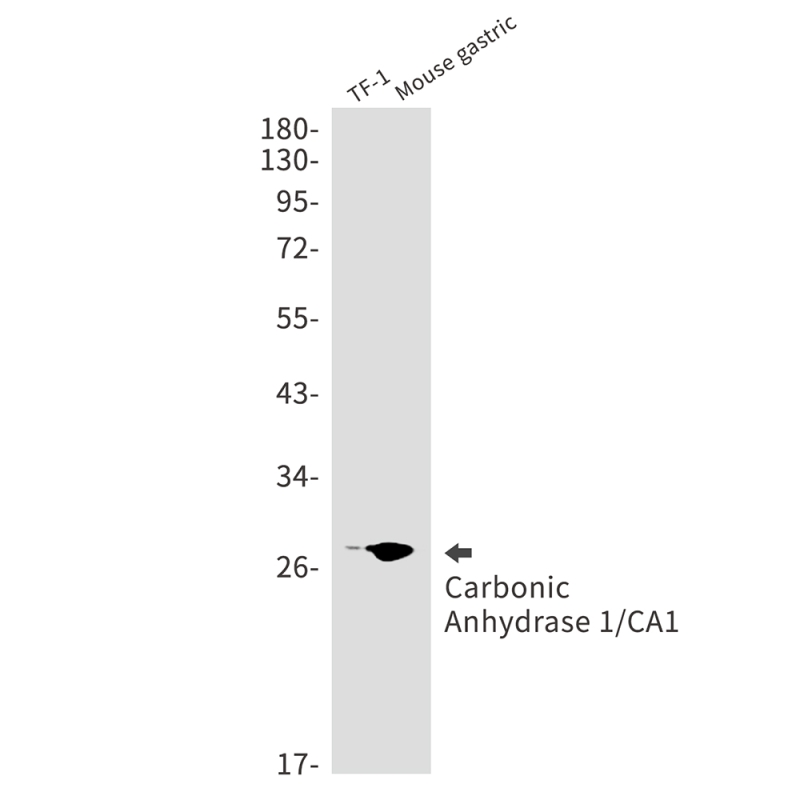
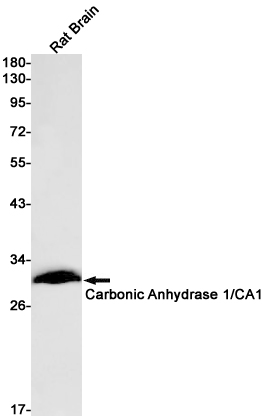
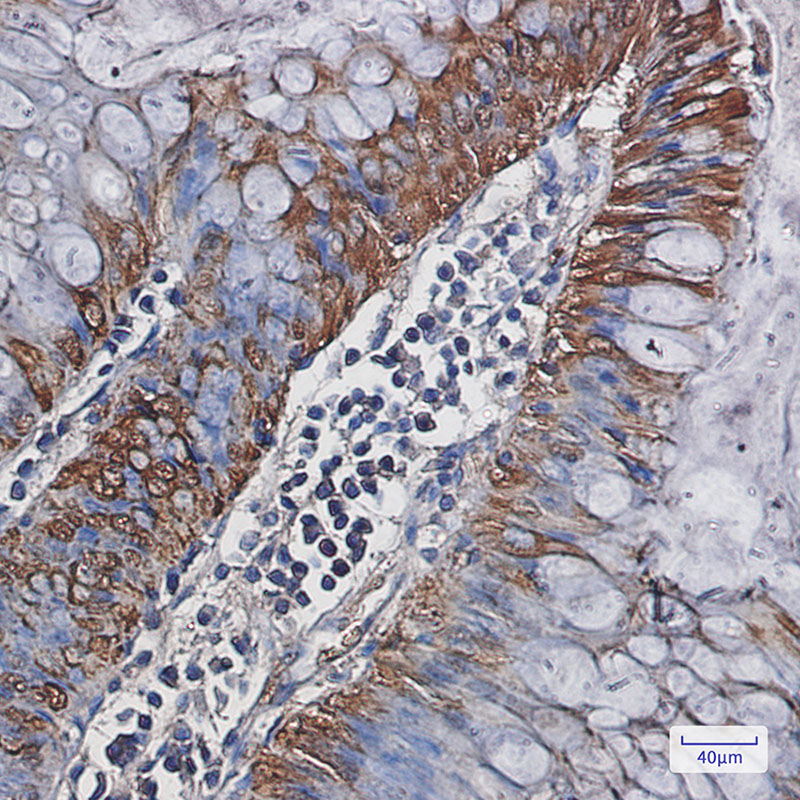
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CA1; Carbonic anhydrase 1; Carbonate dehydratase I; Carbonic anhydrase B; CAB; Carbonic anhydrase I; CA-I |
| Entrez GeneID | 759 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 29 kDa; Observed MW: 29 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Carbonic Anhydrase I |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
Carbonic anhydrase 1 (CA1) is a zinc metalloenzyme belonging to the carbonic anhydrase family, which catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and protons, playing a critical role in pH regulation, ion transport, and metabolic homeostasis. Primarily expressed in erythrocytes, gastrointestinal tissues, and the kidney, CA1 is involved in diverse physiological processes, including respiration, acid-base balance, and fluid secretion.
Antibodies targeting CA1 are valuable tools in biomedical research and diagnostics. They are widely used to study CA1's expression patterns, cellular localization, and functional roles in both normal and pathological conditions. For instance, CA1 antibodies have been employed in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA to investigate its dysregulation in cancers (e.g., colorectal, pancreatic), where altered CA1 levels may correlate with tumor progression or metabolic reprogramming. Additionally, CA1 autoantibodies have been detected in autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis, suggesting a potential link to disease mechanisms.
In neuroscience, CA1 antibodies aid in exploring the enzyme’s role in cerebral pH regulation and its implications for neurodegenerative diseases. The development of specific and high-affinity CA1 antibodies continues to advance research into its physiological significance and therapeutic targeting, particularly in conditions involving acid-base imbalances or abnormal cellular metabolism.
×