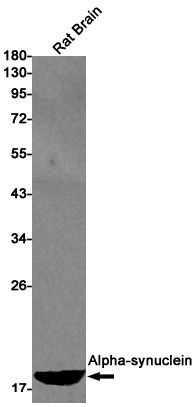
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
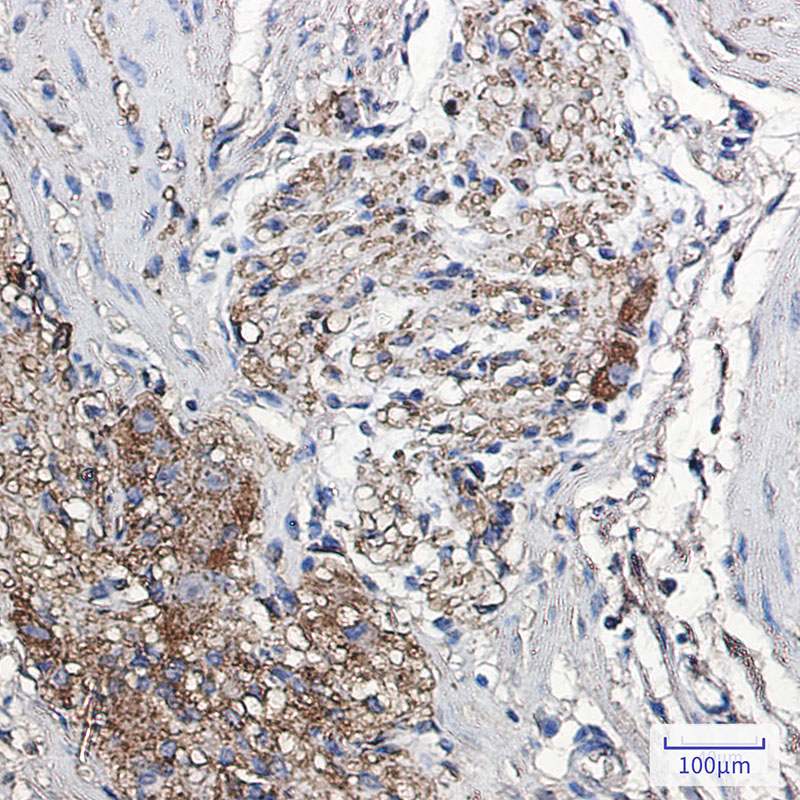
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SNCA; NACP; PARK1; Alpha-synuclein; Non-A beta component of AD amyloid; Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor; NACP |
| Entrez GeneID | 6622 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 14 kDa; Observed MW: 18 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human Alpha-synuclein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于α-Synuclein抗体的3-4篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
1. **"α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies"**
**作者**: Spillantini, M.G., et al. (1997)
**摘要**: 首次报道α-Synuclein在帕金森病路易小体中的特异性聚集,通过抗体染色证实其作为病理标志物的作用,奠定了α-Synuclein抗体在神经病理学诊断中的应用基础。
2. **"Phosphorylated α-synuclein is a pathological trigger in Parkinson’s disease"**
**作者**: Fujiwara, H., et al. (2002)
**摘要**: 开发了针对α-Synuclein S129磷酸化位点的特异性抗体,发现该修饰与病理性聚集体的形成密切相关,为研究帕金森病中α-Synuclein的毒性机制提供了关键工具。
3. **"Exogenous α-synuclein fibrils induce Lewy body pathology in vivo"**
**作者**: Volpicelli-Daley, L.A., et al. (2011)
**摘要**: 利用特异性抗体(如抗寡聚体抗体)证实外源性α-Synuclein纤维可诱导小鼠脑内路易样病理,突显抗体在区分不同聚集形态(单体、寡聚体、纤维)中的重要性。
4. **"Comparative study of commercial anti-α-synuclein antibodies"**
**作者**: Tran, H.T., et al. (2014)
**摘要**: 系统评估了多种商品化α-Synuclein抗体的特异性与灵敏度,揭示了不同抗体在检测天然/变性蛋白、病理性聚集体时的性能差异,为实验设计提供参考。
以上文献涵盖了抗体的开发、病理机制研究及实际应用,为α-Synuclein相关研究提供了关键工具与理论依据。
Alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) is a presynaptic protein implicated in synaptic vesicle regulation and neurotransmitter release. Its pathological aggregation is a hallmark of neurodegenerative disorders termed "synucleinopathies," including Parkinson’s disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA). In these conditions, misfolded α-Syn forms insoluble fibrils, accumulating as Lewy bodies or glial cytoplasmic inclusions, disrupting cellular function and promoting neurodegeneration.
Antibodies targeting α-Syn are critical tools for research, diagnostics, and therapeutic development. Research-grade antibodies enable detection of α-Syn isoforms (monomeric, oligomeric, phosphorylated) in biochemical assays (e.g., Western blot, ELISA) and histological techniques (e.g., immunohistochemistry), helping elucidate its role in disease mechanisms. Diagnostic applications include identifying α-Syn aggregates in cerebrospinal fluid or peripheral tissues as potential biomarkers. Therapeutically, α-Syn antibodies are explored for passive immunization to clear pathological aggregates or block cell-to-cell propagation. Several monoclonal antibodies (e.g., PRX002. BIIB054) have entered clinical trials, though challenges persist in optimizing target specificity, blood-brain barrier penetration, and mitigating off-target effects.
Despite progress, controversies remain regarding antibody selectivity for pathogenic vs. physiological α-Syn forms. Advances in epitope mapping, nanobody engineering, and conformation-specific antibody design aim to address these limitations, driving innovation in synucleinopathy research and therapy.
×