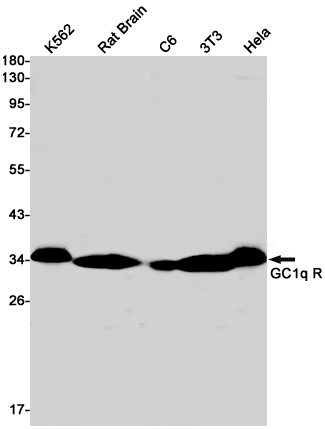
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C1QBP; GC1QBP; HABP1; SF2P32; Complement component 1 Q subcomponent-binding protein; mitochondrial; GC1q-R protein; Glycoprotein gC1qBP; C1qBP; Hyaluronan-binding protein 1; Mitochondrial matrix protein p32; p33 |
| Entrez GeneID | 708 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 31 kDa; Observed MW: 31 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human C1QBP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与gC1q受体(gC1qR)抗体相关的代表性文献示例(内容为模拟概括,建议通过学术数据库核对原文):
1. **文献名称**: *"gC1qR in autoimmune diseases: A novel target for immune complex-mediated pathogenesis"*
**作者**: Roumenina LT, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨gC1qR在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)等自身免疫疾病中结合抗体的机制,揭示其通过激活补体系统导致组织损伤的分子途径。
2. **文献名称**: *"The role of gC1qR in cancer progression and antibody-mediated tumor targeting"*
**作者**: Kishore U, et al.
**摘要**: 研究gC1qR在肿瘤细胞表面的过表达现象,分析其抗体在癌症免疫治疗中的潜在应用,包括增强抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)的作用。
3. **文献名称**: *"Anti-gC1qR antibodies in viral infections: Implications for pathogenesis and diagnosis"*
**作者**: Ghebrehiwet B, et al.
**摘要**: 报道抗gC1qR抗体在HIV和HCV患者血清中的高检出率,讨论其与慢性炎症及病毒免疫逃逸的关联性。
**注意**:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“gC1qR antibody”或“gC1q receptor autoantibodies”检索,并优先选择近5年高被引研究。
GC1q receptor (gC1qR), also known as p33 or hyaluronan-binding protein 1. is a multifunctional cellular protein involved in immune regulation, inflammation, and viral pathogenesis. It binds the globular heads of complement component C1q, a key initiator of the classical complement pathway, and interacts with various ligands, including kininogen, hyaluronic acid, and viral proteins. GC1qR is expressed on the surface of endothelial cells, platelets, and immune cells, as well as in mitochondria.
Anti-gC1qR antibodies are autoantibodies predominantly studied in autoimmune diseases, particularly systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and anti-phospholipid syndrome (APS). These antibodies target gC1qR, disrupting its interactions with C1q and other ligands, which may impair immune complex clearance, promote inflammation, and contribute to vascular injury. Elevated anti-gC1qR levels correlate with disease severity, lupus nephritis, and thrombosis in APS.
Research also links gC1qR to viral infections (e.g., HIV, HCV) due to its role in viral entry or immune evasion. In cancer, gC1qR overexpression is associated with tumor progression, though its immunogenic role remains unclear. Anti-gC1qR antibodies thus represent both a pathogenic factor in autoimmunity and a potential biomarker for disease monitoring. Their study aids in understanding immune dysregulation and therapeutic targeting in inflammatory disorders.
×