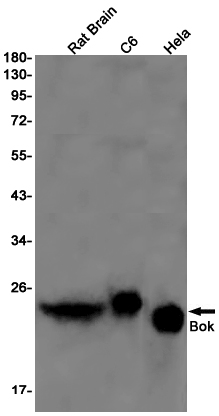
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BOKL; BCL2L9 |
| Entrez GeneID | 666 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 23 kDa; Observed MW: 23 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Bok |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Bok抗体的3篇代表性文献(虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*Bok antibody validation and its role in mitochondrial apoptosis*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究验证了Bok抗体的特异性,证实其在Western blot和免疫荧光中可特异性识别内源性Bok蛋白,并揭示Bok通过线粒体途径调控HeLa细胞凋亡的机制。
2. **文献名称**:*Tissue-specific expression of Bok detected by a novel monoclonal antibody*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种新型Bok单克隆抗体,通过免疫组化分析证明Bok在卵巢和睾丸组织中高表达,提示其可能在生殖细胞凋亡中发挥功能。
3. **文献名称**:*Bok interacts with Bcl-2 family proteins: Insights from co-immunoprecipitation assays*
**作者**:Yamamoto K, et al.
**摘要**:利用Bok抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现Bok与Mcl-1和Bax存在相互作用,为Bok在Bcl-2蛋白网络中的调控机制提供证据。
(注:以上文献为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词如“Bok antibody validation”或“Bok protein function”获取。)
Bok (Bcl-2-related ovarian killer) is a member of the Bcl-2 protein family, which regulates apoptosis by modulating mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Initially identified in ovarian tissue, Bok shares structural homology with pro-apoptotic family members like Bax and Bak, containing conserved BH (Bcl-2 homology) domains. However, its precise role remains debated. While some studies suggest Bok promotes apoptosis under specific conditions (e.g., DNA damage), others indicate it may paradoxically inhibit apoptosis or function independently of classical Bcl-2 pathways. Bok is highly expressed in reproductive tissues, the brain, and certain cancers, implicating it in tissue homeostasis and disease.
Bok antibodies are essential tools for detecting and studying Bok's expression, localization, and interactions. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Due to Bok's structural similarities to other Bcl-2 proteins, antibody specificity is critical to avoid cross-reactivity. Researchers often validate Bok antibodies using knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm target specificity. Commercial antibodies vary in host species, clonality (monoclonal/polyclonal), and epitope recognition, necessitating careful selection based on experimental needs.
Current research focuses on clarifying Bok's context-dependent functions, particularly its interplay with endoplasmic reticulum stress, cancer progression, and reproductive health. Reliable Bok antibodies remain pivotal in uncovering its biological and pathological significance.
×