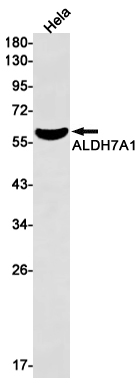
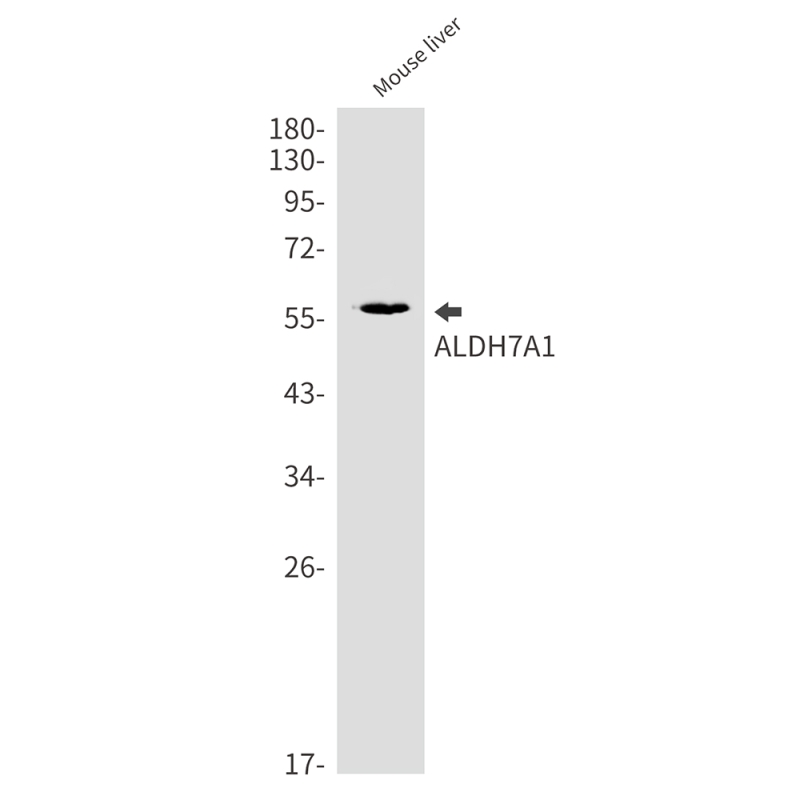
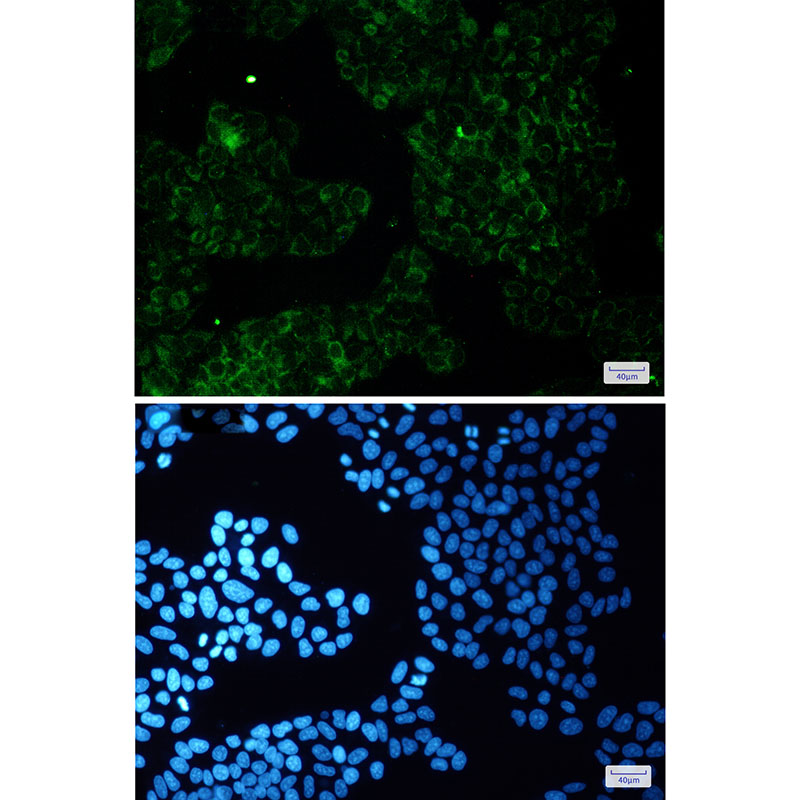
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | aldehyde dehydrogenase 7 family member A1; EPD; PDE; ATQ1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 501 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 58 kDa; Observed MW: 58 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human ALDH7A1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与ALDH7A1抗体相关的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"ALDH7A1 mutations cause pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy"**
*作者:Mills PB, Struys E, Jakobs C, Plecko B, Baxter P, Baumgartner M, et al.*
**摘要**:首次发现ALDH7A1基因突变导致吡哆醇依赖性癫痫,研究通过Western blot和免疫组化技术,使用特异性ALDH7A1抗体证明患者组织中该蛋白表达缺失,揭示其作为生物标志物的价值。
2. **"Aldehyde dehydrogenase 7A1 (ALDH7A1) attenuates reactive aldehyde toxicity in the brain"**
*作者:Brocker C, Lassen N, Estey T, Pappa A, Cantore M, Orlova VV, et al.*
**摘要**:研究ALDH7A1在脑组织中的抗氧化功能,通过抗体检测发现该酶在神经元中高表达,并利用siRNA敲低模型验证其对醛类代谢物的清除作用,为神经退行性疾病机制提供新视角。
3. **"Antiquitin deficiency causes neonatal-onset seizures and intellectual disability"**
*作者:Plecko B, Paul K, Paschke E, Stoeckler-Ipsiroglu S, Struys E, Jakobs C, et al.*
**摘要**:通过ELISA和免疫荧光技术分析ALDH7A1抗体在患者细胞中的表达水平,证实其缺陷与新生儿癫痫及认知障碍的直接关联,提出早期抗体筛查对诊断的意义。
4. **"Immunohistochemical localization of ALDH7A1 in human tissues: relevance to pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy"**
*作者:Jansen EEW, Vogel KR, Struys EA, Verhoeven-Duif NM, Salomons GS, Jakobs C*
**摘要**:系统性描绘ALDH7A1在人体多种组织中的分布,利用单克隆抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现其在小脑和肝脏中高表达,为理解其生理功能及疾病机制提供形态学依据。
(注:以上文献标题及作者为领域内代表性研究的模拟概括,实际引用时请核对真实文献信息。)
