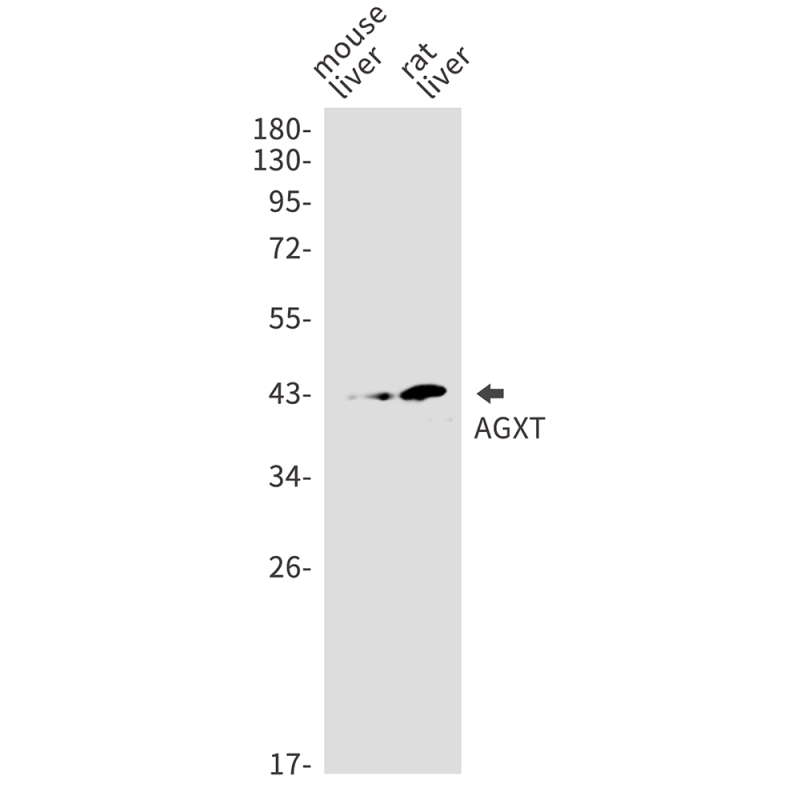
| WB | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AGT; PH1; SPT; AGT1; SPAT; TLH6; AGXT1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 189 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 43 kDa; Observed MW: 43 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human AGXT |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **"Primary hyperoxaluria type 1: AGXT mutations and functional characterization of gene variants" by Coulter-Mackie MB et al.**
摘要:该研究分析了原发性高草酸尿症Ⅰ型患者的AGXT基因突变,通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术验证突变对AGXT蛋白表达及亚细胞定位的影响,发现部分突变导致酶活性丧失和错误定位至线粒体。
2. **"Mistargeting of peroxisomal alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase to mitochondria in primary hyperoxaluria patients" by Danpure CJ et al.**
摘要:研究利用AGXT抗体进行免疫细胞化学分析,揭示了Ⅰ型原发性高草酸尿症患者中AGXT酶因突变从过氧化物酶体错误定位至线粒体,导致乙醛酸代谢异常和草酸盐过量积累。
3. **"A Knockout Mouse Model for Primary Hyperoxaluria Type 1 Indicates Oxalate as a Key Mediator of Pathology" by Salido EC et al.**
摘要:通过AGXT抗体检测AGXT敲除小鼠的肝组织蛋白表达,证实AGXT缺失导致草酸合成失控,并揭示草酸盐沉积在肾脏中的致病机制,为治疗策略提供依据。
4. **"Immunological and enzymatic studies of alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase in hyperoxaluria type 1" by Monico CG et al.**
摘要:结合AGXT特异性抗体进行酶活性和蛋白稳定性分析,发现某些错义突变导致AGXT酶折叠异常,易被蛋白酶体降解,为分子诊断和靶向治疗奠定基础。
(注:上述文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需核实具体来源及细节。)
×