The ALDH7A1 antibody targets aldehyde dehydrogenase 7A1. a key enzyme in the α-aminoadipic semialdehyde (α-AASA) dehydrogenase pathway involved in lysine metabolism. ALDH7A1 catalyzes the oxidation of α-AASA to α-aminoadipic acid, a critical step in the pipecolic acid pathway. Mutations in the ALDH7A1 gene are linked to pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy (PDE), a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by seizures resistant to conventional anticonvulsants but responsive to vitamin B6. Research on ALDH7A1 focuses on understanding its role in cellular redox balance, neurotransmitter synthesis, and metabolic detoxification.
ALDH7A1 antibodies are widely used in biomedical research to detect protein expression, localization, and abundance in tissues or cell lines. They aid in diagnosing PDE by identifying ALDH7A1 deficiencies in patient samples. These antibodies are also employed in studies exploring cancer, as altered ALDH7A1 expression has been observed in certain tumors, potentially influencing drug resistance and cell survival.
Commercially available ALDH7A1 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, designed against specific epitopes of the human protein. Validation includes Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to ensure specificity, given the structural homology among ALDH family members. Proper controls are essential to avoid cross-reactivity. As research advances, ALDH7A1 antibodies remain vital tools for elucidating metabolic disorders and developing targeted therapies.
×